
a.
Classify the costs as prevention, appraisal, internal failure, and external failure.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Total Quality Management:
Total Quality Management is a method that eliminates wasteful activities and improves quality throughout the value chain by allocating quality management responsibility, rewarding low-cost, high-quality results and monitoring quality costs.
Components of the costs of quality:
Prevention costs:
Prevention costs denote the cost of resources consumed in activities that prevents defects from its occurrence. Supplier quality evaluation, employee training is some of the example of prevention costs.
Appraisal costs:
Appraisal costs occur in order to determine if products conform to quality standards. Finished goods inventories, monitoring of production process are some of the examples of appraisal costs.
Internal failure costs:
Internal failure costs include additional production-related costs that are incurred to correct the low-quality output. Disposing of scrap, processing engineering change orders are some of the examples of internal failure costs.
External failure costs:
External failure costs are the largest and hardest to measure. These costs are incurred when the quality failures are allowed to enter the market. Warranty costs, product liability costs are some of the examples of external failure costs.
- Quality training is a prevention costs.
- Product inspection and material inspection are appraisal costs.
- Scrap and network are internal failure costs.
- Product warranty is an external failure costs.
b.
Calculate the total quality cost as a percentage of sales for each of the two years. And state the amount of profit increased because of quality improvements between year 1 and year 2.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The total quality cost as a percentage of sales for each of the two years is calculated below:
| Particulars | Year 1 | Year 2 |
| Total Quality Sales | $10,000,000 | $10,000,000 |
| Total Quality Costs | (2) $2,000,000 | (2) $1,545,000 |
| Percent of Sales | (3) 20% | (4) 15.45% |
| Profit Increase | $455,000 | |
Table (1)
Working note:
Calculate the total quality costs for year 1 and year 2:
(1)
(2)
Calculate the percentage of sales for year 1 and year 2:
(3)
(4)
- Percentage of sales for year 1 is 20%.
- Percentage of sales for year 1 is 15.45%.
- The amount of increase in profit is $455,000.
c.
Graph the prevention and appraisal costs versus the internal and external failure costs for year 1 and year 2.
c.
Explanation of Solution
The prevention and appraisal costs versus the internal and external failure costs for year 1 and year 2 are plotted in a graph:
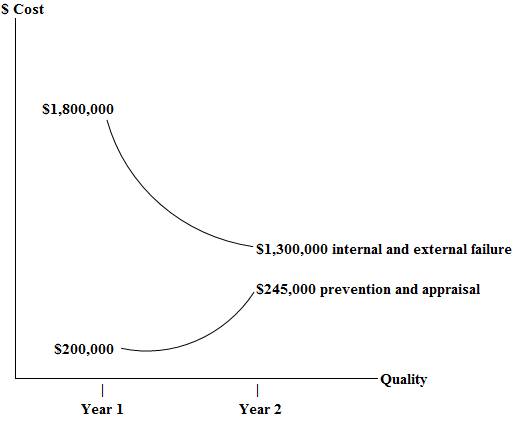
Figure (1)
d.
Identify and explain at least two criticisms associated with the cost-benefit quality model and identify the measures used by Companies to track quality.
d.
Explanation of Solution
- The prevention and appraisal
curves are too steep and in reality they are much flatter. - The relationship between a dollar of prevention and appraisal expended to save some dollars of internal and external failure costs is not stable over time.
- Optimum quality is a moving target and it is a not fixed point.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Financial & Managerial Accounting
- Compare the cost model vs. revaluation model, including pros, cons, and theoretical implications (e.g., relevance vs. reliability).arrow_forwardGeneral accounting questionarrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward
- If the project's cost of capital is 11%, what is the NPV of the project? What is the Year-0 net cash flow? $ -85,000 What are the net operating cash flows in Years 1, 2, and 3? Year 1: $25,403 Year 2: $27,682 Year 3: $21,606arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this general accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





