
Concept explainers
a)
To write:
The linear equation for your current monthly wage
Answer to Problem 1PS
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Definition:
Graph of linear function:
A function f of the form
Given:
The monthly salary of salesperson is
The salary for new job is
Calculation:
From given, it is observed that
Here, the linear equation is,
Compute the linear equation for your current monthly wage
Hence, the linear equation for your current monthly wage
b)
To write:
The linear equation for your current monthly wage
Answer to Problem 1PS
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From given, it is observed that
Here, the linear equation is,
Compute the linear equation for your current monthly wage
Hence, the linear equation for your current monthly wage
c)
To sketch:
The graph of the two equations
Answer to Problem 1PS
Solution:
The point of intersection is
Both jobs gives the same monthly salary when the sales is equals to
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
From part (a) and (b), the two equations are
Draw the graph of the two equations
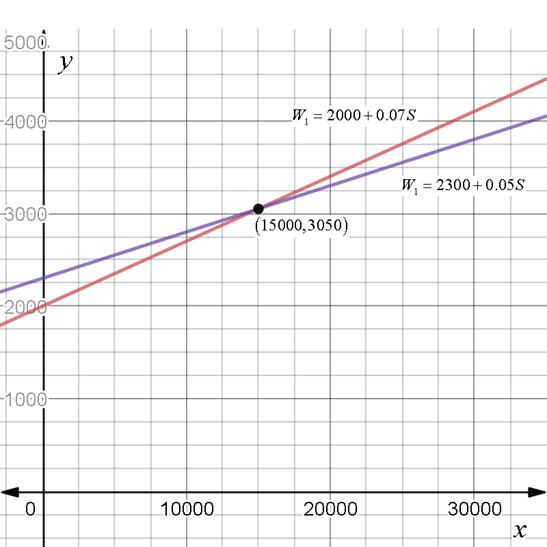
From the above graph, it is observed that the point of intersection is
Therefore, both jobs gives the same monthly salary when the sales is equals to
d)
To find:
The salary when the sales is
Answer to Problem 1PS
Solution:
No, the salesman doesn’t change the job because current job pays $3400 per month but new job pays $3300 per month.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Compute the current job salary when the sales is
Therefore, the current job salary is $3400 when the sales is
Compute the new job salary when the sales is
Therefore, the new job salary is $3300 when the sales is
Hence, the salesman doesn’t change the job because current job pays $3400 per month but new job pays $3300 per month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 1 Solutions
Precalculus (MindTap Course List)
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
- a -> f(x) = f(x) = [x] show that whether f is continuous function or not(by using theorem) Muslim_mathsarrow_forwardUse Green's Theorem to evaluate F. dr, where F = (√+4y, 2x + √√) and C consists of the arc of the curve y = 4x - x² from (0,0) to (4,0) and the line segment from (4,0) to (0,0).arrow_forwardEvaluate F. dr where F(x, y, z) = (2yz cos(xyz), 2xzcos(xyz), 2xy cos(xyz)) and C is the line π 1 1 segment starting at the point (8, ' and ending at the point (3, 2 3'6arrow_forward
- I need help in ensuring that I explain it propleryy in the simplifest way as possiblearrow_forwardI need help making sure that I explain this part accutartly.arrow_forwardPlease help me with this question as I want to know how can I perform the partial fraction decompostion on this alebgric equation to find the time-domain of y(t)arrow_forward
 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
Elementary AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9780998625713Author:Lynn Marecek, MaryAnne Anthony-SmithPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





