
Mixed cost: Mixed cost is a cost that includes both the fixed cost and the variable cost. It represents the total cost of the activity or production.
Variable Cost: Variable cost is a cost that changes when the volume of production changes, in the same direction and in the same proportion.
Fixed Cost: Fixed cost is a cost that remains constant irrespective of the changes in the production volume.
High-low method: High-low method is a method of calculating the variable cost and the fixed cost of a product or service. The calculation of this method is based on the total production/activity cost and the lowest production/activity cost of the product during any period.
Income Statement: Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or loss for a particular period. It is the summary of expenses and income of a particular period.
- Each of the company's expenses (including cost of goods sold) as variable, fixed, or mixed.
- Using the high-low method, separate each mixed expense into variable and fixed elements. State the cost formula for each mixed expense.
- The company's income statement at the 5,000-unit level of activity using the contribution format.
Answer to Problem 16P
Solution:
- Cost classification of the company’s expenses is done.
- Each mixed expense is separated into variable and fixed elements and the cost formula for each mixed expense is prepared.
- Income statement at the 5,000-unit level of activity using the contribution format is prepared.
Explanation of Solution
- Cost classification is as under
- a. Shipping expenses per unit is $4 & fixed shipping expense is $18,000 and the cost formula for each shipping expense is:
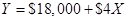
- b. Salaries and commissions per unit is $4 & fixed shipping expense is $18,000 and the cost formula for each shipping expense is:
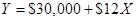
- Income statement at the 5,000-unit level of activity using the contribution format is as below.
| Expenses | Classification |
| Cost of goods sold | Variable |
| Advertising expense | Fixed |
| Shipping expense | Mixed |
| Salaries and commissions | Mixed |
| Insurance expense | Fixed |
| Fixed |
Explanations of the cost classification
| Expenses | Classification | |
| Cost of goods sold | Variable | Per unit cost is same in all month. |
| Advertising expense | Fixed | Constant irrespective of changes in the number of units sold |
| Shipping expense | Mixed | Per unit cost is not same in all month. |
| Salaries and commissions | Mixed | Per unit cost is not same in all month. |
| Insurance expense | Fixed | Constant irrespective of changes in the number of units sold |
| Depreciation expense | Fixed | Constant irrespective of changes in the number of units sold |
| Morrisey & Brown, Ltd. | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the month ended September 30 | ||
| Sales in units | 5,000.00 | |
| Sales ( 5000 unit sold) | $500,000.00 | |
| Less : Variable expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold | $300,000.00 | |
| Shipping expenses | $20,000.00 | |
| Salaries and commissions | $60,000.00 | -$380,000.00 |
| Contribution margin | $120,000.00 | |
| Less : Variable expenses | ||
| Advertising expenses | $21,000.00 | |
| Insurance expense | $6,000.00 | |
| Shipping expenses | $18,000.00 | |
| Salaries and commissions | $30,000.00 | |
| Depreciation expenses | $15,000.00 | $90,000.00 |
| Net Operating Income | $30,000.00 | |
Calculations:
a.) Cost formula for shipping expenses
Step 1: Identify high and low activities level.
| Particulars | Cost/Unit | Month |
| (X1) : Total cost of highest activity | $38,000 | September |
| (X2) : Highest activity unit | 5,000 | September |
| (Y1) : Total cost of lowest activity | $34,000 | July |
| (Y2) : Lowest activity unit | 4,000 | July |
Step 2: Calculate the variable cost per day
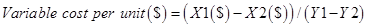
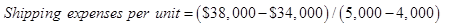
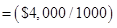
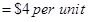
Step 3: Calculate the fixed cost
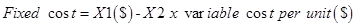
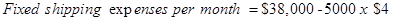
= 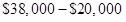
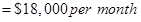
Step 4: Cost formula for shipping expense.
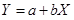
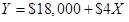
Where X is the number of units sold per month and Y is total shipping expense.
b.) Cost formula for Salaries and commissions
Step 1: Identify high and low activities level.
| Particulars | Cost/Unit | Month |
| (X1) : Total cost of highest activity | $90,000 | September |
| (X2) : Highest activity unit | 5,000 | September |
| (Y1) : Total cost of lowest activity | $78,000 | July |
| (Y2) : Lowest activity unit | 4,000 | July |
Step 2: Calculate the variable cost per day
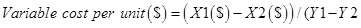
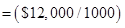
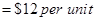
Step 3: Calculate the fixed cost
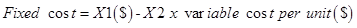
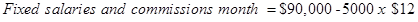
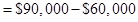
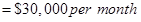
Step 4: Cost formula for shipping expense.
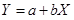
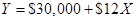
Where X is the number of units sold per month and Y is total Salaries and commission.
Thus, for Morrisey & Brown, Ltd., cost classification is done, the cost formula & the income statement are determined and the calculations are explained.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCT W/CONNECT >IC<
- Please provide answer the following requirements on these financial accounting questionarrow_forwardThe highest value of total cost was $940,000 in August for Honda Foods Ltd. Its lowest value of total cost was $700,000 in February. The company produces onlyone product. The production volumes in August and February were 20,000 and 14,000 units, respectively. What is the fixed cost per month?arrow_forwardFinancial accountingarrow_forward
- Please provide step by step instructions to help me understand the process.arrow_forwardPlease need Help with this Question provide Solution with Correct According Solving methodarrow_forwardI am searching for the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





