
To analyze :
The parts of the bacterium, along with their functions.
Introduction :
Bacteria belong to a group of prokaryotes that is characterized by the presence of a peptidoglycan wall, a naked DNA with attached mesosomes, and reserve food. Ribosomes are the 70S in nature. They multiply through binary fission.
Explanation of Solution
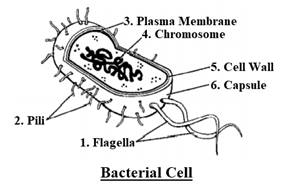
Functions of the parts of the given bacterium: -
- Flagella − Bacterial flagella are involved in locomotion. They are made up of three parts, the basal body, hook, and filament. The basal body is inserted in the cell envelope. The hook connects the basal body to the filament. The filament is a tubular structure responsible for causing turbulence in the liquid medium. Flagella perform to move the bacteria forward by performing rotation type movement that pushes water backward.
- Pili − Pilus is not involved in bacterial locomotion. They are longer, and thicker outgrowths that are developed in response to the fertility factor in Gram-negative bacteria. They help in the attachment of the recipient cell and formation of the conjugation tube.
- Plasma membrane − Plasma membrane forms the innermost component of the cell envelops. It is semipermeable and separated the cytoplasm from the surroundings. It allows selective movement of substances in and out of the bacterial cell. The receptors present on its surface detect and respond to the chemicals present in the surroundings. It also takes part in respiration, lipid synthesis, and synthesis of cell wall components.
- Chromosome − Nucleoid consists of a single circular strand of DNA duplex in a highly coiled form. It is considered as naked because it is not associated with histone proteins, and the nuclear envelope is absent around it. The single chromosome contains genes that code for proteins. It also transfers the traits to the daughter cells.
- Cell wall − Cell wall is a rigid covering that provides structural support to the cell. It prevents bacterial cells against bursting when present in a hypotonic medium.
- Capsule − It is the outermost covering of bacteria that is made up of non cellulosic polysaccharides (in some cases, proteins are also present). It is thick and tough and prevents bacterial cells from phagocytes, toxic chemicals, drugs and some viruses such as bacteriophage. In some cases, it also helps bacteria to attach on different membranes or cells and virulence.
A bacterial cell is one of the most primitive forms of life. All the structures of a bacterial cell help it to thrive and reproduce in a wide variety of environments.
Chapter 19 Solutions
Glencoe Biology (Glencoe Science)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- Can I please get this answered with the colors and how the R group is suppose to be set up. Thanksarrow_forwardfa How many different gametes, f₂ phenotypes and f₂ genotypes can potentially be produced from individuals of the following genotypes? 1) AaBb i) AaBB 11) AABSC- AA Bb Cc Dd EE Cal bsm nortubaarrow_forwardC MasteringHealth MasteringNu × session.healthandnutrition-mastering.pearson.com/myct/itemView?assignment ProblemID=17396416&attemptNo=1&offset=prevarrow_forward10. Your instructor will give you 2 amino acids during the activity session (video 2-7. A. First color all the polar and non-polar covalent bonds in the R groups of your 2 amino acids using the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds in the backbone of each amino acid. B. Next, color where all the hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic interactions and ionic bonds could occur in the R group of each amino acid. Use the same colors as in #7. Do not color the bonds in the backbone of each amino acid. C. Position the two amino acids on the page below in an orientation where the two R groups could bond together. Once you are satisfied, staple or tape the amino acids in place and label the bond that you formed between the two R groups. - Polar covalent Bond - Red - Non polar Covalent boND- yellow - Ionic BonD - PINK Hydrogen Bonn - Purple Hydrophobic interaction-green O=C-N H I. H HO H =O CH2 C-C-N HICK H HO H CH2 OH H₂N C = Oarrow_forwardFind the dental formula and enter it in the following format: I3/3 C1/1 P4/4 M2/3 = 42 (this is not the correct number, just the correct format) Please be aware: the upper jaw is intact (all teeth are present). The bottom jaw/mandible is not intact. The front teeth should include 6 total rectangular teeth (3 on each side) and 2 total large triangular teeth (1 on each side).arrow_forward12. Calculate the area of a circle which has a radius of 1200 μm. Give your answer in mm² in scientific notation with the correct number of significant figures.arrow_forwardDescribe the image quality of the B.megaterium at 1000X before adding oil? What does adding oil do to the quality of the image?arrow_forwardWhich of the follwowing cells from this lab do you expect to have a nucleus and why or why not? Ceratium, Bacillus megaterium and Cheek epithelial cells?arrow_forward14. If you determine there to be debris on your ocular lens, explain what is the best way to clean it off without damaging the lens?arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





