
Concept explainers
Analyzing the Effects of Transactions In T-Accounts
Precision Builders Construction Company was incorporated by Chris Stoschek. The following activities occurred during the year:
- a. Received from three investors $60,000 cash and land valued at $35,000: each investor was issued 1,000 shams of common stock with a par value of $0.10 per share.
- b. Purchased construction equipment for use in the business at a cost of $36,000: one-fourth was paid in cash and the company signed a note for the balance (due in six months).
- c. Lent $2,500 to one of the investors, who signed a note due in six months.
- d. Chris Stoschek purchased a truck for personal use: paid $5,000 down and signed a one-year note for $22,000.
- e. Paid $12,000 on the note for the construction equipment in (b) (ignore interest).
Required:
- 1. Create T-accounts for the following accounts: Cash. Notes Receivable. Equipment, Land, Notes Payable. Common Stock, and Additional Paid-in Capital. Beginning balances are $0. For each of the transactions (a) through (e). record the effects of the transaction in the appropriate T-accounts. Include good referencing and totals for each T-account.
- 2. Using the balances in the T-accounts. Till in the following amounts for the
accounting equation: Assets $_______ = Liabilities $ ______ + Stockholders’ Equity $_________
- 3. Explain your response to event (d).
- 4. Compute the market value per share of the stock issued in (a).
1.
Prepare T-accounts for the given accounts.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts for the given accounts are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| (a) | 60,000 | 9,000 | (b) |
| 2,500 | (c) | ||
| 12,000 | (e) | ||
| 36,500 | |||
| Notes Receivable | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| (c) | 2,500 | ||
| 2,500 | |||
| Land | |||
| Beg. | 0 | ||
| (a) | 35,000 | ||
| 35,000 | |||
| Notes Payable | |||
| 0 | Beg. | ||
| (e) | 12,000 | 27,000 | (b) |
| 15,000 | |||
| Common Stock | |||
| 0 | Beg. | ||
| 300 | (a) (1) | ||
| 300 | |||
| Additional Paid-in Capital | |||
| 0 | Beg. | ||
| 94,700 | (a) (12) | ||
| 94,700 | |||
Working note:
Calculate the value of common stock for event (a).
Calculate the value of additional paid in capital for event (a).
2.
Discuss the accounting equation effect for the given accounts.
Explanation of Solution
Accounting equation:
Accounting equation is an accounting tool expressed in the form of equation, by creating a relationship between the resources or assets of a company, and claims on the resources by the creditors and the owners. Accounting equation is expressed as shown below:
Accounting equation effect for given accounts is as follows:
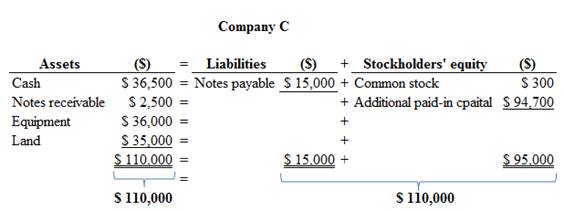
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets are equal to the liabilities and stockholder’s equity.
3.
Explain the response to events (d).
Explanation of Solution
Transaction:
A transaction is a business event which has a monetary value that creates an impact on the business. The process of identifying the economic effects of each transaction of the business is known as transaction analysis.
Event (d) – In this case, there is no exchange of cash, goods or service. So it is not a transaction.
4.
Calculate the market value of per share.
Explanation of Solution
Stock:
Stock represents the number of shares owned by the investors (individual or group) in a Corporation.
Calculate the market value of per share
Here,
Total amount of cash received at the time of issuance of share is $95,000
Number of shares issued is 3,000 shares
Therefore, the market value of per share is $31.67.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- please post this question in Account tutors feedarrow_forwardAnticipated unit sales are January, 5,000, February, 4,000, and March 8,000 Finished goods are consistently maintained at 80% of the following month's sales If units cost $10 each to produce, how much is February's total cost of production?arrow_forwardWhat is its net opreting profit after tax?arrow_forward
- Beethoven Corp. had net sales of 45,600 and ending accounts receivable of 5,700 for the current period. Its days' sales uncollected equals: (Use 365 days a year.) a. 40.25 days b. 36.17 days c. 45.63 days d. 32.43 days e. 30.47 daysarrow_forwardAQUA SYSTEMS REPORTS THE FOLLOWING SALES OF $150,000; INFORMATION: BEGINNING ASSETS OF $300,000, ENDING ASSETS OF OF $360,000; NET INCOME $9,000. OF THE RETURN ON ASSETS (TO THE NEAREST WHOLE NUMBER) IS: A. 555% B. 30% c. 3% D. 6%arrow_forwardDetermine the cash payments made during marcharrow_forward
- Provide answerarrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT considered a fixed asset? A. Machinery B. Accounts Receivable C. Building D. Landarrow_forwardStark Corp is in the process of acquiring another business. In light of the acquisition, shareholders are currently re-evaluating the appropriateness of the firm's capital structure (the types of and relative levels of debt and equity). The two proposals being contemplated are detailed below: Proposal 1 Proposal 2 Estimated earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT) $ 450,000 $ 450,000 Long term debt 1,000,000 2,000,000 Market value of equity 1,000,000 500,000 Interest rate on long term debt 10% 10% Tax rate 25% 25% Required Calculate the estimated return on equity (ROE) under the two proposals. (ROE = net income after taxes / market value of equity; net income after taxes = (EBIT - interest on long-term debt) × (1 - tax rate)).arrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
