
Verify whether the interconnection in the circuit in Figure P2.1 in the textbook is valid or not. Calculate the power developed by the current sources if the circuit is valid. Explain the reason if the interconnection in the circuit is not valid.
Answer to Problem 1P
The interconnection in the given circuit is valid and the power developed by the current sources is 1700 W.
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Refer to Figure P2.1 in the textbook for required data.
Formula used:
Write the expression for power developed by the source (voltage or current) as follows:
Here,
Calculation:
From the given circuit, it is clear that, the voltage drop across the 10 A current source is 100 V and the voltage drop from the negative terminal of the 40 V voltage source to the bottom terminal of the 5 A current source must be 100 V.
In order to maintain the voltage drop of 100 V from the negative terminal of the 40 V voltage source to the bottom terminal of the 5 A current source the voltage drop across 5 A current source must be 140 V.
From the analysis, redraw the circuit as shown in Figure 1.
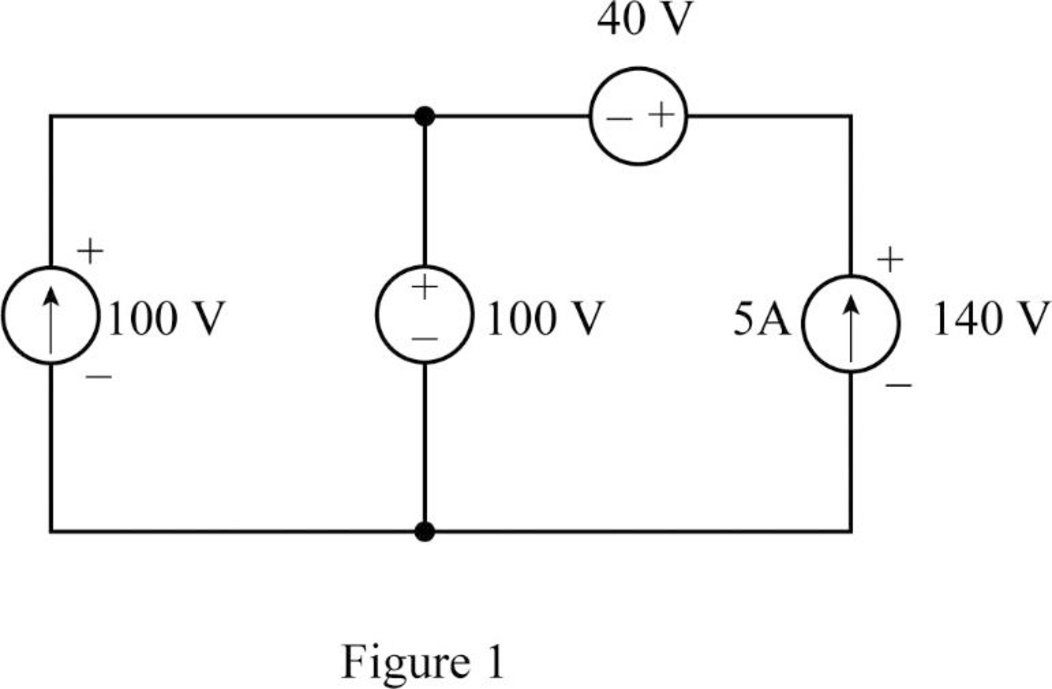
All the sources in the given circuit are independent sources. The independent voltage source can carry any current that required by the connection and the independent current source can support any voltage that required by the connection.
From the analysis, the voltage drop across the sources is satisfied. Therefore, the interconnection in the given circuit is valid.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 10 A current source as follows:
From Figure 1, current 10 A enters from the negative terminal of 100 V. Therefore, the values of
The negative sign indicates the delivered power by the source. Therefore, the power developed by the 10 A current source is 1000 W.
Rewrite the expression in Equation (1) to find the power developed by the 5 A current source as follows:
From Figure 1, current 5 A enters from the negative terminal of 140 V. Therefore, the values of
As the negative sign indicates the delivered power by the source, the power developed by the 5 A current source 700 W.
Write the expression for power developed by the both current sources as follows:
Substitute 1000 W for
Conclusion:
Thus, the interconnection in the given circuit is valid and the power developed by the current sources is 1700 W.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
ELECTRIC CIRCUITS-W/MASTERINGENGINEERING
- 12.4 Determine the Laplace transform of each of the followingfunctions by applying the properties given in the Tables (a) f1(t) = 4te−2t u(t)(b) f2(t) = 10cos(12t +60◦) u(t)*(c) f3(t) = 12e−3(t−4) u(t −4)(d) f4(t) = 30(e−3t +e3t ) u(t)(e) f5(t) = 16e−2t cos4t u(t)(f) f6(t) = 20te−2t sin4t u(t)arrow_forward8. Obtain the inverse Laplace transform of each of the followingfunctions by first applying the partial-fraction-expansionmethod.(a) F1(s) =6(s+2)(s+4)(b) F2(s) =4(s+1)(s+2)2(c) F3(s) =3s3 +36s2 +131s+144s(s+4)(s2 +6s+9)(d) F4(s) =2s2 +4s−10(s+6)(s+2)2arrow_forward12.12 In the circuit of Fig. P12.12(a), is(t) is given by the waveform shown in Fig. P12.12(b). Determine iL (t) for t≥ 0, given that R₁ = R₂ = 2 2 and L = 4 H. is() R₁ R2: (a) Circuit is(t) 8A- 8e-21 elle (b) is(t) Figure P12.12 Circuit and waveform for Problem 12.12. iLarrow_forward
- 12.12 In the circuit of Fig. P12.12(a), is(t) is given by thewaveform shown in Fig. P12.12(b). Determine iL(t) for t ≥ 0,given that R1 = R2 = 2 W and L = 4 H.arrow_forward12.4 Determine the Laplace transform of each of the following functions by applying the properties given in Tables 12-1 and 12-2 on pages 642-643. (a) fi(t)=4tet u(t) (b) f2(t)=10cos (12t+60°) u(t) *(c) f3(t) = 12e−3(t−4) u(t −4) (d) f4(t) = 30(e³ +e³t) u(t) (e) fs(t)=16e2t cos 4t u(t) (f) f6(t)=20te 2 sin 4t u(t)arrow_forwarda) Calculate the values of v and i. + 803 1A Va 82 b) Determine the power dissipated in each resistor. 1A Va (a) + I 50 V 0.2 S (b) + D + 1 Α υ€ 20 Ω 50 V 250 ΩΣ ia (c) (d) Copyright ©2015 Pearson Education, All Rights Reservedarrow_forward
- Exercise 3-12: Find the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit to the left of terminals (a, b) in Fig. E3.12, and then determine the current I. 502 502 0.6 Ω 20 V | + <302 Ω ΣΙΩ b 2025 Ω 15A Figure E3.12arrow_forward2. Consider following feedback system. r(t) e(t) y(t) K G(s) 1 where G(S) = s²+as+b In above, K, a and b are constants. Select the values of K, a and b in a way so that (i) (ii) (iii) the closed loop system is stable, steady-state error of the closed-loop system for step input is 0.2, the closed-loop response has 20% overshoot and 2 seconds as settling time.arrow_forward4. Answer the following questions. Take help from ChatGPT to answer these questions (if you need). But write the answers briefly using your own words with no more than two sentences, and make sure you check whether ChatGPT is giving you the appropriate answers in the context of class. a) What is the advantage of the PI controller over the proportional controller? b) What is the advantage of the PD controller over a proportional controller? c) In the presence of noise, what problem do we face implementing the derivate part of the PID (or PD) controller? To address this, what do we usually use? d) What are the forms of lead compensator and lag compensator? How do these two types of compensators differ?arrow_forward
- 3. Consider the following closed-loop system as shown in the figure. 16 Ge(s) s(s + 4) Suppose Ge(s) is a PID controller with Kp = 1, KD = 2 and K₁ = 3. a) Find the controller transfer function G₁(s). b) Find the open-loop transfer function. c) Find the closed-loop transfer function.arrow_forwardExercise 3-12: Find the Thévenin equivalent of the circuit to the left of terminals (a, b) in Fig. E3.12, and then determine the current I. 502 5 Ω 0.6 Ω a 3Ω ΣΙΩ b 20 V 1 + 2027 15A Figure E3.12arrow_forwardsolve and show workarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





