
Concept explainers
Prepare journal entries and record the above transactions in T-accounts.
Explanation of Solution
General ledger:
General ledger is a book of original entry which records the accounting data in the accounting system of an organisation.
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 1:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 1 | Cash (A+) | 25,000 | |
| Common Stock (E+) | 25,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) |
Table (1)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 2:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 2 | Office Furniture and Fixtures (A+) | 9,800 | |
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 5,000 | ||
| Cash (A–) | 4,800 | ||
| (To record the purchase of office furniture and fixtures) |
Table (2)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 3:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 3 | Tax Library (A+) | 6,700 | |
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 6,700 | ||
| (To record the purchase of Tax library items) |
Table (3)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 4:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 4 | Office Supplies (A+) | 660 | |
| Cash (A–) | 660 | ||
| (To record the purchase of office supplies on cash) |
Table (4)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 5:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 5 | Rent Expense (E–) | 850 | |
| Cash (A–) | 850 | ||
| (To record the payment of rent expense) |
Table (5)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 6:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 6 | Accounts Payable (L–) | 300 | |
| Tax Library (A–) | 300 | ||
| (To record the return of Tax library items) |
Table (6)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 7:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 7 | Accounts Receivable (A+) | 18,600 | |
| Service Revenue (E+) | 18,600 | ||
| (To record the revenues earned) |
Table (7)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 8:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 8 | Accounts Payable (L –) | 1,700 | |
| Cash (A–) | 1,700 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash) |
Table (8)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 9:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 9 | Cash (A+) | 15,900 | |
| Accounts Receivable (A–) | 15,900 | ||
| (To record the receipt of cash from revenues earned) |
Table (9)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 10:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 10 | Salaries Expense (E–) | 4,900 | |
| Cash (A–) | 4,900 | ||
| (To record the payment of salary expenses) |
Table (10)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 11:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 11 | Advertising Expenses (E–) | 400 | |
| Accounts Payable (L+) | 400 | ||
| (To record the advertising expenses on account) |
Table (11)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 12:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 12 | Dividends (E–) | 800 | |
| Cash (A–) | 800 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash dividends) |
Table (12)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 13:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 13 | Utilities expenses (E–) | 160 | |
| Cash (A–) | 160 | ||
| (To record the payment of utility expenses) |
Table (13)
Prepare the journal entry in the general journal on June 14:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| June 14 | Interest Expenses (E–) | 160 | |
| Cash (A–) | 160 | ||
| (To record the payment of interest expenses) |
Table (14)
Prepare T-accounts to record the above transactions:
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
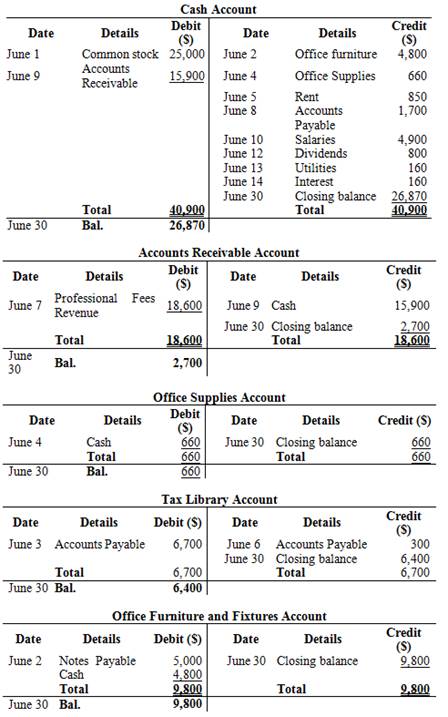
Figure (1)
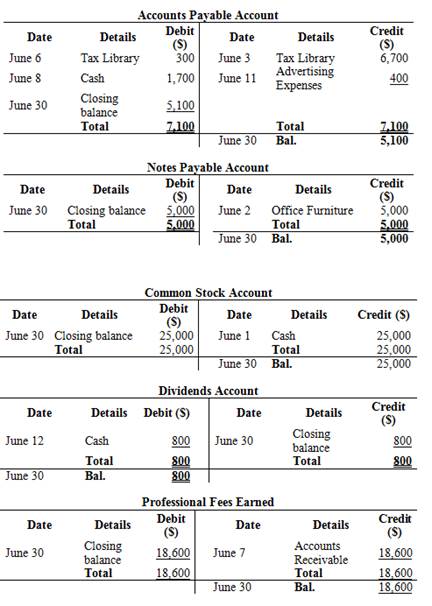
Figure (2)
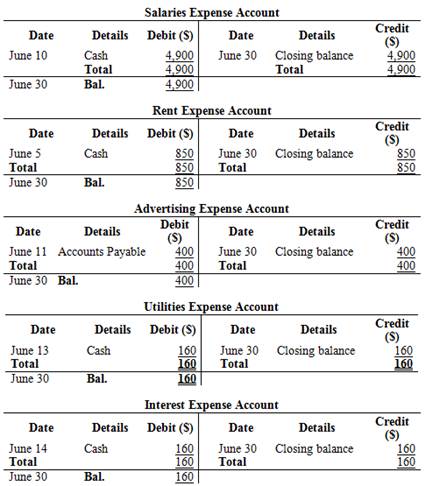
Figure (3)
b.
Prepare
b.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is the summary of accounts, and their debit and credit balances at a given time. It is usually prepared at end of the accounting period. Debit balances are listed in left column and credit balances are listed in right column. The totals of debit and credit column should be equal. Trial balance is useful in the preparation of the financial statements.
| Person W | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| As of June 30 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 26,870 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 2,700 | |
| Tax Library | 6,400 | |
| Office Supplies | 660 | |
| Office Furniture and Fixtures | 9,800 | |
| Accounts Payable | 5,100 | |
| Notes Payable | 5,000 | |
| Common Stock | 25,000 | |
| Dividends | 800 | |
| Professional Fees Earned | 18,600 | |
| Salaries Expense | 4,900 | |
| Rent Expense | 850 | |
| Utilities Expenses | 160 | |
| Advertising Expenses | 400 | |
| Interest Expenses | 160 | |
| Total | 53,700 | 53,700 |
Table (15)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
Financial Accounting for Undergr. -Text Only (Instructor's)
- Lyndon Advisory Group, a consulting firm, had accounts receivable of $22,000 on May 31. During June, payments from customers on account totaled $13,500. At the end of June, Lyndon had accounts receivable amounting to $25,000. What was the amount of consulting services provided to customers on credit during the month of June?arrow_forwardGrant Corporation owns 20% of the common stock of Tanner Industries and uses the fair-value method to account for this investment. Tanner reported net income of $175,000 for 2023 and paid dividends of $95,000 on October 15, 2023. How much income should Grant recognize on this investment in 2023? a. $35,000 b. $19,000 c. $54,000 d. $11,500 e. $70,000arrow_forwardWhat was the direct labor cost on the job?arrow_forward
- What is the answer??arrow_forwardOrville Manufacturing Company's work-in-process inventory on August 1 has a balance of $32,400, representing Job No. 527. During August, $61,500 of direct materials were requisitioned for Job No. 527, and $42,800 of direct labor cost was incurred on Job No. 527. Manufacturing overhead is allocated at 125% of direct labor cost. Actual manufacturing overhead costs incurred in August amounted to $52,500. No new jobs were started during August. Job No. 527 is completed on August 28. Is manufacturing overhead overallocated or underallocated for the month of August and by how much? Correct answerarrow_forwardSolve This Financial Accounting Problemarrow_forward
- Financial Accounting 5 pointsarrow_forwardGiven solution for General accounting question not use aiarrow_forwardGolden State Enterprises had accounts receivable of $215,000 at the beginning of the year. During the year, credit sales amounted to $890,000 and cash collections from customers totaled $825,000. Bad debt write-offs were $18,000. What is the ending accounts receivable balance?need answerarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





