
a.
To find: The five-number summary for the distribution of revenues for the top global 500
To explain: Why the five-number summary suggests that the distribution is right skewed.
a.
Answer to Problem 2.52E
The five-number summary for the distribution of revenues for the top global 500 is
The difference between the
Explanation of Solution
Given info: Table 2.3gives the highest revenues for 30 companies from global 500 companies in 2014.
Calculation:
Five-number summary:
The five-number summary of a distribution consists of minimum, the first
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure for five-number summary using MINITAB software is as follows:
- Choose Stat > Basic Statistics > Display
Descriptive Statistics . - In Variables enter the columns GLOBE500.
- Choose option statistics, and select minimum, first quartile, median, third quartile, maximum.
- Click OK.
Output using MINITAB software is as follows:

The five-number summary for the distribution of the highest revenues of 30 companies for the top global 500 is
Justification:
The distance from median and minimum is,
The distance from the maximum to the median is,
From the five-number summary, the distribution is right skewed because the difference between the median and minimum is less than the difference between the median and maximum.
b.
To find: The companies which are outliers according to the
To check: Whether the
b.
Answer to Problem 2.52E
According to
Yes, the
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From the output in part (a)
The difference between the first quartile and the third quartile is considered as interquartile range.
Thus,
For revenues of 30 companies,
The
A observation is a suspected as outlier if it is more than
The
Stemplot:
Software procedure:
Step-by-step software procedure to draw stemplot using MINITAB software is as follows:
- Select Graph>Stem and leaf.
- Select the column of GLOBE500 in Graph variables.
- Select OK.
Output of stemplot is shown below:
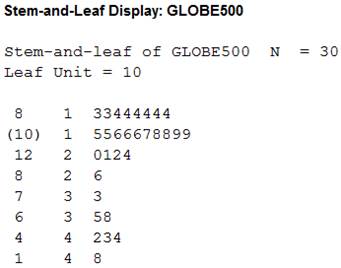
Justification:
The stemplot does not show any outliers which indicates that the
c.
To explain: The common feature that the 30 companies in the Table 2.3 share.
To find: The proportion of the total of the global 500 revenues accounted by the 30 companies.
c.
Answer to Problem 2.52E
The common feature that the 30 companies share is that they are the high outliers and have high revenues out of global 500 companies.
The proportion of the total global 500 revenues by the 30 companies is 0.06.
Explanation of Solution
Justification:
From the global 500 companies, 30 companies in Table2.3 have high revenues than the remaining companies, and these 30 companies are the high outliers that has a common feature of sharing.
The proportion of the total global 500 companies accounted by the 30 companies is:
Thus, the proportion of the total global 500 revenues by the 30 companies is 0.06.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
BASIC PRACTICE OF STATISTICS >C<
- The PDF of an amplitude X of a Gaussian signal x(t) is given by:arrow_forwardThe PDF of a random variable X is given by the equation in the picture.arrow_forwardFor a binary asymmetric channel with Py|X(0|1) = 0.1 and Py|X(1|0) = 0.2; PX(0) = 0.4 isthe probability of a bit of “0” being transmitted. X is the transmitted digit, and Y is the received digit.a. Find the values of Py(0) and Py(1).b. What is the probability that only 0s will be received for a sequence of 10 digits transmitted?c. What is the probability that 8 1s and 2 0s will be received for the same sequence of 10 digits?d. What is the probability that at least 5 0s will be received for the same sequence of 10 digits?arrow_forward
- V2 360 Step down + I₁ = I2 10KVA 120V 10KVA 1₂ = 360-120 or 2nd Ratio's V₂ m 120 Ratio= 360 √2 H I2 I, + I2 120arrow_forwardQ2. [20 points] An amplitude X of a Gaussian signal x(t) has a mean value of 2 and an RMS value of √(10), i.e. square root of 10. Determine the PDF of x(t).arrow_forwardIn a network with 12 links, one of the links has failed. The failed link is randomlylocated. An electrical engineer tests the links one by one until the failed link is found.a. What is the probability that the engineer will find the failed link in the first test?b. What is the probability that the engineer will find the failed link in five tests?Note: You should assume that for Part b, the five tests are done consecutively.arrow_forward
- Problem 3. Pricing a multi-stock option the Margrabe formula The purpose of this problem is to price a swap option in a 2-stock model, similarly as what we did in the example in the lectures. We consider a two-dimensional Brownian motion given by W₁ = (W(¹), W(2)) on a probability space (Q, F,P). Two stock prices are modeled by the following equations: dX = dY₁ = X₁ (rdt+ rdt+0₁dW!) (²)), Y₁ (rdt+dW+0zdW!"), with Xo xo and Yo =yo. This corresponds to the multi-stock model studied in class, but with notation (X+, Y₁) instead of (S(1), S(2)). Given the model above, the measure P is already the risk-neutral measure (Both stocks have rate of return r). We write σ = 0₁+0%. We consider a swap option, which gives you the right, at time T, to exchange one share of X for one share of Y. That is, the option has payoff F=(Yr-XT). (a) We first assume that r = 0 (for questions (a)-(f)). Write an explicit expression for the process Xt. Reminder before proceeding to question (b): Girsanov's theorem…arrow_forwardProblem 1. Multi-stock model We consider a 2-stock model similar to the one studied in class. Namely, we consider = S(1) S(2) = S(¹) exp (σ1B(1) + (M1 - 0/1 ) S(²) exp (02B(2) + (H₂- M2 where (B(¹) ) +20 and (B(2) ) +≥o are two Brownian motions, with t≥0 Cov (B(¹), B(2)) = p min{t, s}. " The purpose of this problem is to prove that there indeed exists a 2-dimensional Brownian motion (W+)+20 (W(1), W(2))+20 such that = S(1) S(2) = = S(¹) exp (011W(¹) + (μ₁ - 01/1) t) 롱) S(²) exp (021W (1) + 022W(2) + (112 - 03/01/12) t). where σ11, 21, 22 are constants to be determined (as functions of σ1, σ2, p). Hint: The constants will follow the formulas developed in the lectures. (a) To show existence of (Ŵ+), first write the expression for both W. (¹) and W (2) functions of (B(1), B(²)). as (b) Using the formulas obtained in (a), show that the process (WA) is actually a 2- dimensional standard Brownian motion (i.e. show that each component is normal, with mean 0, variance t, and that their…arrow_forwardThe scores of 8 students on the midterm exam and final exam were as follows. Student Midterm Final Anderson 98 89 Bailey 88 74 Cruz 87 97 DeSana 85 79 Erickson 85 94 Francis 83 71 Gray 74 98 Harris 70 91 Find the value of the (Spearman's) rank correlation coefficient test statistic that would be used to test the claim of no correlation between midterm score and final exam score. Round your answer to 3 places after the decimal point, if necessary. Test statistic: rs =arrow_forward
- Business discussarrow_forwardBusiness discussarrow_forwardI just need to know why this is wrong below: What is the test statistic W? W=5 (incorrect) and What is the p-value of this test? (p-value < 0.001-- incorrect) Use the Wilcoxon signed rank test to test the hypothesis that the median number of pages in the statistics books in the library from which the sample was taken is 400. A sample of 12 statistics books have the following numbers of pages pages 127 217 486 132 397 297 396 327 292 256 358 272 What is the sum of the negative ranks (W-)? 75 What is the sum of the positive ranks (W+)? 5What type of test is this? two tailedWhat is the test statistic W? 5 These are the critical values for a 1-tailed Wilcoxon Signed Rank test for n=12 Alpha Level 0.001 0.005 0.01 0.025 0.05 0.1 0.2 Critical Value 75 70 68 64 60 56 50 What is the p-value for this test? p-value < 0.001arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





