
An ideal gas is trapped inside a tube of uniform cross-sectional area sealed at one end as shown in Figure P19.49. A column of mercury separates the gas from the outside. The tube can be turned in a vertical plane. In Figure P19.49A, the column of air in the tube has length L1, whereas in Figure P19.49B, the column of air has length L2. Find an expression (in terms of the parameters given) for the length L3 of the column of air in Figure P19.49C, when the tube is inclined at an angle θ with respect to the vertical.
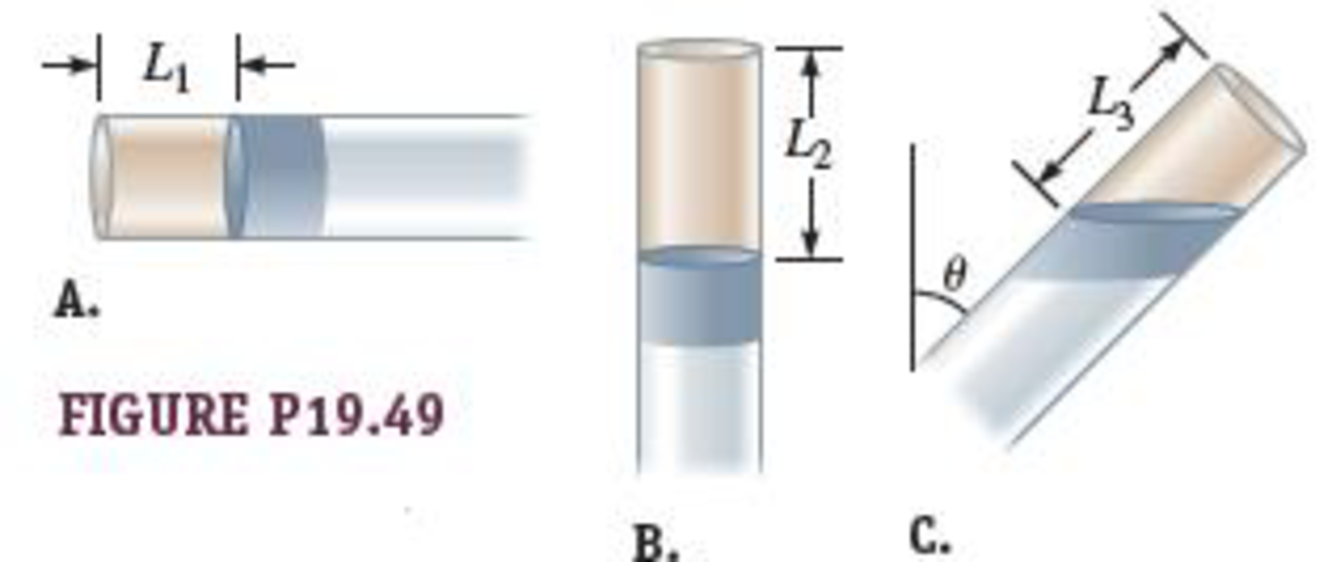
FIGURE P19.49
The expression for the length
Answer to Problem 49PQ
The expression for the length
Explanation of Solution
Three cases are depicted here. The first case in which the length of the air column is
In all the three cases mercury separates the air from outside. In all the three cases mercury should be in static equilibrium. The forces experienced by the mercury are the force due to the pressure inside the tube, the force from the atmospheric pressure, and the force due to the weight of the mercury. Here the tube is maintained at constant pressure. So apply Boyle’s law.
Consider Figure 1.
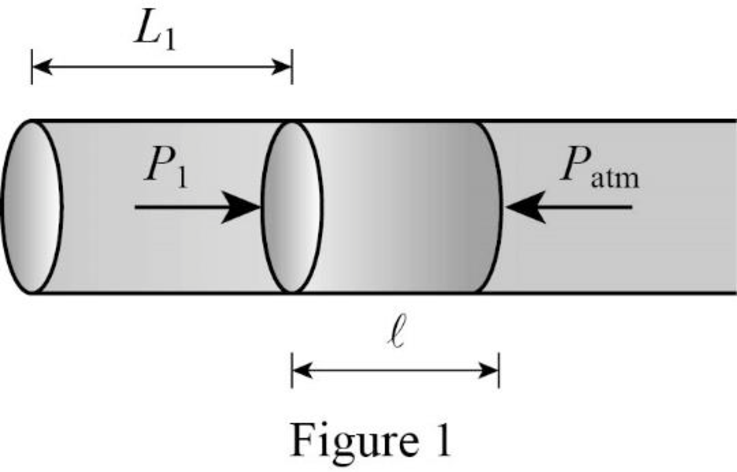
Weight of mercury acts perpendicular to the orientation of the tube. Thus the mercury is in equilibrium whenever the atmospheric pressure is equal to the pressure inside the tube.
Here,
Consider Figure 2.
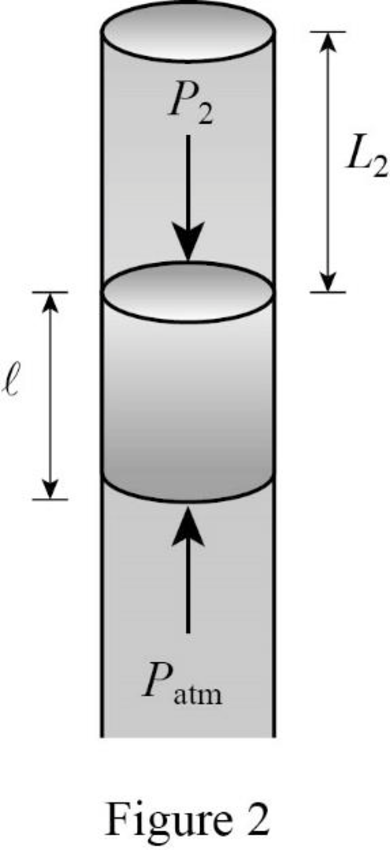
Here the outside atmospheric pressure is balanced by the sum of pressure in the tube due to the air column and the pressure due the weight of mercury.
Write the expression for the pressure due to the weight of mercury in position B.
Here,
Write the expression for the density of mercury.
Here,
Solve equation (III) for
Use expression (IV) in (II).
Here,
The atmospheric pressure at position B is balanced by the sum of pressures due to the weight of mercury, and pressure due to the column of air in the tube.
Here,
Consider the position 3.
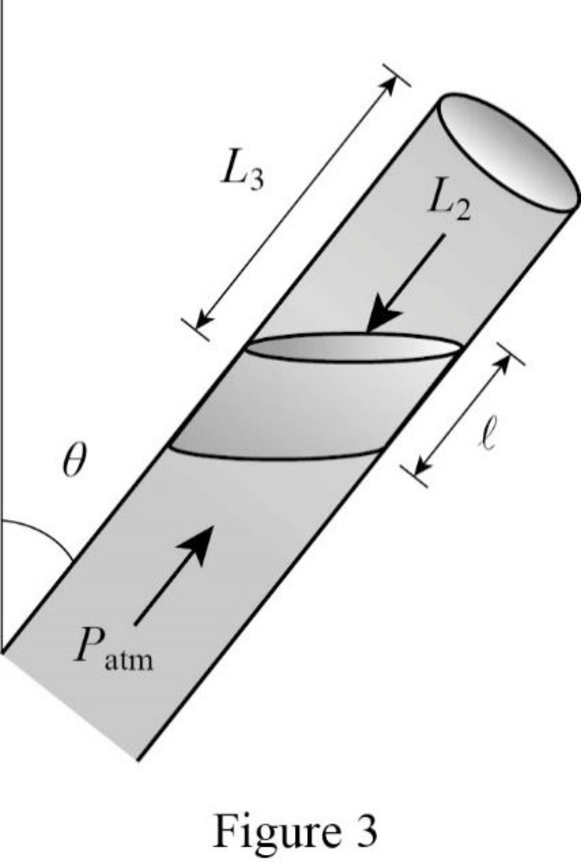
Here the pressure due to atmosphere is balanced by pressure inside the tube due to gas column denoted by
Write the expression for the vertical component of pressure due to the weight of mercury column.
Here,
Write the expression for the balance of pressure in the tube kept in position 3.
Since the temperature is constant, apply Boyle’s law. Boyle’s law states that the volume of a gas is directly proportional to the pressure of the gas at constant temperature.
Write the expression for Boyle’s law for case A and case B.
Write the expression for volume of air in tube 1.
Here,
Write the expression for volume of air in tube 2.
Here,
Use expression (XI), (VII), (XII) and (I) in expression (X).
Solve expression for
Write the expression for Boyle’s law for case A and case C.
Write the expression for volume of air in tube 3.
Here,
Use expression (XI), (XVI), (IX) and (I) in expression (XV).
Solve expression (XVII) for
Equate the right hand sides of equations (XIV) and (XVIII) and solve for
Solve expression (XIX) for
Conclusion:
Therefore, the expression for the length
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations and Connections
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardThe spring in the figure has a spring constant of 1300 N/m. It is compressed 17.0 cm, then launches a 200 g block. The horizontal surface is frictionless, but the block’s coefficient of kinetic friction on the incline is 0.200. What distance d does the block sail through the air?arrow_forwardSolve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the problem correctly and be sure to check your work. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA 10-m-long glider with a mass of 680 kg (including the passengers) is gliding horizontally through the air at 28 m/s when a 60 kg skydiver drops out by releasing his grip on the glider. What is the glider's speed just after the skydiver lets go?arrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 A cube of mass m is placed in a rotating funnel. (The funnel is rotating around the vertical axis shown in the diagram.) There is no friction between the cube and the funnel but the funnel is rotating at just the right speed needed to keep the cube rotating with the funnel. The cube travels in a circular path of radius r, and the angle between the vertical and the wall of the funnel is 0. Express your answers to parts (b) and (c) in terms of m, r, g, and/or 0. (a) Sketch a free-body diagram for the cube. Show all the forces acting on it, and show the appropriate coordinate system to use for this problem. (b) What is the normal force acting on the cube? FN=mg58 (c) What is the speed v of the cube? (d) If the speed of the cube is different from what you determined in part (c), a force of friction is necessary to keep the cube from slipping in the funnel. If the funnel is rotating slower than it was above, draw a new free-body diagram for the cube to show which way friction…arrow_forward
- Circular turns of radius r in a race track are often banked at an angle θ to allow the cars to achieve higher speeds around the turns. Assume friction is not present. Write an expression for the tan(θ) of a car going around the banked turn in terms of the car's speed v, the radius of the turn r, and g so that the car will not move up or down the incline of the turn. tan(θ) =arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forwardSlinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again. How high is the bed? What is Woody’s velocity halfway down? Enter just the magnitude of velocity.arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA positive charge of 91 is located 5.11 m to the left of a negative charge 92. The charges have different magnitudes. On the line through the charges, the net electric field is zero at a spot 2.90 m to the right of the negative charge. On this line there are also two spots where the potential is zero. (a) How far to the left of the negative charge is one spot? (b) How far to the right of the negative charge is the other?arrow_forwardA charge of -3.99 μC is fixed in place. From a horizontal distance of 0.0423 m, a particle of mass 7.31 x 103 kg and charge -9.76 µC is fired with an initial speed of 84.1 m/s directly toward the fixed charge. How far does the particle travel before its speed is zero?arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





