
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron and molecular geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is trigonal planar and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
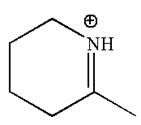
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is nitrogen. Nitrogen has two single bonds and one double bond thus, there are three electron groups around the nitrogen atom. According to the VSEPR chart, the electron geometry about nitrogen is trigonal planar and as there are no lone pairs around it, the molecular geometry is also trigonal planar. The bond angle in the orientation of three electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
(b)
Interpretation:
The electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is trigonal planar, molecular geometry is bent and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
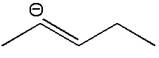
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is carbon; the negative charge indicates the lone pairs of electrons. The charged carbon atom has one single bond and one double bond and one lone pair thus there are three electron groups around this charged carbon atom. According to the VSEPR chart, the molecular geometry is bent, since there are two bonds around the charged carbon atom. And the electron geometry about charged carbon is trigonal planar as there is one lone pairs of electrons along with two bonds. The bond angle in the orientation of three electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
(c)
Interpretation:
The electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is trigonal planar, molecular geometry is bent and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
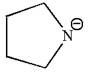
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is nitrogen; the negative charge indicates the lone pairs of electrons. The charged nitrogen atom has two single bonds and one lone pair of electrons, thus there are three electron groups. According to the VSEPR chart, the electron geometry about charged nitrogen should be trigonal planar and as there is one lone pair around it, the molecular geometry is bent. The bond angle in the orientation of three electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry, and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron and molecular geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is tetrahedral and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
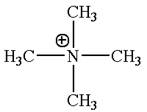
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is nitrogen. The charged nitrogen atom has four single bonds and no lone pair thus there are four electron groups. According to the VSEPR chart the electron geometry about charged nitrogen should be tetrahedral and as there is no lone pair around it, the molecular geometry as same as the electron geometry, that is tetrahedral. The bond angle in the orientation of four electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be identified the electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron and molecular geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is trigonal planar and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
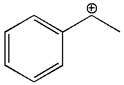
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is carbon. The carbon atom bearing the positive charge has three bonds, two with carbons and one with hydrogen. This carbon has an incomplete octet and thus it has no lone pairs of electrons on it. Thus there are three electron groups around this carbon atom. According to the VSEPR chart, the electron geometry about charged carbon is trigonal planar and as there is no lone pair around it, the molecular geometry is also trigonal planar. The bond angle in the orientation of four electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
(f)
Interpretation:
The electron geometry, molecular geometry, and bond angle about the charged atom in the given molecule is to be identified.
Concept introduction:
The VSEPR chart depicts the electron and molecular geometry on the basis of numbers of electron groups. The Electron geometry about an atom describes the orientation of a group of electrons around it. A lone pair of electrons, a single bond, a double bond, a triple bond each is considered as one group of electrons. Molecular geometry describes the arrangement of surrounding atoms about a particular atom. Molecular geometry is governed by electron geometry of an atom. If all the electron groups around an atom are bonds, then the molecular geometry will be the same as electron geometry. The electron and molecular geometry about a particular atom will be different when one or more of the electron group is lone pair. The bond angle is the angle between two bonds originating from the same atom in a covalent molecule or ion. The bond angle depends on the molecular geometry around the atom.
Answer to Problem 2.34P
The electron and molecular geometry about the charged atom in the given molecular ion is linear and the bond angle is
Explanation of Solution
The given molecular ion is:
![]()
In this molecular ion, the charged atom is oxygen. The charged oxygen atom has one triple bond and one lone pair thus there are two electron groups. According to the VSEPR chart, the two electron group tends to have linear electron and molecular geometry. The bond angle in the orientation of tow electron groups is
The electron geometry, molecular geometry and the bond angle about charged atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- 6. A solution (0.0004 M) of Fe(S2CNEt2)3 (see the structural drawing below) in chloroform has absorption bands at: 350 nm (absorbance A = 2.34); 514 nm(absorbance A = 0.0532); Calculate the molar absorptivity values for these bands. Comment on their possible nature (charge transfer transitions or d-d S N- transitions?). (4 points)arrow_forwardWhat is the mechanism for this?arrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6], [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 4. Room temperature (20°C) measurement of molar magnetic susceptibility (Xm) for Fe(NH4)2(SO4)2×6H2O is 1.1888 x 102 cgs (Gaussian units). Calculate effective magnetic moment and provide a number of unpaired electrons for the iron ion. Use this number to rationalize the coordination geometry around iron center. (4 points)arrow_forward
- 7. Describe the expected 31P and 19F (where applicable) NMR spectral patterns for the following compounds (indicate number of signals and their splitting patterns). a) tetraphenyldiphosphine Ph Ph P-P Ph Ph Ph Ph ' b) tetraphenyldiphosphine monoxide P-P-Ph Ph (2 points) (2 points c) tetrafluorophosphonium hexafluorophosphate [PF4]*[PF6]¯ (4 points)arrow_forward3. For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ Which (if any) of these complexes would be expected to display Jahn-Teller distortion? (2 points)arrow_forwardWhat is Instrumental Neutron Activation and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications? (I'm doing an in class assignment and need better understanding of what the instrument can be used for) Please include references so that I can better understand the application of how the instrument works!arrow_forward
- What is Isotope Analysis and what are the advantages and disadvantages in using its applications and instrumentalization? Please include references so that I can better understand how the instrument works!arrow_forward5. Count the electrons on the following complexes and state whether they follow the 18- electron rule: (3 points) Fe(CO)5 Ni(PMe3)4 PMe3 is trimethylphosphine Mn(CO)5Brarrow_forwardFor questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]+, [CoCl4]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 2. Draw the corresponding d-orbital splitting for each of the complexes; predict the spin- state (low-spin/high spin) for each of the complexes (if applicable); explain your arguments. Calculate the crystal field stabilization energy for each complex (in Ao or At). (6 points)arrow_forward
- For questions 1-4, consider the following complexes: [Co(CN)6]4, [COC14]², [Cr(H2O)6]²+ 1. Assign oxidation number to the metal, then indicate d-electron count. (3 points)arrow_forwardUsing iodometry I want to titrate a sodium thiosulfate solution and I use 15 mL. If I have 50 mL of a 0.90 M copper solution and KI, what will be the molarity of sodium thiosulfate?arrow_forwardDraw the product formed when the following pair of compounds is treated with NaOEt in ethanol. + i CNarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning  Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER





