
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781260048469
Author: Griffith
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 2, Problem 22CQ
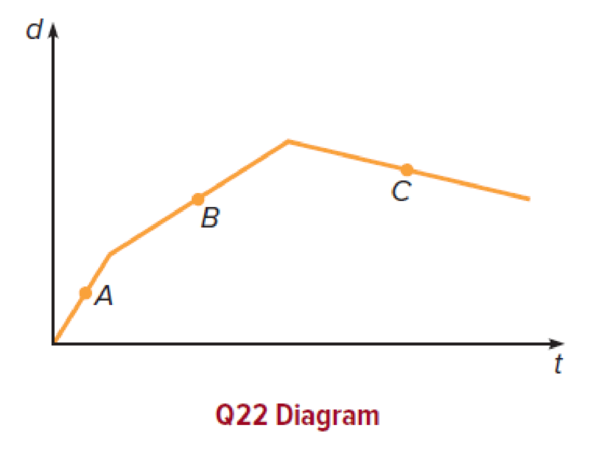
A car moves along a straight line so that its position (distance from some starting point) varies with time as described by the graph shown here.
- a. Does the car ever go backward? Explain.
- b. Is the instantaneous velocity at point A greater or less than that at point B? Explain.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
A Van de Graff generator, if the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each other using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force.
Give your answer as the number of Coulombs
Please help me answer the following question. I am having trouble understanding the directions of the things the question is asking for. Please include a detailed explanation and possibly drawings of the directions of Bsource, Binduced, and Iinduced.
43. A mass må undergoes circular
motion of radius R on a hori-
zontal frictionless table, con-
nected by a massless string
through a hole in the table to
a second mass m² (Fig. 5.33).
If m₂ is stationary, find expres-
sions for (a) the string tension
and (b) the period of the circu-
lar motion.
m2
R
m₁
FIGURE 5.33 Problem 43
Chapter 2 Solutions
Physics of Everyday Phenomena
Ch. 2 - Prob. 1CQCh. 2 - Suppose we choose inches as our basic unit of...Ch. 2 - What units would have an appropriate size for...Ch. 2 - A tortoise and a hare cover the same distance in a...Ch. 2 - A driver states that she was doing 80 when stopped...Ch. 2 - Does the speedometer on a car measure average...Ch. 2 - Is the average speed over several minutes more...Ch. 2 - The highway patrol sometimes uses radar guns to...Ch. 2 - Is the term vehicle density (as used in everyday...Ch. 2 - Prob. 10CQ
Ch. 2 - At the front end of a traffic jam, is the vehicle...Ch. 2 - A hockey puck is sliding on frictionless ice. It...Ch. 2 - A ball attached to a string is whirled in a...Ch. 2 - Prob. 14CQCh. 2 - A dropped ball gains speed as it falls. Can the...Ch. 2 - A driver of a car steps on the brakes, causing the...Ch. 2 - At a given instant in time, two cars are traveling...Ch. 2 - A car just starting up from a stop sign has zero...Ch. 2 - A car traveling with constant speed rounds a curve...Ch. 2 - A racing sports car traveling with a constant...Ch. 2 - In the graph shown here, velocity is plotted as a...Ch. 2 - A car moves along a straight line so that its...Ch. 2 - For the car whose distance is plotted against time...Ch. 2 - A car moves along a straight section of road so...Ch. 2 - For the car whose velocity is plotted in question...Ch. 2 - Look again at the velocity-versus-time graph for...Ch. 2 - Suppose the acceleration of a car increases with...Ch. 2 - When a car accelerates uniformly from rest, which...Ch. 2 - The velocity-versus-time graph of an object curves...Ch. 2 - For a uniformly accelerated car, is the average...Ch. 2 - A car traveling in the forward direction...Ch. 2 - A car starts from rest, accelerates uniformly for...Ch. 2 - Suppose that two runners run a 100-meter dash, but...Ch. 2 - Sketch a graph showing velocity-versus-time curves...Ch. 2 - A physics instructor walks with increasing speed...Ch. 2 - Prob. 36CQCh. 2 - Return to example box 2.4, but this time assume...Ch. 2 - A traveler covers a distance of 413 miles in a...Ch. 2 - A walker covers a distance of 2.4 km in a time of...Ch. 2 - Grass clippings are found to have an average...Ch. 2 - A driver drives for 2.5 hours at an average speed...Ch. 2 - A woman walks a distance of 504 m, with an average...Ch. 2 - A person in a hurry averages 70 MPH on a trip...Ch. 2 - A hiker walks with an average speed of 1.3 m/s....Ch. 2 - Prob. 8ECh. 2 - A car travels with an average speed of 65 MPH....Ch. 2 - Starting from rest and moving in a straight line,...Ch. 2 - Starting from rest, a car accelerates at a rate of...Ch. 2 - The velocity of a car decreases from 28 m/s to 20...Ch. 2 - A car traveling with an initial velocity of 16 m/s...Ch. 2 - A runner traveling with an initial velocity of 1.1...Ch. 2 - A car moving with an initial velocity of 32 m/s...Ch. 2 - A runner moving with an initial velocity of 4.0...Ch. 2 - If a world-class sprinter ran a distance of 100...Ch. 2 - Starting from rest, a car accelerates at a...Ch. 2 - A railroad engine moves forward along a straight...Ch. 2 - The velocity of a car increases with time, as...Ch. 2 - A car traveling due west on a straight road...Ch. 2 - A car traveling in a straight line with an initial...Ch. 2 - Just as car A is starting up, it is passed by car...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- CH 70. A block is projected up an incline at angle 0. It returns to its initial position with half its initial speed. Show that the coefficient of ki- netic friction is μk = tano.arrow_forwardPassage Problems A spiral is an ice-skating position in which the skater glides on one foot with the other foot held above hip level. It's a required element in women's singles figure-skating competition and is related to the arabesque performed in ballet. Figure 5.40 shows Canadian skater Kaetlyn Osmond executing a spiral during her medal-winning perfor- mance at the 2018 Winter Olympics in Gangneung, South Korea. 77. From the photo, you can conclude that the skater is a. executing a turn to her left. b. executing a turn to her right. c. moving in a straight line out of the page. 78. The net force on the skater a. points to her left. b. points to her right. c. is zero. 79. If the skater were to execute the same maneuver but at higher speed, the tilt evident in the photo would be a. less. b. greater. c. unchanged. FIGURE 5.40 Passage Problems 77-80 80. The tilt angle 0 that the skater's body makes with the vertical is given ap- proximately by 0 = tan¯¹(0.5). From this you can conclude…arrow_forwardFrictionless surfarrow_forward
- 71. A 2.1-kg mass is connected to a spring with spring constant 72 k = 150 N/m and unstretched length 18 cm. The two are mounted on a frictionless air table, with the free end of the spring attached to a frictionless pivot. The mass is set into circular mo- tion at 1.4 m/s. Find the radius of its path. cor moving at 77 km/h negotiat CH —what's the minimum icient of frictioarrow_forward12. Two forces act on a 3.1-kg mass that undergoes acceleration = 0.91 0.27 m/s². If one force is -1.2î – 2.5ĵ N, what's the other?arrow_forward36. Example 5.7: You whirl a bucket of water around in a vertical circle of radius 1.22 m. What minimum speed at the top of the circle will keep the water in the bucket?arrow_forward
- Passage Problems Laptop computers are equipped with accelerometers that sense when the device is dropped and then put the hard drive into a protective mode. Your computer geek friend has written a program that reads the accel- erometer and calculates the laptop's apparent weight. You're amusing yourself with this program on a long plane flight. Your laptop weighs just 5 pounds, and for a long time that's what the program reports. But then the "Fasten Seatbelt" light comes on as the plane encounters turbu- lence. Figure 4.27 shows the readings for the laptop's apparent weight over a 12-second interval that includes the start of the turbulence. 76. At the first sign of turbulence, the plane's acceleration a. is upward. b. is downward. c. is impossible to tell from the graph. 77. The plane's vertical ac- celeration has its greatest magnitude a. during interval B. b. during interval C. c. during interval D. 78. During interval C, you can conclude for certain that the plane is Apparent…arrow_forwardIf the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each otherarrow_forwardIf the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere? Assume you can treat both the person and the metal sphere as point charges a distance 25 cm from each other (so that you can use Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force).arrow_forward
- Using Coulomb's Law, calculate the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other. (Give your answer as the number of Newtons but as usual you only need to include the number, not the unit label.)arrow_forwardPart A You want to get an idea of the magnitude of magnetic fields produced by overhead power lines. You estimate that a transmission wire is about 12 m above the ground. The local power company tells you that the line operates at 12 kV and provide a maximum of 60 MW to the local area. Estimate the maximum magnetic field you might experience walking under such a power line, and compare to the Earth's field. [For an ac current, values are rms, and the magnetic field will be changing.] Express your answer using two significant figures. ΟΤΕ ΑΣΦ VAΣ Bmax= Submit Request Answer Part B Compare to the Earth's field of 5.0 x 10-5 T. Express your answer using two significant figures. Ο ΑΣΦ B BEarth ? ? Tarrow_forwardHo propel 9-kN t. Boat 27. An elevator accelerates downward at 2.4 m/s². What force does the elevator's floor exert on a 52-kg passenger?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Position/Velocity/Acceleration Part 1: Definitions; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4dCrkp8qgLU;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY