
a.
Record the given transactions in an
a.
Explanation of Solution
Record the given transactions in an
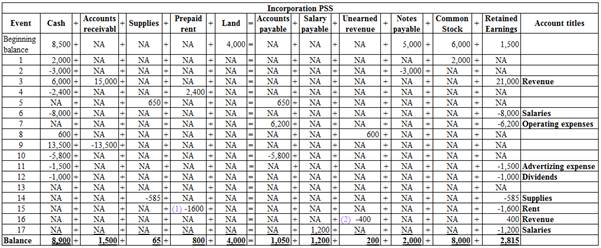
Table (1)
Cash: Cash represents the cash reserves available with the company at a point of time.
Accounts receivable: Accounts receivable refers to the amounts to be received within a short period from customers upon the sale of goods and services on account. In other words, accounts receivable are amounts customers owe to the business. Accounts receivable is an asset of a business.
Prepaid Expense: Prepaid expense refers to the expense made for the service prior to the consumption or utilization, and is recorded as an asset.
Accounts payable: Accounts payable is a liability of the firm, which refers to the accounts which the company owes for purchase of certain goods or services in the past; hence it is shown in the
Unearned revenue: It is an advance made by the buyer before receiving the product or service. In upcoming period, the seller will have an obligation to provide goods or perform the services to the buyer for the payment already received. It is a current liability until the goods are delivered or the service is performed.
Common stock: These are the ordinary shares that a corporation issues to the investors in order to raise funds. In return, the investors receive a share of profit from the profits earned by the corporation in the form of dividend.
Retained earnings: Retained earnings are the portion of earnings kept by the business for the purpose of reinvestments, payment of debts, or for future growth. In other words, Accumulated amount of all net income less the accumulated amount of dividends declared till date is known as retained earnings.
Revenues: Revenue refers to the income received from the business activity or sale of the output, during the accounting period.
Expenses: Expenses refer to the cost incurred on the necessary purchases of the fixed assets by the firm, or the production of the goods and services, during the accounting period.
Working notes:
Calculate the rent expense
$4,800 paid in advance for one year contract to rent office space (event no. 4). Rent expense recognized for eight months.
Calculate revenue recognized from transaction 8.
b)
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in
b)
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement, statement of changes in stockholders’ equity, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows for Year 2.
Income statement: Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues.
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Service Revenue | $21,400 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Salaries Expense | $9,200 | |
| Other Operating Expenses | 6,200 | |
| Advertising Expense | 1,500 | |
| Supplies Expense | 585 | |
| Rent Expense | 1,600 | |
| Total Expenses | 19,085 | |
| Net Income | $ 2,315 | |
Table (2)
Statement of changes in stockholders’ equity: It is one of the financial statements which report the changes in the stockholders equity from the beginning stockholder's equity to ending stockholder's equity.
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Statement of changes in stockholders’ Equity | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Beginning Common Stock | 6,000 | |
| Add: Common Stock Issued | 2,000 | |
| Ending Common Stock | 8,000 | |
| Beginning Retained Earnings | 1,500 | |
| Add: Net Income | 2,315 | |
| Less: Dividends | (1,000) | |
| Ending Retained Earnings | 2,815 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 10,815 | |
Table (3)
Balance Sheet: Balance Sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the Shareholder’s equity of a company at a given date. It is also known as the statement of financial status of the business
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| As of December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Assets | ||
| Cash | $8,900 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 1,500 | |
| Supplies | 65 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 800 | |
| Land | 4,000 | |
| Total Assets | $15,265 | |
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | $1,050 | |
| Unearned Revenue | 200 | |
| Salaries Payable | 1,200 | |
| Notes Payable | 2,000 | |
| Total Liabilities | $ 4,450 | |
| Stockholders’ Equity | ||
| Common Stock | $8,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 2,815 | |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | 10,815 | |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity | $15,265 | |
Table (4)
Statement of cash flows: This statement reports all the cash transactions which are responsible for inflow and outflow of cash, and result of these transactions is reported as ending balance of cash at the end of reported period.
| Incorporation PSS | ||
| Statement of cash flows | ||
| For the Year Ended December 31, Year 2 | ||
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
Amount ($) |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Customers (3) | $20,100 | |
| Cash Payment for Expenses (4) | (17,700) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operating Activities | $2,400 | |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | 0 | |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | ||
| Cash Receipts from Stock Issue | $ 2,000 | |
| Cash Payments on Loan | (3,000) | |
| Cash Payments for Dividends | (1,000) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing Activities | (2,000) | |
| Net Increase in Cash | 400 | |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | 8,500 | |
| Ending Cash Balance | $8,900 | |
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculate the cash receipts from the customers.
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
| Cash sales | 6,000 |
| Cash received from unearned income | 600 |
| Collection of accounts receivables | 13,500 |
| Cash receipts from the customers | 20,100 |
(3)
Table (6)
Calculate the cash payments for expenses.
| Particulars |
Amount ($) |
| Payment of prepaid rent | 2,400 |
| Payment of salaries | 8,000 |
| Payment of accounts payable | 5,800 |
| Payment of advertising expenses | 1,500 |
| Cash payments for expenses | 17,700 |
(4)
Table (7)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Loose-Leaf Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts
- At the end of the first year, ClearStream Supplies had net accounts receivable of $54,000, and at the end of the second year, the company had net accounts receivable of $60,000. If the company's net sales revenue during the second year was $720,000, what was the receivables turnover ratio for the second year? a) 12.86 b) 13.85 c) 11.48 d) 6.38arrow_forwardHello tutor please given General accounting question answer do fast and properly explain all answerarrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forward
- Dexter Equipment Co. had: • Net sales of $150,000 • Total assets of $100,000 • Year-end receivables of $18,000 . Inventory of $27,000 The company uses a 365-day year for calculations. What is Dexter's total asset turnover ratio? a) 1.25 b) 1.50 c) 1.33 d) 1.75 e) 1.85arrow_forwardGeneral accountingarrow_forwardKelton Corp. completed its first year of operations with 1,200 units of inventory remaining on hand. The variable and fixed manufacturing costs per unit were $85 and $25, respectively. If Kelton uses absorption costing rather than variable (direct) costing, the result would be a higher pretax income of:arrow_forward
- See an attachment for details General accounting question not need ai solutionarrow_forwardDon't use ai given answer accountingarrow_forwardCollins Corporation reported $120,000 of income for the year by using variable costing. The company had no beginning inventory, planned and actual production of 60,000 units, and sales of 55,000 units. Standard variable manufacturing costs were $18 per unit, and total budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead was $180,000. If there were no variances, income under absorption costing would be__.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





