
Concept explainers
DRAW IT Label IgE, antigen, and mast cell, and add an antihistamine to the following figure. What type of cell is this? Singulair stops inflammation by blocking leukotriene receptors. Add this action to the figure.
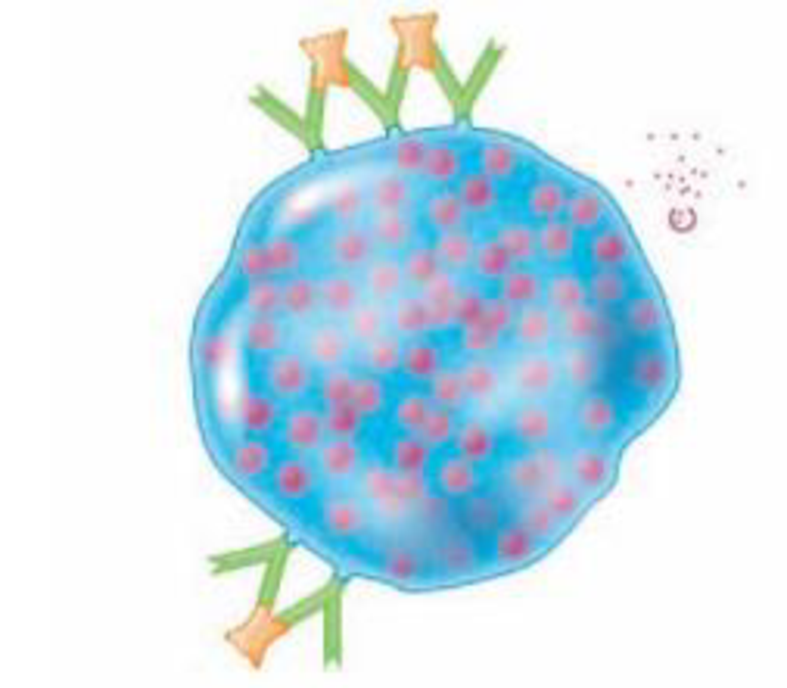
To determine:
The inflammation of singuliar blocks by blocking leukotriene’s receptors.
Introduction:
Type 1 hypersensitivity can cause immune response to the exposure of antigens. When IgE antibodies bind to the receptors on mast cells, then they will bind to the antigen. It causes degranulation of mast cells and the release of granules like histamine and leukotrienes. It leads to inflammation and breathing difficulties. This is blocked by giving singuliar drug.
Answer to Problem 1R
Correct answer:
A mast cell is given in this figure. An antihistamine is added to the mast cell; it blocks the inflammation.
Explanation of Solution
Diagram:
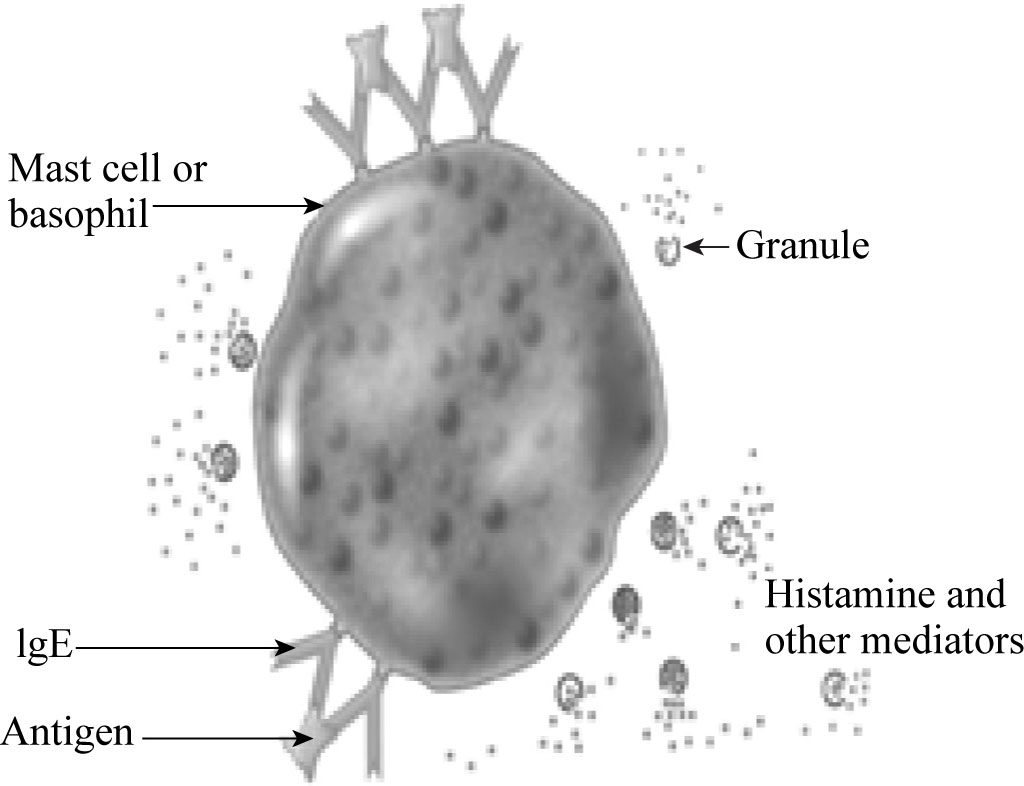
Leukotrienes attach to the receptors of mast cells; they cause inflammation. When a leukotriene receptor is blocked by singuliar, it stops inflammation. Mast cells play a role in autoimmune disorders. Singuliar (Montelukost) relieve the symptoms of hay fever, asthma, inflammation, and redness in skin. Singuliar mimics as leukotriene receptors.
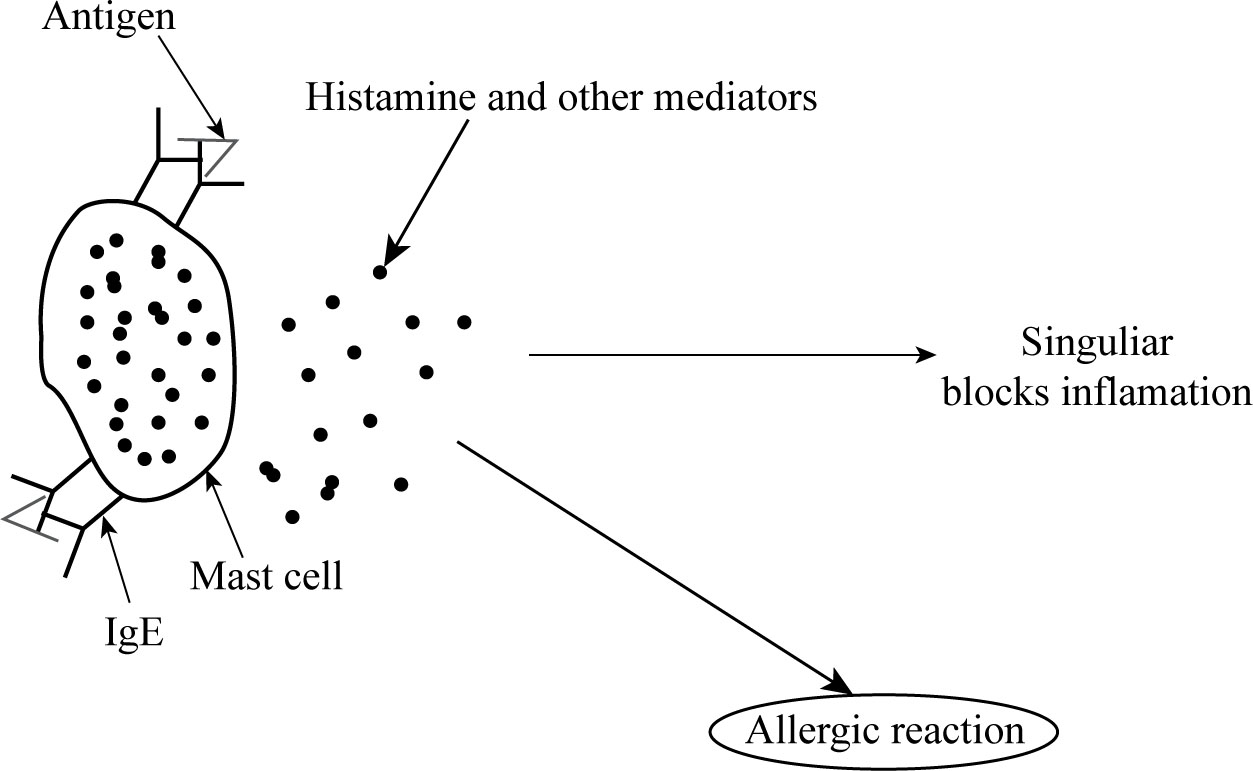
Anaphylactic hypersensitivity mast cell releases histamine, leukotriene, and other mediators when it binds to the antigen and IgE antibody. When leukotriene receptors are blocked by singuliar, an allergic response does not occur.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Microbiology: An Introduction, Books a la Carte Plus Mastering Microbiology with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (13th Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity
Genetics: From Genes to Genomes
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- 1. Match each vocabulary term to its best descriptor A. affinity B. efficacy C. inert D. mimic E. how drugs move through body F. how drugs bind Kd Bmax Agonist Antagonist Pharmacokinetics Pharmacodynamicsarrow_forward50 mg dose of a drug is given orally to a patient. The bioavailability of the drug is 0.2. What is the volume of distribution of the drug if the plasma concentration is 1 mg/L? Be sure to provide units.arrow_forwardDetermine Kd and Bmax from the following Scatchard plot. Make sure to include units.arrow_forward
- Choose a catecholamine neurotransmitter and describe/draw the components of the synapse important for its signaling including synthesis, packaging into vesicles, receptors, transporters/degradative enzymes. Describe 2 drugs that can act on this system.arrow_forwardThe following figure is from Caterina et al. The capsaicin receptor: a heat activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature, 1997. Black boxes indicate capsaicin, white circles indicate resinferatoxin. a) Which has a higher potency? b) Which is has a higher efficacy? c) What is the approximate Kd of capsaicin in uM? (you can round to the nearest power of 10)arrow_forwardWhat is the rate-limiting-step for serotonin synthesis?arrow_forward
 Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





