
1.
Prepare the journal entries for the formation of the
1.
Explanation of Solution
Partnership:
A partnership is an unincorporated form of business which is formed by an agreement, owned and managed mutually by two or more individuals, who invest their assets in the business and share the liabilities and profits among themselves.
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Accounting rules for Journal entries:
- To record increase balance of account: Debit assets, expenses, losses and credit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
- To record decrease balance of account: Credit assets, expenses, losses and debit liabilities, capital, revenue and gains.
Record the journal entry:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1 | Cash | $13,544 | |
| Accounts Receivable | $15,280 | ||
| Merchandise Inventory | $89,692 | ||
| Supplies | $1,286 | ||
| Office Equipment | $18,000 | ||
| Store Equipment | $8,000 | ||
| Allowance for | $1,720 | ||
| Notes payable | $36,000 | ||
| Accounts payable | $18,082 | ||
| Partner F, Capital | $90,000 | ||
| (To record investment of Partner F in partnership) |
Table (1)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash by $13,544.
- Accounts receivable is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit accounts receivable account by $15,280.
- Merchandise inventory is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit merchandise inventory account by $89,692.
- Supplies are asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit supplies account by $1,286.
- Office equipment is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit office equipment account by $18,000.
- Store equipment is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit store equipment account by $8,000.
- Allowance for bad debts is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit allowance for bad debts account by $1,720.
- Notes payable is a liability and it is increased. Therefore, credit notes payable account by $36,000.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased. Therefore, credit accounts payable account by $18,082.
- Partner F, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner F, capital account by $90,000.
Record the investment made by Partner B:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1 | Cash | $50,000 | |
| Partner B, Capital | $50,000 | ||
| ( To record investment of Partner B in partnership) |
Table (2)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash account by $50,000
- Partner B, Capital is a component of
stockholders’ equity and it is increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner B, capital account by $50,000.
2.
Prepare the lower portion of the income statement reporting the allocation of the profits to each partner.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement. In partnership, the division is often recorded in the lower portion of the income statement.
Prepare the lower portion of the income statement reporting the allocation of the profits to each partner.
| Partnership F and B Plumbing supplies | |||
| Income Statement (Partial) | |||
| For Year Ended December 31 | |||
| Net income | $150,000 | ||
| Allocation of net income: | Partner F | partner B | Total |
| Salary allowances | $50,000 | $30,000 | $80,000 |
| Interest allowances | $9,000 | $5,000 | $14,000 |
| Remaining income | $33,600 | $22,400 | $56,000 |
| Allocation of net income | $92,600 | $57,400 | $150,000 |
Table (3)
3.
Prepare journal entry for the investment of Partner P.
3.
Explanation of Solution
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| January 1 | Cash | $30,000 | |
| Partner F, Capital | $30,000 | ||
| ( To record investment of Partner F in partnership) |
Table (4)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash account by $30,000
- Partner B, Capital is a component of stockholders’ equity and it is increases the partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner B, capital account by $30,000.
4.
Prepare a statement of partnership liquidation and related journal entries.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Liquidation of partnership:
Liquidation is the process where assets are sold, gains and losses are allocated to the partners, liabilities are paid out and the cash that is remaining cash or other assets are distributed to partners.
The statement of partnership liquidation statement is prepared as follows:
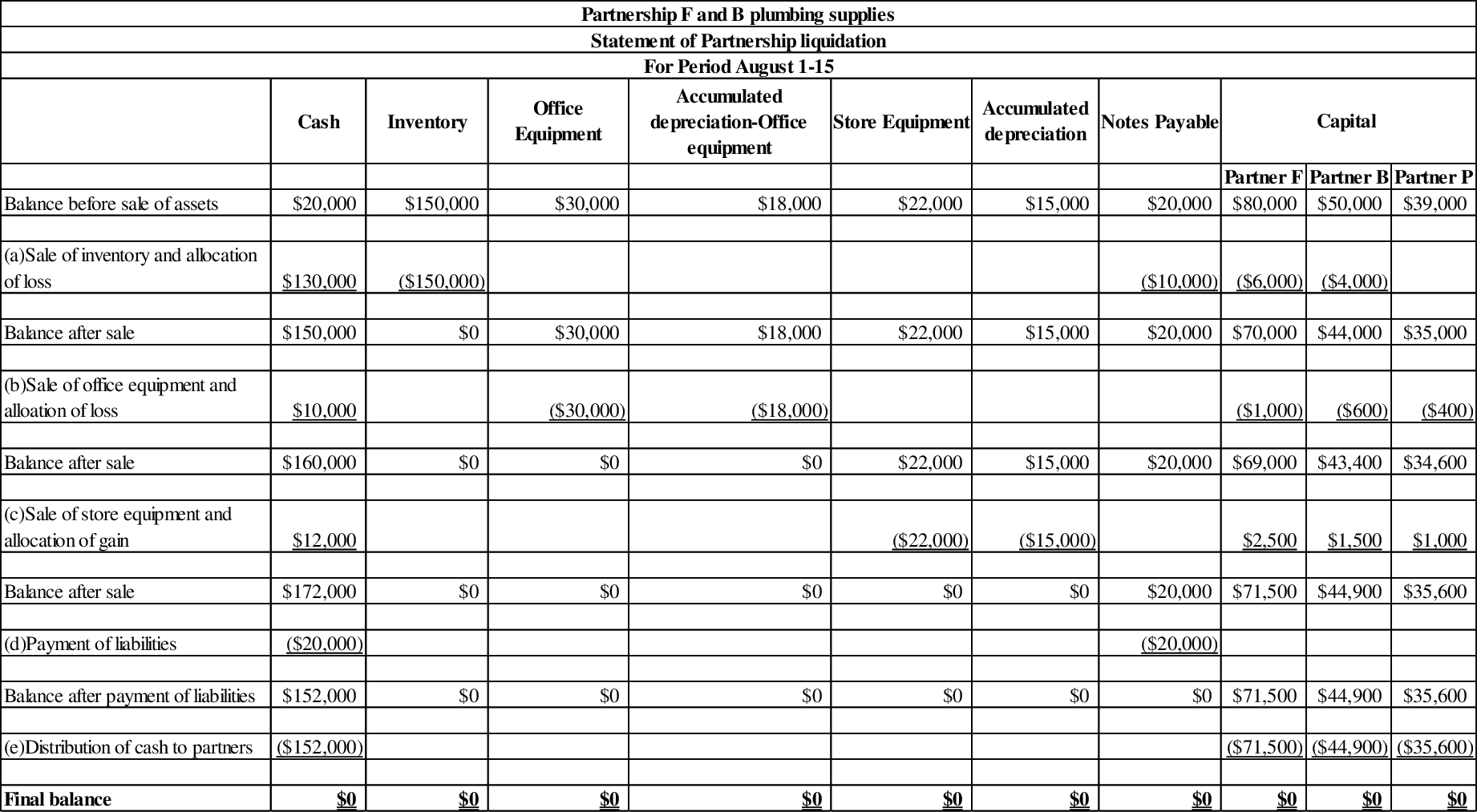
Figure (1)
Record the journal entry:
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 1 | Cash | $130,000 | |
| Loss on sale of assets | $20,000 | ||
| Inventory | $150,000 | ||
| (To record sale of assets) |
Table (5)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash account by $130,000.
- Loss on sale of assets is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit loss on sale of assets account, by $20,000.
- Inventory is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit inventory account by $150,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 1 | Partner F, Capital | $10,000 | |
| Partner B, Capital | $6,000 | ||
| Partner P, Capital | $4,000 | ||
| Loss on sale of assets | $20,000 | ||
| ( To record allocation of loss) |
Table (6)
- Partner F, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner F, capital account by $10,000.
- Partner B, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner B, capital account by $6,000.
- Partner P, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner P, capital account by $4,000.
- Loss on sale of assets is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit loss on sale of assets account, by $20,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 3 | Cash | $10,000 | |
| $18,000 | |||
| Loss on sale of inventory | $2,000 | ||
| Office equipment | $30,000 | ||
| ( To record Sale of office equipment) |
Table (7)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash account by $10,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset and it is decreased. Therefore, debit accumulated depreciation account by $18,000.
- Loss on sale of assets is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit loss on sale of assets account, by $2,000.
- Office equipment is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office equipment account by $30,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 3 | Partner F, Capital | $10,000 | |
| Partner B, Capital | $6,000 | ||
| Partner P, Capital | $4,000 | ||
| Loss on sale of office furniture | $20,000 | ||
| ( To record distribution of cash to partners) |
Table (8)
- Partner F, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner F, capital account by $10,000.
- Partner B, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner B, capital account by $6,000.
- Partner P, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner P, capital account by $4,000.
- Loss on sale of assets is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit loss on sale of assets account, by $20,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 5 | Cash | $120,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation-Store equipment | $150,000 | ||
| Store equipment | $22,000 | ||
| Gain on sale of store equipment | $5,000 | ||
| (To record sale of store equipment) |
Table (9)
- Cash is an asset and it is increased. Therefore, debit cash account by $120,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset and it is decreased. Therefore, debit accumulated depreciation account by $150,000.
- Office equipment is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office equipment account by $22,000.
- Gain on sale of asset is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit gain on sale of assets account, by $5,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 5 | Gain on sale of assets | $5,000 | |
| Partner F, Capital | $2,500 | ||
| Partner B, Capital | $1,500 | ||
| Partner P, Capital | $1,000 | ||
| ( To record allocation of gain) |
Table (10)
- Gain on sale of assets is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit gain on sale of assets account, by $5,000.
- Partner F, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner F, capital account by $2,500.
- Partner B, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner B, capital account by $1,500.
- Partner P, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is increased which decreases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, credit Partner P, capital account by $1,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 10 | Notes payable | $20,000 | |
| Cash | $20,000 | ||
| ( To record payment of notes payable) |
Table (11)
- Notes payable is a liability and it is decreased. Therefore, debit notes payable account by $20,000.
- Cash is an asset and it decreased. Therefore, debit cash account by $20,000.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit | Credit |
| August 15 | Partner F, Capital | $71,500 | |
| Partner B, Capital | $ 44,900 | ||
| Partner P Capital | $35,600 | ||
| Cash | $152,000 | ||
| ( To record distribution of cash) |
Table (12)
- Partner F, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner F, capital account by $71,500.
- Partner B, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner B, capital account by $44,900.
- Partner P, Capital is a component of partners’ equity and it is decreased which increases the value of partners’ equity. Therefore, debit Partner P, capital account by $35,600.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account by $152,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 19 Solutions
Bundle: College Accounting, Chapters 1-9, Loose-Leaf Version, 22nd + LMS Integrated for CengageNOWv2, 2 terms Printed Access Card for Heintz/Parry's College Accounting, Chapters 1-27, 22nd
- On January 3, 2020, Salma industries acquired equipment for $420,000.arrow_forwardJamison Electronics applies overhead using a normal costing approach based on direct labor hours. Budgeted factory overhead was $486,000, and budgeted direct labor hours were 27,000. Actual factory overhead was $502,200, and actual direct labor hours were 27,900. How much is the over- or underapplied overhead? Need helparrow_forwardAccounting questionarrow_forward
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27 (New in Account...AccountingISBN:9781305666160Author:James A. Heintz, Robert W. ParryPublisher:Cengage Learning
