
Concept explainers
a.
Prepare journal entries and record the above transactions in T-account.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
Record the journal entries for the month of May date from May 1 to May 15.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 1 | Cash | 60,000 | |||
| Common Stock | 60,000 | ||||
| ( To record the issue of | |||||
| Common stock.) | |||||
Table (1)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 2 | Equipment | 4,200 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 4,200 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of | |||||
| Equipment on account.) | |||||
Table (2)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 3 | Accounts Payable | 200 | |||
| Equipment | 200 | ||||
| (To record the return of | |||||
| Equipment.) | |||||
Table (3)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 4 | Supplies | 860 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 860 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of | |||||
| Supplies on account.) | |||||
Table (4)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 5 | Truck | 12,500 | |||
| Cash | 5,500 | ||||
| Note Payable | 7,000 | ||||
| (To record the purchase of | |||||
| Cash and note payable.) | |||||
Table (5)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 6 | Rent | 875 | |||
| Cash | 875 | ||||
| ( To record the payment | |||||
| Of rent.) | |||||
Table (6)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 7 | Truck expense | $60 | |||
| Cash | $60 | ||||
| ( To record the expense | |||||
| of fuel cost made for the | |||||
| Truck.) | |||||
Table (7)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 8 | 15,700 | ||||
| Service Revenue | 15,700 | ||||
| (To record the billing made | |||||
| For the services rendered.) | |||||
Table (8)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 9 | Accounts Payable | 5,000 | |||
| Cash | 5,000 | ||||
| (To record the payment for | |||||
| the purchase of | |||||
| Equipment.) | |||||
Table (9)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 10 | Utilities expense | 210 | |||
| Cash | 210 | ||||
| (To record the utilities | |||||
| Expense.) | |||||
Table (10)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 11 | Advertising Expense | 280 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 280 | ||||
| ( To record the advertising | |||||
| expense to be paid on | |||||
| June.) | |||||
Table (11)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 12 | Employee Wages | 5,350 | |||
| Cash | 5,350 | ||||
| ( To record the payment | |||||
| Of employee wages.) | |||||
Table (12)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 13 | Cash | 8,600 | |||
| Account Receivables | 8,600 | ||||
| (To record the collection | |||||
| Of account receivables.) | |||||
Table (13)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 14 | Dividends | 2,500 | |||
| Cash | 2,500 | ||||
| (To record the payment of | |||||
| Dividends amount.) | |||||
Table (14)
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| May 15 | Interest Expenses | 80 | |||
| Cash | 80 | ||||
| (To record the payment | |||||
| Of interest expenses.) | |||||
Table (15)
Record the above transactions in to T-accounts:
Prepare T- accounts
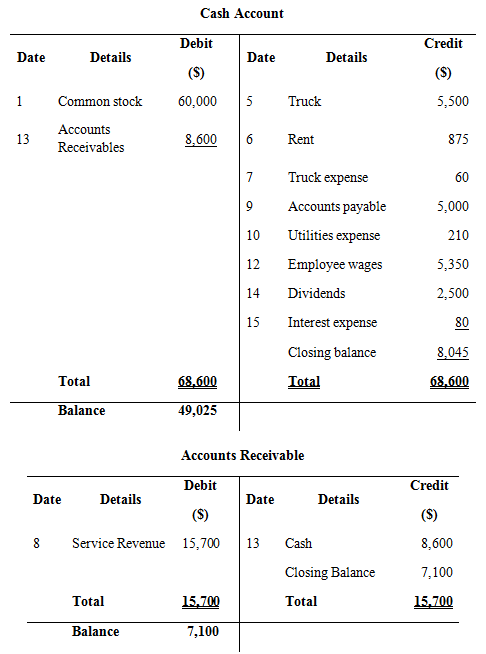
Figure (1)
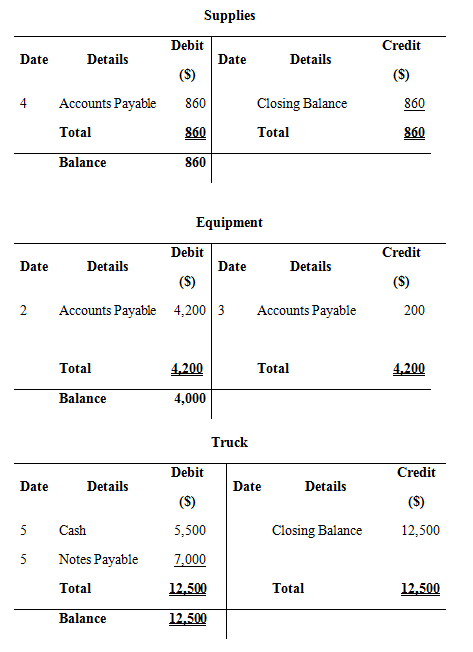
Figure (2)
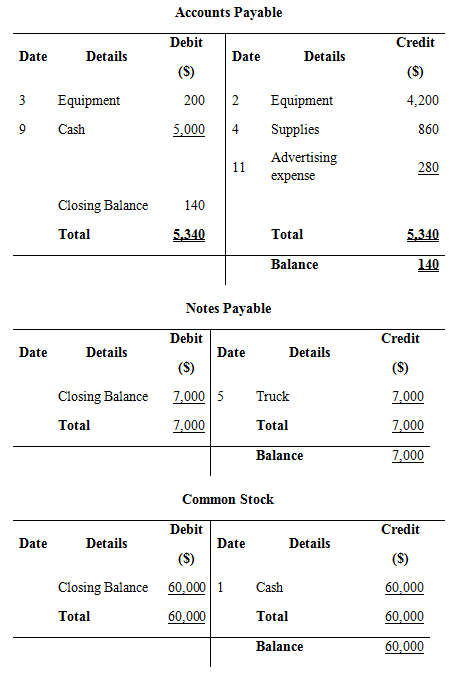
Figure (3)
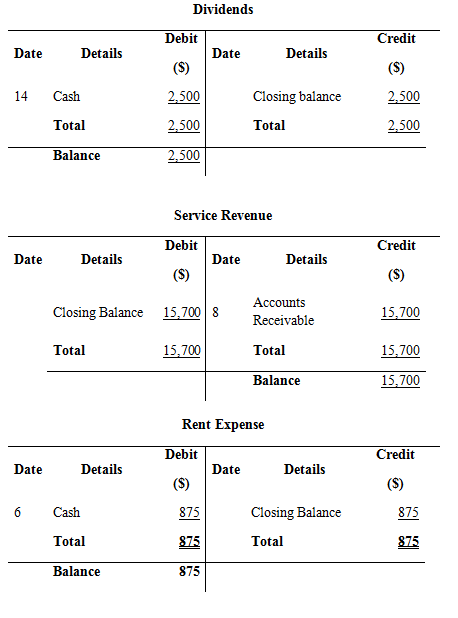
Figure (4)
b.
Prepare
b.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
| Company W | ||
| Trial Balance as of May 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | 49,025 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 7,100 | |
| Supplies | 860 | |
| Equipment | 4,000 | |
| Truck | 12,500 | |
| Accounts Payable | 140 | |
| Notes Payable | 7,000 | |
| Common Stock | 60,000 | |
| Dividends | 2,500 | |
| Service Revenue | 15,700 | |
| Rent Expense | 875 | |
| Wage Expense | 5,350 | |
| Utilities Expense | 210 | |
| Truck Expense | 60 | |
| Advertising Expense | 280 | |
| Interest Expense | 80 | |
| Total | 82,840 | 82,840 |
Table (16)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Accounting for Undergr. -Text Only (Instructor's)
- Vistar Manufacturing bases its manufacturing overhead budget on budgeted direct labor-hours. The direct labor budget indicates that 8,200 direct labor-hours will be required in July. The variable overhead rate is $4.85 per direct labor-hour. The company's budgeted fixed manufacturing overhead is $125,000 per month, which includes depreciation of $10,500. All other fixed manufacturing overhead costs represent current cash flows. What should be the July cash disbursements for manufacturing overhead on the manufacturing overhead budget?arrow_forwardPlease explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- In June, one of the processing departments at Amy Manufacturing had beginning work in process inventory of $45,000 and ending work in process inventory of $21,000. During the month, the cost of units transferred out from the department was $632,000. In the department's cost reconciliation report for June, the total cost to be accounted for under the weighted-average method would be____.arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardUsing the information below for sapphirearrow_forwardOakridge Manufacturing applies overhead to jobs using a predetermined rate of 125% of direct labor cost. At year-end, the company had actual overhead costs of $487,500, while applied overhead totaled $512,500. The company's unadjusted cost of goods sold was $1,250,000. If the company closes any over- or underapplied overhead to cost of goods sold, what is the adjusted cost of goods sold? Need helparrow_forward
- Martin Manufacturing prepared a fixed budget of 85,000 direct labor hours, with estimated overhead costs of $425,000 for variable overhead and $120,000 for fixed overhead. Martin then prepared a flexible budget of 78,000 labor hours. How much are total overhead costs at this level of activity?arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate principles.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





