
Concept explainers
An element is a shiny, silver-colored solid at room temperature and pressure. It conductselectricity and can be found in nature in its pure form. Whichelement on the periodic table (a−d) would have these properties?
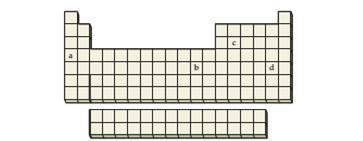
Interpretation:
Whether the element is metal, nonmetal, and semimetal should be classified. Also, the general location of element in periodic table should be determined.
Concept introduction:
Periodic table represents a systematic arrangement according to element’s physical as well as chemical properties. Here, elements are represented as a two-letter symbol and are arranged in increasing order of atomic number. Periodic table contains 18 groups (columns) and 7 periods (rows). In periodic table, groups from 1-2 and 13-18 are called main group elements. The 10 middle groups from 3-12 are known as transition elements. There are also 14 elements that started with lanthanum are called lanthanides and 14 elements started with actinium are known as actinides.
Explanation of Solution
The metals are characterized by their silvery shiny appearance and good conductor of electricity and given elements is a silvery shiny and good conductor of electrical energy (electricity), therefore the given element must be a metal. Metals that are occurred in pure form in nature known as native metals and native metals are silver, gold, and copper. Among these metals, silver is the only metal that has a silver coating. Hence the given metal is silver.
The silver metal present in periodic table in 11th group and 5th period, therefore, the location of given silver metal is b.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
CHEMISTRY-MASTERINGCHEMISTRY W/ETEXT
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth (11th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
- Select the product for the following reaction. HO HO PCC OH ○ OH O HO ○ HO HO HOarrow_forward5:45 Х Select the final product for the following reaction sequence. O O 1. Mg. ether 2.D.Oarrow_forwardBased on the chart Two similarities between the molecule with alpha glycosidic linkages. Two similarities between the molecules with beta glycosidtic linkages. Two differences between the alpha and beta glycosidic linkages.arrow_forward
- please help fill in the tablearrow_forwardAnswer F pleasearrow_forward4. Refer to the data below to answer the following questions: The octapeptide saralasin is a specific antagonist of angiotensin II. A derivative of saralasin is used therapeutically as an antihypertensive. Amino acid analysis of saralasin show the presence of the following amino acids: Ala, Arg, His, Pro, Sar, Tyr, Val, Val A.Sar is the abbreviation for sarcosine, N-methyl aminoethanoic acid. Draw the structure of sarcosine. B. N-Terminal analysis by the Edman method shows saralasin contains sarcosine at the N-terminus. Partial hydrolysis of saralasin with dilute hydrochloric acid yields the following fragments: Tyr-Val-His Sar-Arg-Val His-Pro-Ala Val-Tyr-Val Arg-Val-Tyr What is the structure of saralasin?arrow_forward
- What is the structure of the DNA backbone?arrow_forwardPLEASE PLEASE PLEASE use hand drawn structures when possarrow_forward. M 1- MATCH each of the following terms to a structure from the list below. There is only one correct structure for each term and structures may be used more than once. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the corresponding term. A. Sanger dideoxy method C. Watson-Crick B. GAUCGUAAA D. translation E. HOH2C OH OH G. transcription I. AUGGCUGAG 0 K. OPOH2C 0- OH N- H NH2 F. -OPOH2C 0- OH OH H. Maxam-Gilbert method J. replication N L. HOH2C a. b. C. d. e. f. g. B M. AGATCGCTC a pyrimidine nucleoside RNA base sequence with guanine at the 3' end. DNA base sequence with cytosine at the 3' end. a purine nucleoside DNA sequencing method for the human genome 2'-deoxyadenosine 5'-phosphate process by which mRNA directs protein synthesis OH NH2arrow_forward
- Please use hand drawn structures when neededarrow_forwardB. Classify the following amino acid. Atoms other than carbon and hydrogen are labeled. a. acidic b. basic C. neutral C. Consider the following image. Which level of protein structure is shown here? a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary D. Consider the following image. H RH H HR H R HR HR RH Which level of protein structure is shown in the box? a. primary b. secondary R c. tertiary d. quaternary コー Rarrow_forwardBriefly answer three from the followings: a. What are the four structures of the protein? b. Why is the side chain (R) attached to the alpha carbon in the amino acids is important for the function? c. What are the types of amino acids? And how is it depend on the (R) structure? d. Write a reaction to prepare an amino acid. prodarrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning  Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning




