
Concept explainers
a)
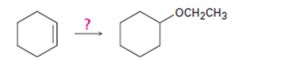
Interpretation:
How to bring out the transformation given is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
To show:
How to bring out the transformation given.
Answer to Problem 45AP
Cyclohexene can be transformed into cyclohexyl ethyl ether by subjecting cyclohexene to alkoxymercuration-reduction process.
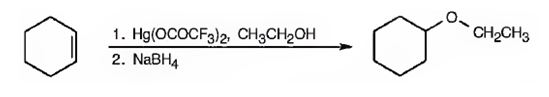
Explanation of Solution
When cyclohexene is treated with trifluoromercuric acetate, a mercurinium ion is formed. The attack of ethanol on the mercurinium ion leads to the formation of an organomercuric compound. Subsequent treatment of the mercuric compound with NaBH4 breaks the C-Hg bond and yields the ether.
Cyclohexene can be transformed into cyclohexyl ethyl ether by subjecting cyclohexene to alkoxymercuration-reduction process.

b)
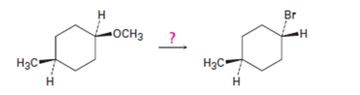
Interpretation:
How to bring out the transformation given is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single
To give:
How to bring out the transformation given.
Answer to Problem 45AP
The transformation required can be brought about by treating the ether with HBr.
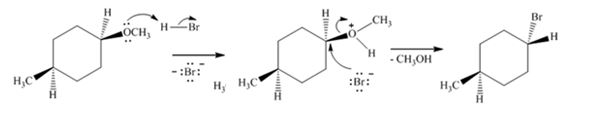
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has an oxygen atom attached to a primary and a secondary carbon. The protonation of the ethereal oxygen by the acid and the subsequent elimination of methanol by the attack of the bromide ion from the less hindered side through SN2 mechanism results in the formation of 1-bromo-4-methylcyclohexane with inversion of configuration (The methyl and methoxy groups are in the same faces in the reactant while the methyl and bromine are in the opposite faces in the product).
The transformation required can be brought about by treating the ether with HBr.

c)
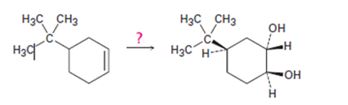
Interpretation:
How to transform 4-tert-butylcyclohex-1-ene into 1,2-trans-4-tert-butylcyclohex-1,2-
Concept introduction:
Alkenes when treated with peracids yield
To give:
How to transform 4-tert-butylcyclohex-1-ene into 1,2-trans-4-tert-butylcyclohex-1,2-diol.
Answer to Problem 45AP
4-tert-butylcyclohex-1-ene can be converted into 1,2-trans-4-tert-butylcyclohex-1,2-diol by following the steps shown below.
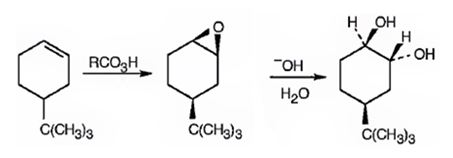
Explanation of Solution
When 4-tert-butylcyclohex-1-ene is treated peracids like m-chloroperbenzoic acids, an oxygen atom is transformed to the double bond in alkene in a syn manner to produce an epoxide in a single step. The attack of the hydroxide ion on the epoxide leads to the formation of an anionic intermediate which the picks up a proton to yield the diol.
4-tert-butylcyclohex-1-ene can be converted into 1,2-trans-4-tert-butylcyclohex-1,2-diol by following the steps shown below.

d)
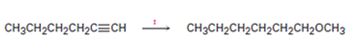
Interpretation:
How to transform 1-hexyne into n-hexyl methyl ether is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An ether is to be prepared from an
To show:
How to transform 1-hexyne into n-hexyl methyl ether.
Answer to Problem 45AP
1-hexyne can be converted into n-hexyl methyl ether by following the steps shown below.
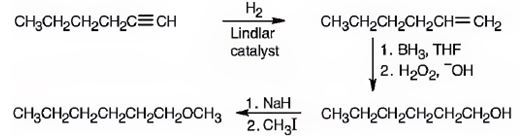
Explanation of Solution
1-Hexyne when reduced with Lindler catalyst yields 1-hexene as the reduction will stop at the alkene stage. Hydroboration with BH3 followed by oxidation with H2O2, OH- results in 1-hexanol by the addition of water, following anti-Markovnikov regiochemistry, to the double bond. The alcohol is converted into its alkoxide when treated with with NaH which then reacts with methyl iodide to yield n-hexyl methyl ether.
1-hexyne can be converted into n-hexyl methyl ether by following the steps shown below.

e)
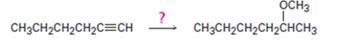
Interpretation:
How to convert 1-hexyne into 2-methoxyhexane is to be shown.
Concept introduction:
An ether is to be prepared from an alkyne. The alkyne is first converted into an alkene by reduction with Lindlar catalyst. The alkene is subjected to alkoxymercuration and the product when reduced with NaBH4 yields the ether required.
To show:
How to convert 1-hexyne into 2-methoxyhexane.
Answer to Problem 45AP
1-Hexyne can be converted into 2-methoxyhexane by following the steps shown below.
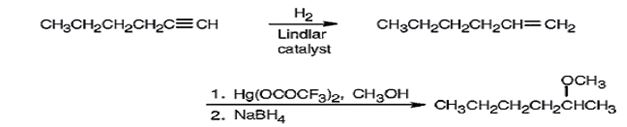
Explanation of Solution
1-Hexyne when reduced with Lindler catalyst yields 1-hexene as the reduction will stop at the alkene stage. Alkoxymercuration of 1-hexene with trifluoromercuric acetate and ethanol yields an intermediate organomercury compound which when reduced with NaBH4 yields 2-methoxyhexane. The net result is the Markovnikov addition of methanol to the double bond in 1-hexene.
1-Hexyne can be converted into 2-methoxyhexane by following the steps shown below.

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- K Draw the starting structure that would lead to the major product shown under the provided conditions. Drawing 1. NaNH2 2. PhCH2Br 4 57°F Sunny Q Searcharrow_forward7 Draw the starting alkyl bromide that would produce this alkyne under these conditions. F Drawing 1. NaNH2, A 2. H3O+ £ 4 Temps to rise Tomorrow Q Search H2arrow_forward7 Comment on the general features of the predicted (extremely simplified) ¹H- NMR spectrum of lycopene that is provided below. 00 6 57 PPM 3 2 1 0arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

