
Concept explainers
(a)
The equation of motion of particle and resolve into three components, also show that the motion of the particle remains constant in the plane
(a)
Answer to Problem 2.55P
The equation of motion of the charged particle is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for force experienced by a particle moving in electric and magnetic field.
Here,
The above can also be written as
In terms of component along
Equate the components along
Since
Equate the components along
Since
Equate the components along
From the above equation it is clear that
Conclusion:
Therefore, the equation of motion of the charged particle is
(b)
To show that for a unique value of
(b)
Answer to Problem 2.55P
As
Explanation of Solution
Let the initial speed of the particle for which the particle remains undeflected is
Write the expression for electrostatic force on the particle.
Here,
Write the expression for magnetic force.
Here,
Since the initial speed of the particle is equal to the drift speed of the particle, the above equation is reduced to
For a particle to be undeflected, the magnitude of electrostatic force and magnetic force should be equal.
Using the above condition, equate equation (VI) and (VII).
Rearrange the above equation.
As
Conclusion:
Therefore, as
(c)
To solve the equation of motion of the particle, and to obtain the velocity of as a function of
(c)
Answer to Problem 2.55P
The velocity of the particle as a function of
Explanation of Solution
The speed of the particle along
Differentiating the above equation with respect to time.
The above equation can also be written as
The solution of the above equation is given by
Given that the speed of the particle along
Differentiating the above equation with respect to time.
The above equation is written as
The solution of the above equation is given by
Since
Use equation (IX) in equation (VIII).
At time
Use the above equation in equation (XII).
Use equation (XIII) in equation (XI).
And speed along
Conclusion:
Therefore, the velocity of the particle as a function of
(d)
The position of the particle as a function of time
(d)
Answer to Problem 2.55P
The position of the particle as a function of time
Explanation of Solution
From subpart (c),
The above equation is written as
Replace
Similarly position
Assuming
Use the above equation in equation (XVII).
Use equation (XIV) in equation (XVI).
For
For
Figure 1 represents the trajectory of
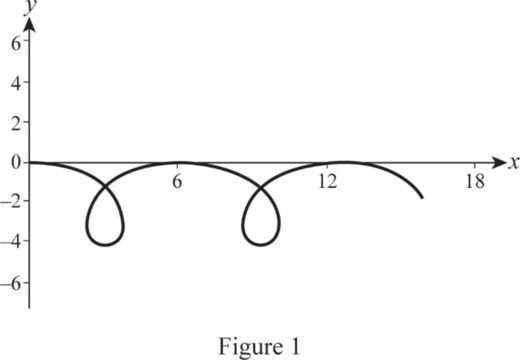
Figure 2 represents the trajectory of
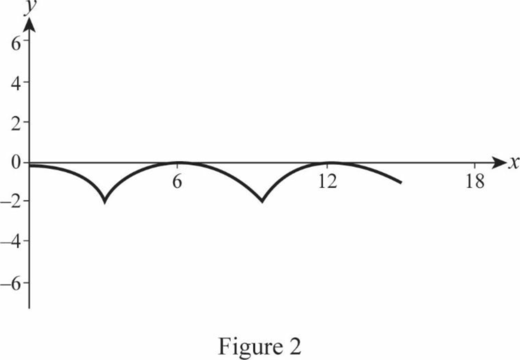
Figure 3 represents the trajectory of
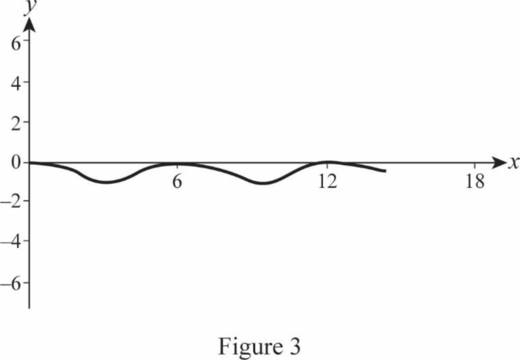
Figure 4 represents the trajectory of

Figure 5 represents the trajectory of
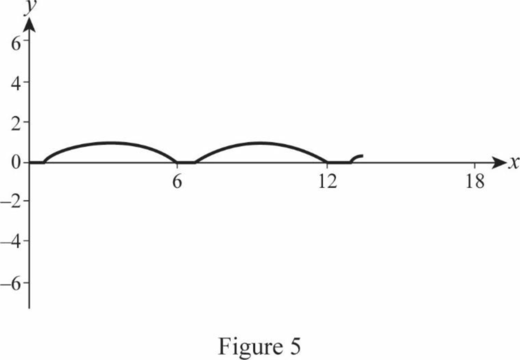
Figure 6 represents the trajectory of
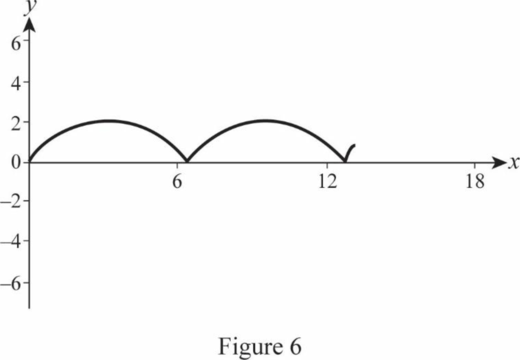
Figure 7 represents the trajectory of
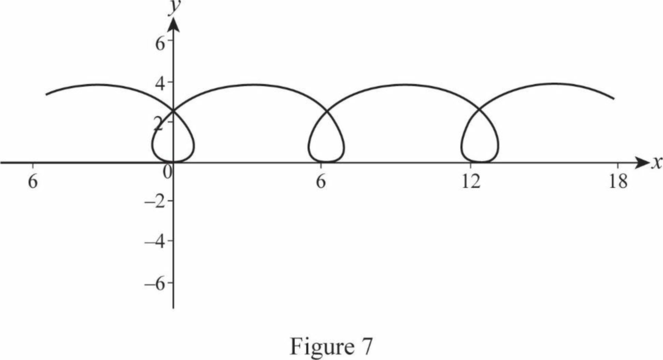
Conclusion:
Therefore, the position of the particle as a function of time
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Classical Mechanics
- Three identical capacitors are connected in parallel. When this parallel assembly of capacitors is connected to a 12 volt battery, a total of 3.1 x 10-5 coulombs flows through the battery. What is the capacitance of one individual capacitor? (Give your answer as the number of Farads.)arrow_forwardSuppose you construct your own capacitor by placing two parallel plates at a distance 0.27 meters apart. The plates each have a surface area of 0.64 square meters. What is the capacitance of this setup? (Give your answer as the number of Farads.)arrow_forwardDraw a diagram with the new arrows. No they do not point all towards the center.arrow_forward
- Example In Canada, the Earth has B = 0.5 mŢ, pointing north, 70.0° below the horizontal. a) Find the magnetic force on an oxygen ion (O2) moving due east at 250 m/s b) Compare the |FB| to |FE| due to Earth's fair- weather electric field (150 V/m downward).arrow_forwardFour charges, qa, qb, qa, and qd are fixed at the corners of a square. A charge q that is free to move located at the exact center of the square. Classify the scenarios described according to the force that would be exerted on the center charge q. Assume in each case that q is a positive charge. Do not assume that the fixed charges have equal magnitudes unless the scenario defines such an equality. qa Яс q %b Force is zero Force is to the left Force is to the right Force is undeterminedarrow_forwardCharge qi = -q is located at position (0, d). Charge q = −2q₁ is located at position (d,0). Charge q3 = located at position (2d, 2d). 5qi is y Determine the net electric field Ĕ net at the origin. Enter your expression using ij unit vector notation in terms of the given quantities, the permittivity of free space €0, and exact rational and irrational numbers. d 9₁ d TH net = 92 d d Xarrow_forward
- solve pleasearrow_forward= = R4 R5 = 12.5 Q. A - In the circuit shown, R₁ = R₂ = R 3 voltmeter measures the potential difference across the battery. When the switch is in position 1, the voltmeter measures V₁ = 13.8 V. When the switch is in position 2, the voltmeter measures V2 = 13.4 V. What is the emf ☐ of the battery? 14.93 = What is the battery's internal resistance r? r = V CH Ω R₁₂ V S R₁ 02 2 R₁ 4 R3 R 5arrow_forwardConsider the arrangement of charges shown in the figure. Four charges of equal magnitude Q but varying sign are placed at the corners of a square as indicated. A positive charge q is placed in the center. What is the direction of the net force, if any, on the center charge? Indicate your answer by placing the appropriate label in the first box. Then, suppose that the charge q were to be displaced slightly from the center position. On the figure, label each box with the arrow that best indicates the direction of the net force that would act on q if it were moved to that location. Net Force Answer Bank no force ↑ +2 0 -Q -Q +Qarrow_forward
- Don't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardWhen an electromagnetic wave is reflected at normal incidence on a perfectly conducting surface, the electric fieldvector of the reflected wave at the reflecting surface is the negative of that of the incident wave.a) Explain why this should be so.b) Show that the superposition of the incident and reflected waves results in a standing wave.c) What is the relationship between the magnetic field vector of the incident and reflected waves at the reflectingsurface?arrow_forwardSuppose there are two transformers between your house and the high-voltage transmission line that distributes the power. In addition, assume your house is the only one using electric power. At a substation the primary of a step-down transformer (turns ratio = 1:23) receives the voltage from the high-voltage transmission line. Because of your usage, a current of 51.1 mA exists in the primary of the transformer. The secondary is connected to the primary of another step- down transformer (turns ratio = 1:36) somewhere near your house, perhaps up on a telephone pole. The secondary of this transformer delivers a 240-V emf to your house. How much power is your house using? Remember that the current and voltage given in this problem are rms values.arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





