
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by whichenergy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 8P
a) Light reactions − generates ATP, NADPH and O2
Explanation of Solution
Photosynthesis consists of two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
In light reaction, two photo systems (PS I and PS II) participate.
PSII absorb680 nmwavelengthof sunlight. After absorbing energy from the sunlight, chlorophyll a molecule in PSII release excited high energy electrons. The electron defect occurred in PSII is fulfilled by hydrolysis of water which produce O2as by product. Consider this as reaction 1.
Theelectronsfrom reaction I are used to fulfill the electron defect inphotosystem. The high energy electrons go through the series of electron acceptorsto assimilate this energy. ADP takes up the energy of these electrons to form ATP. This is known as photophosphorylation.
Similar reaction occurs in PS I. PSI absorb 700 nm wavelength of sunlight, followed by high energy electrons release. Like PSII, the high energy electron goes through a series of electron acceptors. At the end of this series NADP+accepts the electron to form NADPH. Consider this as reaction 2.
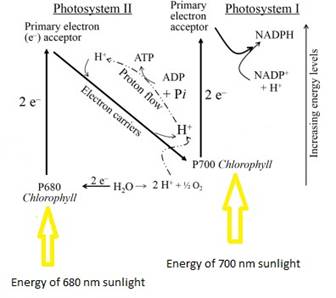
Figure 1: A diagrammatic representation of light reaction
(b)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 8P
b) Chloroplasts − cellular location of photosynthesis
Explanation of Solution
Chloroplast is the organelle in a plant cell which is responsible for conducting photosynthesis. Chloroplast consists of a double membrane structure known as thylakoid. Thylakoids are the primary site for light reaction which assimilate the light energy to produce the energy moieties, ATP and NADPH. These energy molecules are used in the dark reaction to produce six carbon sugar molecule and oxygen as byproduct. The dark reaction takes place in the stroma of chloroplast.
(c)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 8P
c) Reaction Center − site of photoinduced charge separation.
Explanation of Solution
In light reaction, two photosystems called PS I and PS II participate.
In these photosystems, the reaction center is a special chlorophyll a molecule, chlorophyll a. The process happening in these two systems is quite similar.
PSII absorbs light energy of 680 nm wavelength of light while PS I absorb energy of 700 nm wavelength of light, followed by releasing high energy electrons.
When the chlorophyll a molecule releases its electrons, the chlorophyll molecule gets positively charged. It generates the charge separation at the chlorophyll molecules. This charge separation is due to the absorbed light energy. So, it is known as photo induced charge separation.
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex structural view. It is composed of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors. It is a collection of CF1− CF0 complex. This is responsible for executing the primary energy conversion reactions related to photosynthesis. Molecular excitations occur at the reaction center give rise to electron transfer reactions along the path of a series of protein-bound co-factors like chlorophylls.
(d)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 8P
d) Light-harvesting complex- Primary photosynthetic pigment
Explanation of Solution
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction. In the light reaction, the sunlight is assimilated, and the energy is stored in the
The photosynthetic pigments such as chlorophyll a and b, xanthophyll and carotenoids form the two photosystems (Photosystem I and II) which absorbs different wavelength of light. Chlorophyll a form the reaction center of the photosystems.
(e)
Interpretation:
The most suitable, matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
A light-harvesting complex is a collection of subunit proteins. These subunit proteins are again a part of largersupercomplex of a photosystem.
Answer to Problem 8P
e) Light − harvesting complex − uses resonance energy transfer to reach the reaction center
Explanation of Solution
A light-harvestingcomplex (also known as photosystem)is a collection of proteins.The light harvest system is used by plants and photosynthetic bacteria to collect energy from sun light. During photosynthesis, the reaction centers absorbs light energy of 680nm and 700 nm sun light. This reaction center is a special chlorophyll a molecule. Light harvesting complex assist on this energy absorbance.
Light-harvesting complexes show a huge variation among the different photosynthetic organisms. The complexes consist of proteins and photosynthetic pigments like chlorophylls and surround by the photosynthetic reaction center. This special structural adaptation is to focus energy, absorbed from the photons toward the reaction center as resonance transfer.
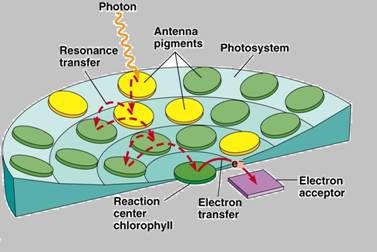
Figure 3: close view of a light harvesting complex
(f)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
For the light reaction two photosystems called PS I and PS II participate.
Answer to Problem 8P
f) Photosystem I − powers the formation of NADPH
Explanation of Solution
Photosystem is a collection of pigment moleculesand is known as light harvest complex. In photosystem I, PS I absorb energy from 700 nm photons of sunlight, followed by releasing high energy electrons. The electron goes through a series of electron acceptors. At the end of this series NADP reacts with electron to form NADPH.
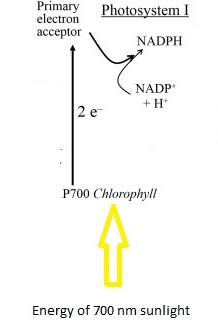
Figure 4: Figure 5: Diagrammatic representation of reactions happen in photosystem one
(g)
Interpretation:
The most suitable, matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by which energy of the sunlight is stored as chemical energy. The process takes place in the chloroplast of the plant cells in two main stages - light reaction and dark reaction.
For the light reaction two photosystems called PS I and PS II participate.
Answer to Problem 8P
g) Photosystem II − Transfer electron from H2O to P680.
Explanation of Solution
For the light reaction two photosystems called PS I and PS II participate. PSII absorbs light energy of 680 nm wavelength of sun light After absorbing energy the chlorophyll a molecule in PSII releases excited, high energy electrons. To fulfill the electron defect occurred at PSII water hydrolysistakes place at PSII.
These released electrons are used to overcome the electron defect in photosystemII.
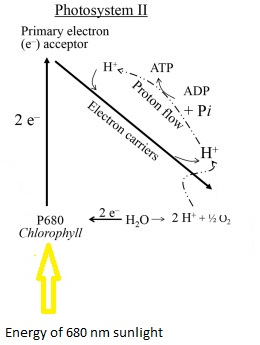
Figure : Diagrammatic representation of reactions happen in photosystem one
(h)
Interpretation:
The most suitable, matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
The chloroplast cytochrome bf complex is a collection of multiple numbers of subunit proteins.
Answer to Problem 8P
h) Cytochrome bf complex − pumps protons
Explanation of Solution
The chloroplast cytochrome bf complex is a collection of multiple numbers of subunit proteins. These subunit proteinsconsist of four polypeptides. These four types are
- Cytochrome f
- Heme containing cytochrome b 6
- Rieske iron-sulfur protein
- 17 kD polypeptide
Most mechanisms suggest that the transfer of a single reducing equivalent which is an electron results in the translocation of two protons across the membrane. So, this complex mainly workes as a proton pump.
(i)
Interpretation:
The most suitable, matching pair of answers should be selected.
Concept introduction:
Photosynthesis is the process by storing energy of sunlight as chemical energy in glucose. Process happens in the chloroplast of a plant cell. Photosynthesis happens via two main stages as light reaction and dark reaction.
Answer to Problem 8P
i) Water -oxidizing complex- site of oxygen generation.
Explanation of Solution
For the light reaction, two photosystems called PS I and PS II participate. PSII absorbs light energy of 680 nm wavelength of sun light After absorbing energy the chlorophyll a molecule in PSII releases excited, high energy electrons. To fulfill the electron defect occurred at PSII water hydrolysis takes place at PSII.
The hydrolysis of water is taken care of by water oxidizing complex. Thereleased electrons are used to overcome the electron defect in photosystem II.
(j)
Interpretation:
The most suitable matching pair should be selected.
Concept introduction:
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex structural. It is composed of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors. It is a collection of CF1− CF0complex.
Answer to Problem 8P
j) ATP synthase − CF1- CF0 complex
Explanation of Solution
A photosynthetic reaction center is a complex structural. It is composed of several proteins, pigments and other co-factors.It is a collection of CF1− CF0 complex. This is responsible for executing the primary energy conversion. The energy is stored in the form of ATP via this complex.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
BIOCHEMISTRY-ACHIEVE (1 TERM)
- You’ve isolated a protein and determined that the Native molecular weight of the holoenzyme is 160 kD using size exclusion chromatography. Analysis of this protein using SDS-PAGE revealed 2 bands, one at 100 kD and one at 30 kD. The enzyme was found to be 0.829% NAD (by weight). What further can be said regarding the structure of the polypeptide?arrow_forwardWhat is the formation of glycosylated hemoglobin (the basis for the HbA1c test)? Can you describe it?arrow_forwardPlease analze the gel electrophoresis column of the VRK1 kinase (MW: 39.71 kDa). Also use a ruler to measure the length of the column in centimeters and calculate the MW of each band observed. Lane 1: buffer Lane 2 : Ladder Lane 3: Lysate Lane 4: Flowthrough Lane 5: Wash Lanes 6-8: E1, E2, E3 Lane 9: Dialyzed VRK1 Lane 10: LDHarrow_forward
- Do sensory neurons express ACE2 or only neurolipin-1 receptors for COVID19 virus particle binding?arrow_forwardExplain the process of CNS infiltration of COVID19 through sensory neurons from beginning to end, including processes like endocytosis, the different receptors/proteins that are involved, how they are transported and released, etc.,arrow_forwardH2C CH2 HC-COOO CH2 ܘHO-C-13c-O isocitrate C-S-COA H213c CH2 C-OO 13C-S-COA CH2 C-00 the label will not be present in succinyl CoA C-S-COA succinyl-CoAarrow_forward
- A culture of kidneys cells contains all intermediates of the citric acid cycle. It is treated with an irreversible inhibitor of malate dehydrogenase, and then infused withglucose. Fill in the following list to account for the number of energy molecules that are formed from that one molecule of glucose in this situation. (NTP = nucleotidetriphosphate, e.g., ATP or GTP)Net number of NTP:Net number of NADH:Net number of FADH2:arrow_forward16. Which one of the compounds below is the final product of the reaction sequence shown here? OH A B NaOH Zn/Hg aldol condensation heat aq. HCI acetone C 0 D Earrow_forward2. Which one of the following alkenes undergoes the least exothermic hydrogenation upon treatment with H₂/Pd? A B C D Earrow_forward
- 6. What is the IUPAC name of the following compound? A) (Z)-3,5,6-trimethyl-3,5-heptadiene B) (E)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadiene C) (E)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene D) (Z)-5-ethyl-2,3-dimethyl-1,5-hexadiene E) (Z)-2,3,5-trimethyl-1,4-heptadienearrow_forwardConsider the reaction shown. CH2OH Ex. CH2 -OH CH2- Dihydroxyacetone phosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate The standard free-energy change (AG) for this reaction is 7.53 kJ mol-¹. Calculate the free-energy change (AG) for this reaction at 298 K when [dihydroxyacetone phosphate] = 0.100 M and [glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate] = 0.00300 M. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forwardIf the pH of gastric juice is 1.6, what is the amount of energy (AG) required for the transport of hydrogen ions from a cell (internal pH of 7.4) into the stomach lumen? Assume that the membrane potential across this membrane is -70.0 mV and the temperature is 37 °C. AG= kJ mol-1arrow_forward
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





