
Two distances are required to specify the location of a point relative to an origin in two-dimensional space (Fig. P2.14):
The horizontal and vertical distances
The radius and angle
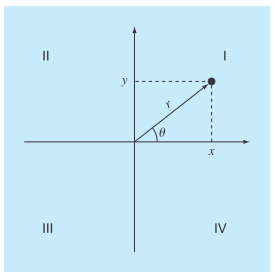
FIGURE P2.14
It is relatively straight forward to compute Cartesian coordinates
If the coordinates lie within the first and fourth coordinates
The difficulty arises for the other cases. The following table summarizes the possibilities:
| x | Y |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
0 |
(a) Write a well-structured flowchart for a subroutine procedure to calculate r and
(b) Write a well-structured function procedure based on your flowchart. Test your program by using it to fill out the following table:
| x | Y | r |
|
| 1 | 0 | ||
| 1 | 1 | ||
| 0 | 1 | ||
| –1 | 1 | ||
| –1 | 0 | ||
| –1 | –1 | ||
| 0 | –1 | ||
| 1 | –1 | ||
| 0 | 0 |
(a)
A well-structured flowchart for a subordinate procedure to calculate r and
Answer to Problem 14P
Solution:
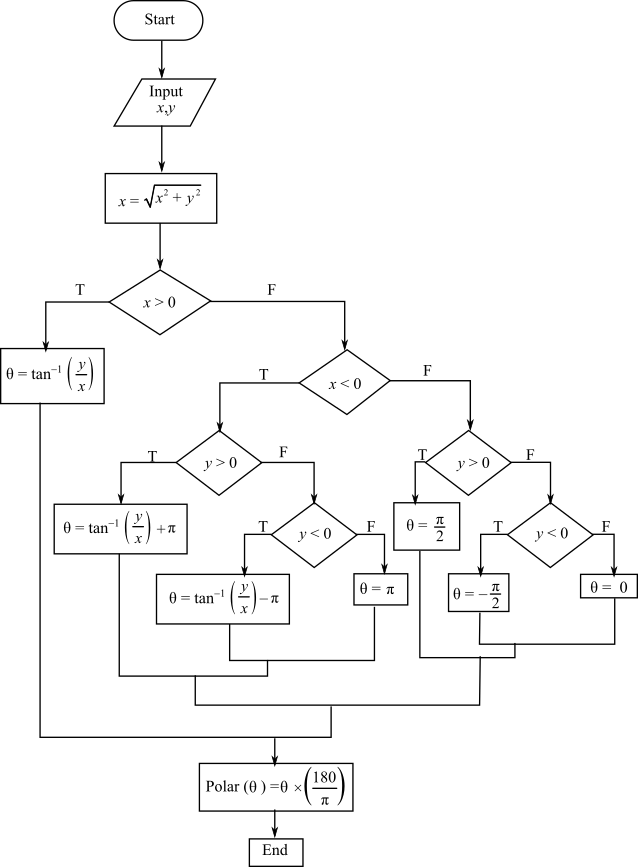
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
To specify the location of a point relative to origin, cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates can be easily computed from the polar coordinates.
Polar coordinates are computed as follows:
Formula used:
Calculation:
The flowchart for converting from Cartesian to polar coordinates is as follows

(b)
A well-structured function procedure based on flowchart of part (a) if two distances are required to specify the location of a point relative to an origin in two-dimensional space. Also, test the program by filling the table given below:
Answer to Problem 14P
Solution:
The values of r and
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
To specify the location of a point relative to origin, cartesian coordinates
Cartesian coordinates can be easily computed from the polar coordinates.
Polar coordinates are computed as follows:
Calculation:
The MATLAB program for converting Cartesian to polar coordinates is as follows:
% Define a function polar()
function polar(x, y)
% Formula to calculate r
r = sqrt (x.^ 2+ y.^ 2);
if x > 0
% Formula to calculate theta
th= atan(y/ x);
elseif x < 0
% Use for loop to check the condition
if y > 0
th= atan(y / x)+ pi;
elseif y < 0
th= atan(y / x)- pi;
else
th= pi;
end
else
if y > 0
th= pi / 2;
elseif y < 0
th=- pi / 2;
else
th= 0;
end
end
theta = th* 180 / pi;
% Display the polar coordinates
fprintf('r = %4.4f theta = %4.2f\n',r,theta);
Now, to test the program use the following command.
First find polar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
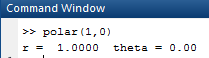
Now, for polar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
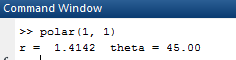
Now, for polar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
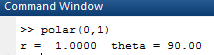
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
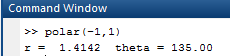
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
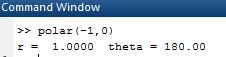
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
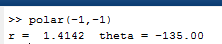
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
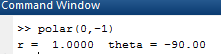
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
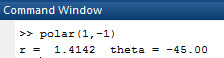
Now, forpolar coordinates for
OUTPUT:
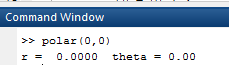
Hence, the values of r and
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 2 Solutions
EBK NUMERICAL METHODS FOR ENGINEERS
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
Math in Our World
Intermediate Algebra (13th Edition)
APPLIED STAT.IN BUS.+ECONOMICS
- Complex Analysis 2 First exam Q1: Evaluate f the Figure. 23+3 z(z-i)² 2024-2025 dz, where C is the figure-eight contour shown in C₂arrow_forwardQ/ Find the Laurent series of (2-3) cos around z = 1 2-1arrow_forward31.5. Let be the circle |+1| = 2 traversed twice in the clockwise direction. Evaluate dz (22 + 2)²arrow_forward
- Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative; 1. The distance x of a runner from a fixed point is measured (in meters) at an interval of half a second. The data obtained is: t 0 x 0 0.5 3.65 1.0 1.5 2.0 6.80 9.90 12.15 Use CDF to approximate the runner's velocity at times t = 0.5s and t = 1.5s 2. Using FDF, BDF, and CDF, find the first derivative of f(x)=x Inx for an input of 2 assuming a step size of 1. Calculate using Analytical Solution and Absolute Relative Error: = True Value - Approximate Value| x100 True Value 3. Given the data below where f(x) sin (3x), estimate f(1.5) using Langrage Interpolation. x 1 1.3 1.6 1.9 2.2 f(x) 0.14 -0.69 -0.99 -0.55 0.31 4. The vertical distance covered by a rocket from t=8 to t=30 seconds is given by: 30 x = Loo (2000ln 140000 140000 - 2100 9.8t) dt Using the Trapezoidal Rule, n=2, find the distance covered. 5. Use Simpson's 1/3 and 3/8 Rule to approximate for sin x dx. Compare the results for n=4 and n=8arrow_forward1. A Blue Whale's resting heart rate has period that happens to be approximately equal to 2π. A typical ECG of a whale's heartbeat over one period may be approximated by the function, f(x) = 0.005x4 2 0.005x³-0.364x² + 1.27x on the interval [0, 27]. Find an nth-order Fourier approximation to the Blue Whale's heartbeat, where n ≥ 3 is different from that used in any other posts on this topic, to generate a periodic function that can be used to model its heartbeat, and graph your result. Be sure to include your chosen value of n in your Subject Heading.arrow_forward7. The demand for a product, in dollars, is p = D(x) = 1000 -0.5 -0.0002x² 1 Find the consumer surplus when the sales level is 200. [Hints: Let pm be the market price when xm units of product are sold. Then the consumer surplus can be calculated by foam (D(x) — pm) dx]arrow_forward
- 4. Find the general solution and the definite solution for the following differential equations: (a) +10y=15, y(0) = 0; (b) 2 + 4y = 6, y(0) =arrow_forward5. Find the solution to each of the following by using an appropriate formula developed in the lecture slides: (a) + 3y = 2, y(0) = 4; (b) dy - 7y = 7, y(0) = 7; (c) 3d+6y= 5, y(0) = 0arrow_forward1. Evaluate the following improper integrals: (a) fe-rt dt; (b) fert dt; (c) fi da dxarrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning

