
Concept explainers
Entries and schedules for unfinished jobs and completed jobs
Hildreth Company uses a
- A. Materials purchased on account, $147,000.
- B. Materials requisitioned and factory labor used:
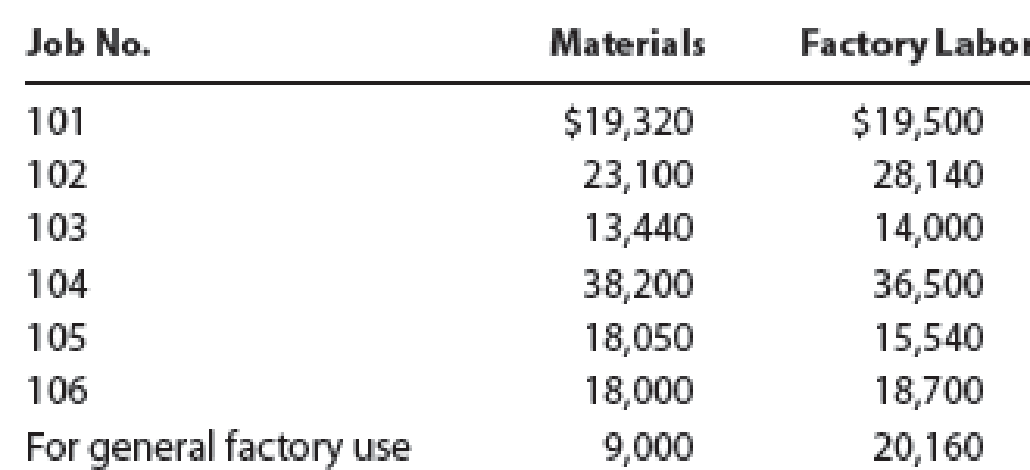
- C.
Factory overhead costs incurred on account, $6,000. - D.
Depreciation of machinery and equipment, $4,100. - E. The factory overhead rate is $40 per machine hour. Machine hours used:
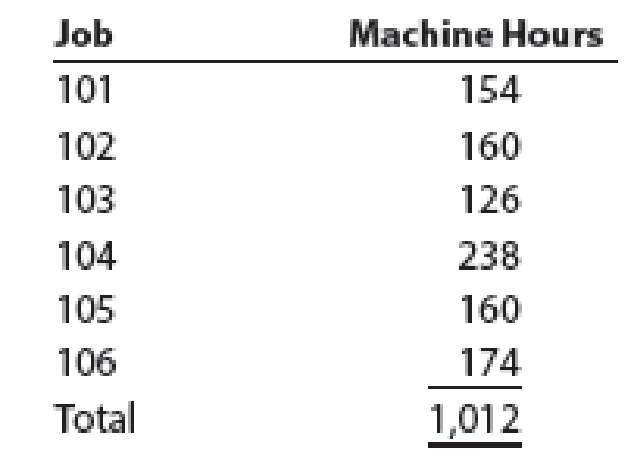
- F. Jobs completed: 101, 102, 103, and 105.
- G. Jobs were shipped and customers were billed as follows: Job 101, $62,900; Job 102, $80,700; Job 105, $45,500.
Instructions
- 1.
Journalize the entries to record the summarized operations. - 2.
Post the appropriate entries to T accounts for Work in Process and Finished Goods, using the identifying letters as transaction codes. Insert memo account balances as of the end of the month. - 3. Prepare a schedule of unfinished jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
- 4. Prepare a schedule of completed jobs on hand to support the balance in the finished goods account.
(1)
Journalize the entries to record summarized operations.
Explanation of Solution
Job order costing
Job order cost system provides a separate record of each particular quantity of product that passes through the factory. Each quantity that is manufactured in the business is known as job. Job order costing is used when the products produced are significantly different from each other.
The journal entries of operations of Company H is as follows:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| a | Materials | 147,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 147,000 | ||
| (Record materials purchased) | |||
| b | Work in process Table (2) | 130,110 | |
| Factory overhead | 9,000 | ||
| Materials | 139,110 | ||
| (Record material requisitioned to jobs) | |||
| Work in process Table (2) | 132,380 | ||
| Factory overhead | 20,160 | ||
| Wages payable | 152,540 | ||
| (Record factory labor used in production) | |||
| c | Factory overhead | 6,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 6,000 | ||
| (Record factory overhead cost incurred on account) | |||
| d | Factory overhead | 4,100 | |
| Accumulated depreciation – Machinery & Equipment | 4,100 | ||
| (Record depreciation on account) | |||
| e | Work in process | 40,480 | |
| Factory overhead (1,012 hours × $40) | 40,480 | ||
| (Record overhead applied to jobs) | |||
| f | Finished goods Table (3) | 175,090 | |
| Work in process | 175,090 | ||
| (Record completion of job) | |||
| g | Accounts Receivable | 189,100 | |
| Sales | 189,100 | ||
| (Record sales on account) | |||
| h | Cost of goods sold Table (4) | 142,610 | |
| Finished goods | 142,610 | ||
| (Record cost of goods sold) |
Table (1)
Justification:
- a) The material is purchased on account. In regard to this, the material account is debited (Increased) and Accounts Payable is a liability and it is credited (Increased).
- b) The materials are requisitioned to jobs which includes direct and indirect cost. In regard to this, Work in process account is debited (Increased), Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), Material account is credited (Decreased), and Wages payable account is credited (Increased).
- c) The factory overhead costs are incurred on account. In regard to this, Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), and Accounts payable account is a liability and is credited (Increased).
- d) Depreciation on machinery is recorded. In regard to this, Factory overhead account is debited (Increased), and Accumulated depreciation – Machinery account is a contra asset and is credited (Increased).
- e) Factory overhead cost is applied to jobs. The work in process account is debited (Increased) and factory overhead account is credited (Decreased).
- f) The jobs are completed in the process. Finished goods account is debited (Increased) and Work in process account is credited (Decreased).
- g) Goods sold on account. Accounts receivable is an asset and is debited (Increased) and Sales affects stockholders’ equity and is credited (Increased).
- h) The cost of goods sold is recorded. Cost of goods sold account is debited (Increased), and Finished goods account is credited (Decreased).
Working note:
The material requisitioned to jobs is calculated as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials | Directlabor |
| 101 | 19,320 | 19,500 |
| 102 | 23,100 | 28,140 |
| 103 | 13,440 | 14,000 |
| 104 | 38,200 | 36,500 |
| 105 | 18,050 | 15,540 |
| 106 | 18,000 | 18,700 |
| 130,110 | 132,380 |
Table (2)
Compute the cost of jobs finished as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials | Directlabor | Factory overhead | Total |
| 101 | 19,320 | 19,500 | 6,160 | 44,980 |
| 102 | 23,100 | 28,140 | 6,400 | 57,640 |
| 103 | 13,440 | 14,000 | 5,040 | 32,480 |
| 105 | 18,050 | 15,540 | 6,400 | 39,990 |
| 175,090 |
Table (3)
Compute the cost of goods sold as follows:
| Job | Amount ($) |
| 101 | 44,980 |
| 102 | 57,640 |
| 103 | 39,990 |
| 142,610 |
Table (4)
(2)
Prepare appropriate T-accounts for work in process and Finished goods account.
Explanation of Solution
The T-account is prepared as follows:
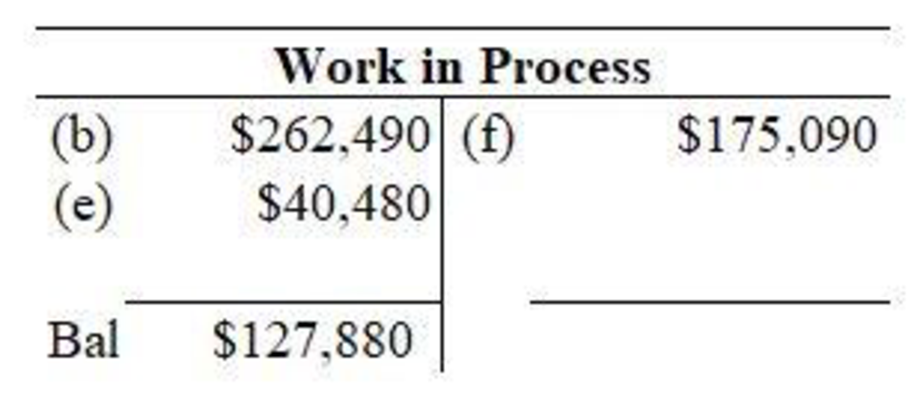
Figure (1)
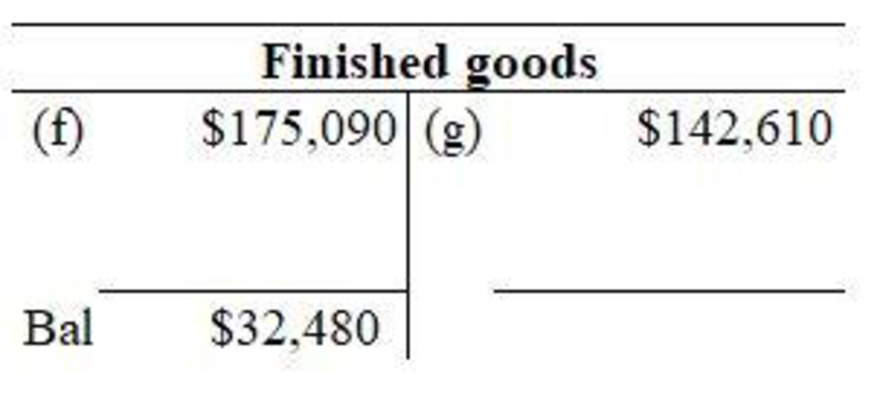
Figure (2)
In the work in process account, materials requisitioned for jobs is debited, application of factory overhead to jobs is debited and jobs that are completed are credited. Then, closing balance of work in process is determined.
In finished goods account, Jobs that are completed are debited and sale of goods is credited. Then, closing balance of finished goods is determined.
(3)
Prepare schedule of unfinished jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
Explanation of Solution
The schedule of unfinished jobs is prepared as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials ($) | Directlabor ($) | Factory overhead ($) | Total($) |
| No. 104 | 38,200 | 36,500 | 9,520 | 84,220 |
| No. 106 | 18,000 | 18,700 | 6,960 | 43,660 |
| Balance of work in process, Jan 30 | 127,880 |
Table (5)
The unfinished jobs are Job 104 and Job 106. The direct material cost, direct labor cost and factory overhead cost consists of jobs cost. The total of uncompleted jobs constitutes balance of work in process as on April 30.
(4)
Prepare schedule of completed jobs to support the balance in the work in process account.
Explanation of Solution
The schedule of completed jobs is prepared as follows:
| Job | Directmaterials ($) | Directlabor ($) | Factory overhead ($) | Total($) |
| No. 105 (Finished goods, January 30) | 13,440 | 14,000 | 5,040 | 32,480 |
Table (6)
The completed job is Job 105. The direct material cost, direct labor cost and factory overhead cost consists of jobs cost. The total of completed jobs constitutes balance of finished goods as on April 30.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Managerial Accounting
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning





