
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Molecular geometry and electron geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is to be predicted using VSEPR theory.
Concept introduction:
Electron geometry and molecular geometry of molecules are determined by using Valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) theory. According to VSEPR theory, electron geometry describes the orientation of the electron groups about a particular atom and molecular geometry describes the arrangement of atoms about a particular atom.
The number of electron pairs describes the electron and molecular geometry. If all the electron pairs are bonds, then the molecular geometry is the same as the electron geometry. Electron geometry is different from molecular geometry if some electron groups are present as lone pairs. The bond angle depends on the electron geometry around the atom.
Electron geometry and molecular geometry from the number of electron pairs and bond angle according to VSEPR theory are as follows:
| Number of Electron Groups |
Number of Bonds |
Number of Lone Pairs |
Bond Angle (o) |
Electron Geometry | Molecular Geometry |
| 2 | 2 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 3 | 3 | 0 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Trigonal planer |
| 3 | 2 | 1 | 120 | Trigonal planar | Bent |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Tetrahedral |
| 4 | 4 | 0 | 180 | Linear | Linear |
| 4 | 2 | 2 | 109.5 | Tetrahedral | Bent |
Answer to Problem 2.2P
According to VSEPR theory, the electron and molecular geometry about each of the non-hydrogen atom in the structure is as follows:
Oxygen = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is bent.
C1 carbon atom = Electron geometry is tetrahedral while molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
C2 and C3 carbon atoms = Electron geometry is linear while molecular geometry is also linear.
Explanation of Solution
The given structure for
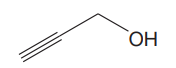
The structure showing all the atoms and lone pairs is:
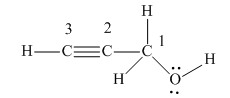
There are four non-hydrogen atoms in the above structure. They are numbered from 1 to 4.
There are four groups of electrons around the oxygen atom: two lone pairs of electrons and two single bonds. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is bent.
There are four groups of electrons around the C1 carbon: four single bonds and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is tetrahedral, and its molecular geometry is also tetrahedral.
There are two groups of electrons around the C2 carbon: one triple bond, and one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
There are two groups of electrons around the C3 carbon: one triple bond, one single bond, and no lone pairs of electrons. According to VSEPR theory, its electron geometry is linear, and its molecular geometry is also linear.
The electron geometry and molecular geometry about each non-hydrogen atom in the given molecule is predicted on the basis of VSEPR chart.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK GET READY FOR ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- One liter of chlorine gas at 1 atm and 298 K reacts completely with 1.00 L of nitrogen gas and 2.00 L of oxygen gas at the same temperature and pressure. A single gaseous product is formed, which fills a 2.00 L flask at 1.00 atm and 298 K. Use this information to determine the following characteristics of the product:(a) its empirical formula;(b) its molecular formula;(c) the most favorable Lewis formula based on formal charge arguments (the central atom is N);(d) the shape of the molecule.arrow_forwardHow does the square root mean square velocity of gas molecules vary with temperature? Illustrate this relationship by plotting the square root mean square velocity of N2 molecules as a function of temperature from T=100 K to T=300 K.arrow_forwardDraw product B, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CF3 NH2 Me O .N. + B OMearrow_forward
- Benzimidazole E. State its formula. sState the differences in the formula with other benzimidazoles.arrow_forwardDraw product A, indicating what type of reaction occurs. F3C CN CF3 K2CO3, DMSO, H₂O2 Aarrow_forward19) Which metal is most commonly used in galvanization to protect steel structures from oxidation? Lead a. b. Tin C. Nickel d. Zinc 20) The following molecule is an example of a: R₁ R2- -N-R3 a. Secondary amine b. Secondary amide c. Tertiary amine d. Tertiary amidearrow_forward
- pls helparrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward35) Complete the following equation by drawing the line the structure of the products that are formed. Please note that in some cases more than one product is possible. You must draw all possible products to recive full marks! a. ethanol + 2-propanol + H2SO4 → b. OH conc. H2SO4 CH2 H3C CH + K2Cr2O7 C. d. H3C A pressure CH3 + H2 CH Pt catalystarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





