
Concept explainers
PROBLEM A race car starting from rest accelerates at a constant rate of 5.00 m/s2, (a) What is the velocity of the car after it has traveled 1.00 × 102 ft? (b) How much time has elapsed? (c) Calculate the average velocity two different ways.
STRATEGY We’ve read the problem, drawn the diagram in Figure 2.16, and chosen a coordinate system (steps 1 and 2). We'd like to find the velocity v after a certain known displacement Δx. The acceleration a is also known, as is the initial velocity v0 (step 3, labeling, is complete), so the third equation in Table 2.4 looks most useful for solving part (a). Given the velocity, the first equation in Table 2.4 can then be used to find the time in part (b). Part (c) requires substitution into Equations 2.2 and 2.7, respectively.
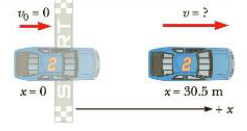
Figure 2.16 (Example 2.4)
SOLUTION
(a) Convert units of Δx to SI, using the information in the inside front cover.
Write the
Solve for v, taking the positive square root because the car moves to the right (step 5):
Substitute v0 = 0, a = 5.00 m/s2, and Δx = 30.5 m:
1.00 × 102ft = (1.00 × 102 ft)
v2 = v02 + 2a Δx
v =
v =
(b) Find the trooper's speed at that time. Substitute the time into the trooper’s velocity equation:
vtrooper = v0 + atrooper t = 0 + (3.00m/s2)(16.9s)
= 50.7 m/s
Solve Example 2.5, “Car Chase,” by a graphical method. On the same graph, plot position versus time for the car and the trooper. From the intersection of the two curves, read the time at which the trooper overtakes the car.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 2 Solutions
COLLEGE PHYSICS (LL W/WEBASSIGN)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Fundamentals Of Thermodynamics
MARINE BIOLOGY
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
- 7. Are all scientific theories testable in the commonly understood sense? How does this make you feel? How should you proceed as a scientist or engineer with this understanding?arrow_forwardWhat is an an example of a hypothesis that sounds scientific but is notarrow_forwardWhat is an example of a scientific hypothesisarrow_forward
- Multiverse is called a theory. It has been proposed to account for the apparent and uncanny fine tuning of our own universe. The idea of the multiverse is that there are infinite, distinct universes out there - all with distinct laws of nature and natural constants - and we live in just one of them. Using the accepted definition of the universe being all that there is (matter, space and energy), would you say that multiverse is a scientific theory?arrow_forwardHow is a law usually different than a theoryarrow_forwardA 1.50 mLmL syringe has an inner diameter of 5.00 mmmm, a needle inner diameter of 0.270 mmmm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cmcm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. Part A What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s)for Part A Hint 1for Part A. How to approach the question The force the nurse applies to the syringe can be determined from the fluid pressure and the area of the plunger. The minimum force corresponds to the patient's lowest blood pressure. Use the following equality 760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa.arrow_forward
- A 1.50 mLmL syringe has an inner diameter of 5.00 mmmm, a needle inner diameter of 0.270 mmmm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cmcm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. Part A What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s)for Part A Hint 1for Part A. How to approach the question The force the nurse applies to the syringe can be determined from the fluid pressure and the area of the plunger. The minimum force corresponds to the patient's lowest blood pressure. Use the following equality 760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa.arrow_forwardIs a scientific theory supposed to just be someone's idea about somethingarrow_forwardwhat is the agenda of physicsarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





