
Concept explainers
1)a.
Whether the cost of instruction is fixed or variable cost
1)a.
Explanation of Solution
The cost of instruction is fixed cost as the total cost $7,500 remains constant irrespectively of number of C Courses candidates attends the courses
b.
Determine the profit
b.
Explanation of Solution
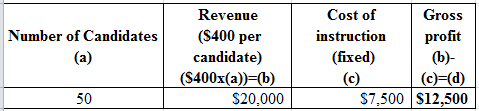
Table (1)
c.
Determine the profit and 10% of increase in enrolment.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Excel spreadsheet:
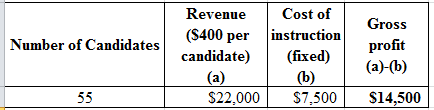
Table (2)
Percentage change in revenue and profitability:
Hence, the percentage change in profitability is 16%.
Percentage change in revenue:
Hence, the percentage change in revenue is 10%.
d.
Determine the profit and 10% of decrease in enrolment.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the profit:
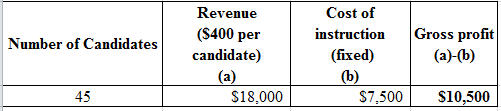
Table (3)
Percentage change in revenue and profitability:
Hence, the percentage change in profitability is 16%.
Hence, the percentage change in revenue is 10%.
e.
The reason for 10% shift in enrollment produces more than 10% shift in profitability and the term identifies this phenomenon.
e.
Explanation of Solution
The term which identifies these phenomena is operating leverage. This causes the percentage change in profitability to higher than the percentage change in revenue.
This is because that the fixed cost remains same and covered and there is no variable cost. So each additional dollar of revenue pays directly to the profitability.
2)f.
Whether the cost of instruction is fixed or variable cost
Given information:
The fee per candidate is $150.
2)f.
Explanation of Solution
The cost of instruction is variable cost as the total cost varies respectively of number of candidates attends the courses
g.
Determine the profit
g.
Explanation of Solution
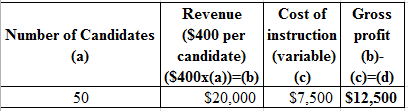
Table (4)
h.
Determine the profit and 10% of increase in enrolment.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Excel spreadsheet:
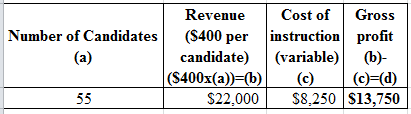
Table (5)
Percentage change in revenue and profitability:
Hence, the percentage change in profitability is 10%.
Hence, the percentage change in revenue is 10%.
i.
Determine the profit and 10% of decrease in enrolment.
i.
Explanation of Solution
Excel spreadsheet:
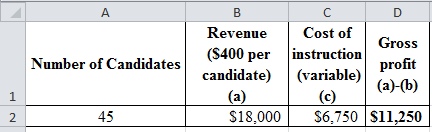
Table (6)
Excel workings:
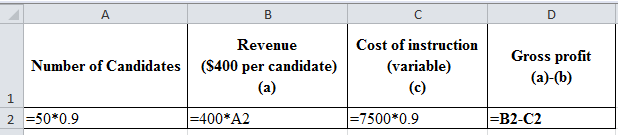
Table (7)
Percentage change in revenue:
Hence, the percentage change in profitability is 10%.
Hence, the percentage change in revenue is 10%.
j.
The reason for 10% shift in enrollment produces relative 10% shift in profitability.
j.
Explanation of Solution
The change in profit is relative to change in revenue because the revenue as well as cost changes relatively to the change in number of candidates attending the course.
3)k.
The total cost and the cost per candidate
3)k.
Explanation of Solution
The formula to calculate the cost per candidate:
Compute the total cost:
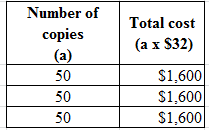
Table (8)
Compute the cost per candidate:
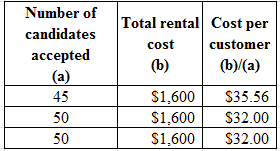
Table (9)
l.
Whether the cost of work book is fixed or variable cost
l.
Explanation of Solution
The cost of work book is fixed cost as the cost incurred is before the sale of work book. Therefore, sales of number of work book will not affect the total cost.
Thus, it is fixed cost.
m.
The risk of holding inventory as it applies to workbooks
m.
Explanation of Solution
The risk faced by the company is that it produces very few or too many books. If the company produces too many books then the expenses will more due to wastage.
When the company produces less numbers then the will not get the opportunity to earn any additional profits.
It will also incur costs like maintenances, interest and storage.
n.
Whether just in time can reduce the cost and risk of holding inventory
n.
Explanation of Solution
JIT-Just in time produces only when there is any demand of goods. There will not be any risk on over or under production.
There will not be any stock piling of inventory as it will avoid the cost of storage, interest and maintenance
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts with Access
- Accounting problemarrow_forwardTrent Manufacturing Company produces and sells 95,000 units of a single product. Variable costs total $285,000 and fixed costs total $390,000. If each unit is sold for $11, what markup percentage is the company using?arrow_forwardWhat is the company's overhead application ratearrow_forward
- Answerarrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardDavis Company reported an increase of $350,000 in its accounts receivable during the year 2023. The company's statement of cash flows for 2023 reported $980,000 of cash received from customers. What amount of net sales must Davis have recorded in 2023?arrow_forward
- Given the solution and accounting questionarrow_forwardSalem Enterprises reports its accounts receivable on the balance sheet. The gross receivable balance is $78,000, and the allowance for uncollectible accounts is estimated at 12% of gross receivables. At what amount will accounts receivable be reported on the balance sheet?arrow_forwardNet income for the year isarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





