
Concept explainers
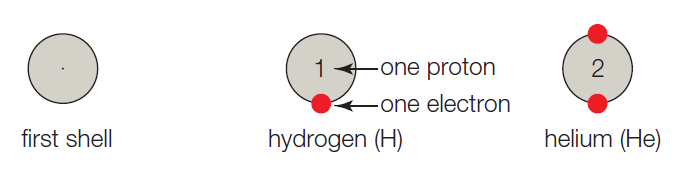
- A. The first shell corresponds to the first energy level, and it can hold up to 2 electrons. Hydrogen has one proton, so it has 1 electron and one vacancy. A helium atom has 2 protons, 2 electrons, and no vacancies.
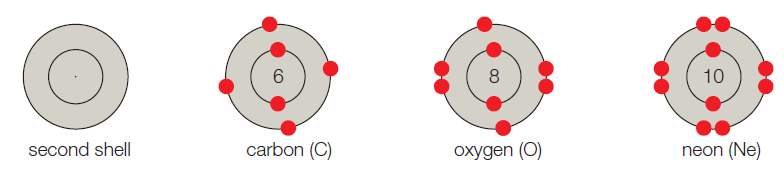
- B. The second shell corresponds to the second energy level, and it can hold up to 8 electrons. Carbon has 6 electrons, so its first shell is full. Its second shell has 4 electrons and four vacancies. Oxygen has 8 electrons and two vacancies. Neon has 10 electrons and no vacancies.
- C. The third shell corresponds to the third energy level, and it can hold up to 8 electrons. A sodium atom has 11 electrons, so its first two shells are full; the third shell has one electron. Thus, sodium has seven vacancies. Chlorine has 17 electrons and one vacancy. Argon has 18 electrons and no vacancies.
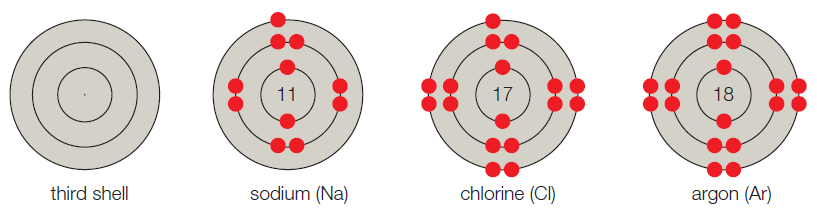
Figure It Out: Which of these models have unpaired electrons in their outer shell?
The atoms are referred to as building blocks of all substances. In other words, it is the basic fundamental unit of the matter. In every atom, the uncharged neutron and positively charged protons are present in the nucleus whereas the negatively charged electron moves around the nucleus. Generally, the shell model system is used to study the valence status of an atom. The atomic number is the number of protons present in the atom which determines the type of the atom
Explanation of Solution
The given shell model consists of about eight atoms namely helium, neon, hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, sodium, chloride, and argon. Of this given atom in the model the hydrogen, carbon, oxygen, chlorine and sodium have unpaired electrons in the outer shell. These unpaired electrons are available to pair with other unpaired electrons in another atom. Thus these atoms combine to form molecules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK BIOLOGY TODAY AND TOMORROW WITH PHY
- Selection of Traits What adaptations do scavengers have for locating and feeding on prey? What adaptations do predators have for capturing and consuming prey?arrow_forwardCompetition Between Species What natural processes limit populations from growing too large? What are some resources organisms can compete over in their natural habitat?arrow_forwardSpecies Interactions Explain how predators, prey and scavengers interact. Explain whether predators and scavengers are necessary or beneficial for an ecosystem.arrow_forward
- magine that you are conducting research on fruit type and seed dispersal. You submitted a paper to a peer-reviewed journal that addresses the factors that impact fruit type and seed dispersal mechanisms in plants of Central America. The editor of the journal communicates that your paper may be published if you make ‘minor revisions’ to the document. Describe two characteristics that you would expect in seeds that are dispersed by the wind. Contrast this with what you would expect for seeds that are gathered, buried or eaten by animals, and explain why they are different. (Editor’s note: Providing this information in your discussion will help readers to consider the significance of the research).arrow_forwardWhat is the difference between Uniporters, Symporters and Antiporters? Which of these are examples of active transport?arrow_forwardWhat are coupled transporters?arrow_forward
- How do histamine and prostaglandins help in the mobilization of leukocytes to an injury site? What are chemotactic factors? How do they affect inflammation process?arrow_forwardCompare and contrast neutrophils and macrophages. Describe two ways they are different and two ways they are similar.arrow_forwardDescribe the effects of three cytokines (not involved in the initial inflammation response). What cells release them?arrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning



