
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The
Concept introduction:
An
Answer to Problem 2.11P
(A) The names of the functional groups from the given table that possess at least one
(B) The names of the functional groups from the given table which possess at least one
(C) The functional groups from the given table which possess no H-bond donors and no
Explanation of Solution
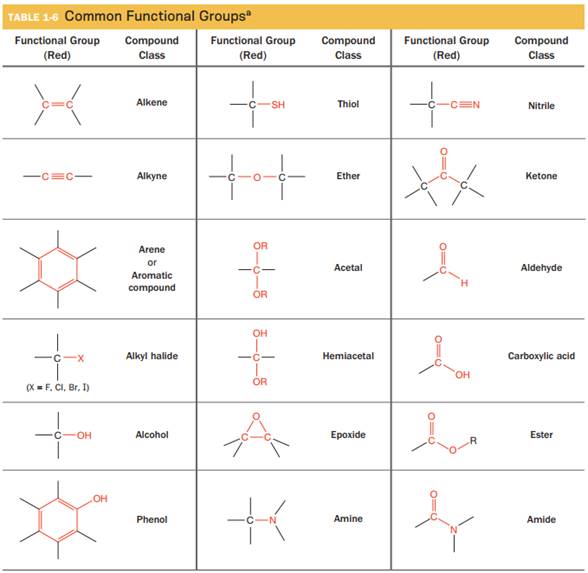
(A) The functional groups from the given table which possess at least one
- The given functional group is Nitrile:
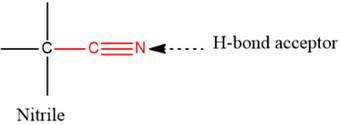
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the N atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
2) The given functional group is Ether:
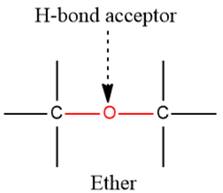
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
3) The given functional group is Ketone:
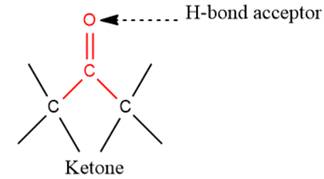
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
4) The given functional group is Acetal:
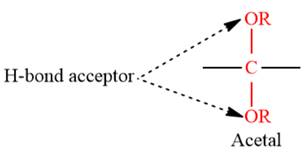
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atom with a lone pair of electrons, there are two H-bond acceptors.
- The given functional group is Aldehyde:

In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Alkyl halide (Only if X = F):
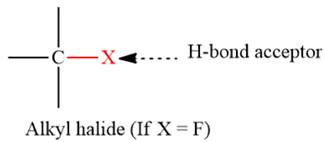
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the F atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Epoxide:
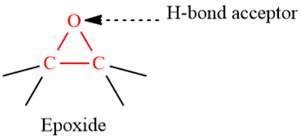
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Ester:
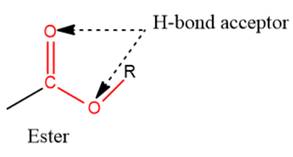
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the O atoms with a lone pair of electrons, there are two H-bond acceptors.
- The given functional group is Amine:
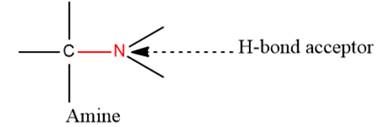
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the N atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Amide:
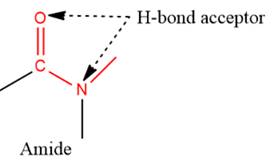
In this functional group, due to the high electronegativity of the N atom with a lone pair of electrons, there is one H-bond acceptor.
(B) The functional groups possessing at least one H-bond donor and one H-bond acceptor are:
1) The given functional group is Hemiacetal:
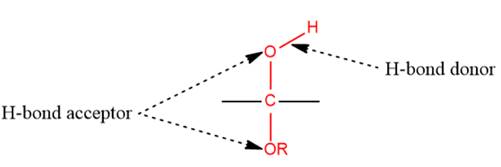
In this functional group, there is one H-bond donor and two H-bond acceptors. The high electronegativity of the O atom ensures that the O-H bond is highly polar and gives the H atom a large partial positive charge. This sets up a strong attraction between the H atom and the oppositely charged acceptor.
2) The given functional group is Carboxylic acid:
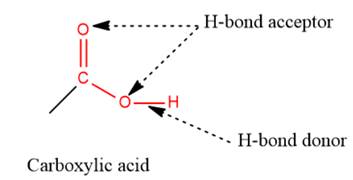
In this functional group, there is one H-bond donor and two H-bond acceptors. The high electronegativity of the O atom ensures that the O-H bond is highly polar and gives the H atom a large partial positive charge. This sets up a strong attraction between the H atom and the oppositely charged acceptor.
- The given functional group is Alcohol:
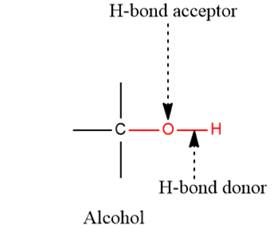
In this functional group, there is one H-bond donor and one H-bond acceptor. The high electronegativity of the O atom ensures that the O-H bond is highly polar and gives the H atom a large partial positive charge. This sets up a strong attraction between the H atom and the oppositely charged acceptor.
4) The given functional group is Phenol:
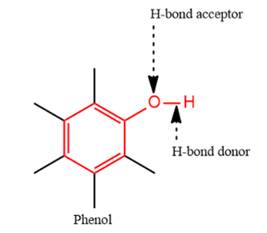
In this functional group, there is one H-bond donor and one H-bond acceptor. The high electronegativity of the O atom ensures that the O-H bond is highly polar and gives the H atom a large partial positive charge. This sets up a strong attraction between the H atom and the oppositely charged acceptor.
(C) The functional groups from the given table which possess no H-bond donor and no H-bond acceptor are:
1) The given functional group is Alkene:
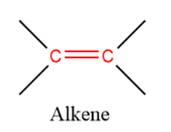
In this functional group, there is no H atom which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as N, O, or F. Therefore, there is no H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor.
2) The given functional group is Thiol:
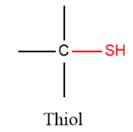
In this functional group, there is no H atom which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as N, O, or F. Therefore, there is no H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor.
3) The given functional group is Alkyne:

In this functional group, there is no H atom which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as N, O, or F. Therefore, there is no H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Arene or aromatic compound:
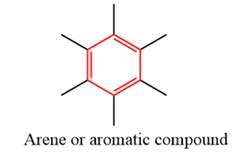
In this functional group, there is no H atom which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as N, O, or F. Therefore, there is no H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor.
- The given functional group is Alkyl halide (Only if X = Cl, Br, I):
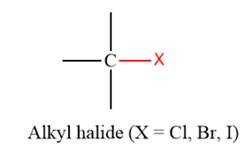
In this functional group, there is no H atom which is covalently bonded to a strongly electronegative atom such as N, O, or F. Therefore, there is no H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor.
The H-bond donor and H-bond acceptor of the given compounds are predicted on the basis of the number of electronegative atoms that are covalently bonded with hydrogen atoms and with a large concentration of negative charge and lone pair of electrons.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY: PRINCIPLES AND M
- V Biological Macromolecules Drawing the Haworth projection of an aldose from its Fischer projection Draw a Haworth projection of a common cyclic form of this monosaccharide: H C=O HO H HO H H OH CH₂OH Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forwardComplete the mechanismarrow_forward
- 8 00 6 = 10 10 Decide whether each of the molecules in the table below is stable, in the exact form in which it is drawn, at pH = 11. If you decide at least one molecule is not stable, then redraw one of the unstable molecules in its stable form below the table. (If more than unstable, you can pick any of them to redraw.) Check OH stable HO stable Ounstable unstable O OH stable unstable OH 80 F6 F5 stable Ounstable X Save For Later Sub 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy C ཀྭ་ A F7 매 F8 F9 4 F10arrow_forwardJust try completing it and it should be straightforward according to the professor and TAs.arrow_forwardThe grading is not on correctness, so if you can just get to the correct answers without perfectionism that would be great. They care about the steps and reasoning and that you did something. I asked for an extension, but was denied the extension.arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
