
Price − Earnings (P/E) Ratio:
The Price − Earnings (P/E) Ratio is used to find out the market value of a firm. It helps to find out whether the stock is over-valued or under-valued considering the idea that the stock value should be proportionate to the earnings it generates for the shareholders of the firm. The firms that have high growth rate will have a higher price − earnings ratio as compared to those firms that grow at lower pace. It can be calculated either by dividing the market value of equity to earnings or by dividing the price of the shares to the earning per share of the firm. It can be demonstrated as under:
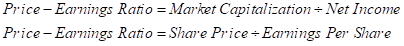
Book Value
The book value of an asset refers to that value at which the asset is posted in the company’s financial statement, the
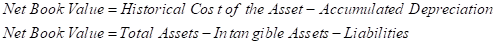
Market Value
The market keeps on changing every time. Market value refers to the value of the asset at which it is valued in the market at a particular time. The market value is also referred to as the market capitalization of those companies that are traded publically. It can be calculated as under:
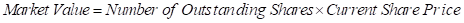
To Identify:
The method to use the Price − Earnings (P/E) ratio to gauge the market value of a firm.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 2 Solutions
Fundamentals of Corporate Finance (3rd Edition) (Pearson Series in Finance)
- Chee Chew's portfolio has a beta of 1.27 and earned a return of 13.6% during the year just ended. The risk-free rate is currently 4.6%. The return on the market portfolio during the year just ended was 10.5%. a. Calculate Jensen's measure (Jensen's alpha) for Chee's portfolio for the year just ended. b. Compare the performance of Chee's portfolio found in part a to that of Carri Uhl's portfolio, which has a Jensen's measure of -0.25. Which portfolio performed better? Explain. c. Use your findings in part a to discuss the performance of Chee's portfolio during the period just ended.arrow_forwardDuring the year just ended, Anna Schultz's portfolio, which has a beta of 0.91, earned a return of 8.1%. The risk-free rate is currently 4.1%, and the return on the market portfolio during the year just ended was 9.4%. a. Calculate Treynor's measure for Anna's portfolio for the year just ended. b. Compare the performance of Anna's portfolio found in part a to that of Stacey Quant's portfolio, which has a Treynor's measure of 1.39%. Which portfolio performed better? Explain. c. Calculate Treynor's measure for the market portfolio for the year just ended. d. Use your findings in parts a and c to discuss the performance of Anna's portfolio relative to the market during the year just ended.arrow_forwardNeed answer.arrow_forward
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





