
a)
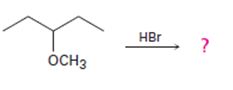
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which it/they is/are formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
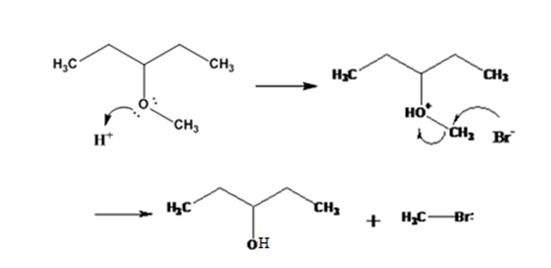
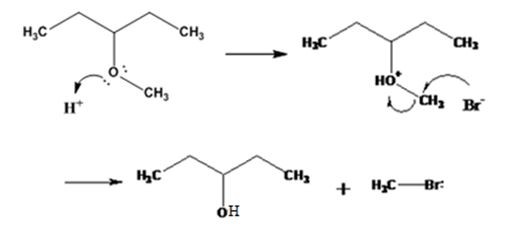
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The products formed when 3-methoxypentane is treated with HBr are 3-pentanol and methyl bromide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
b)
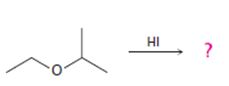
Interpretation:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
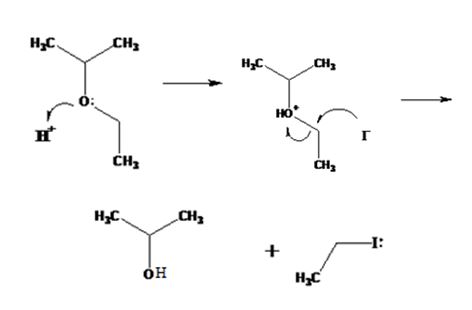
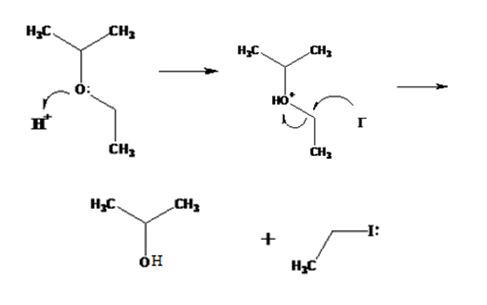
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The products formed when ethyl isopropyl ether is treated with HBr are 2-propanol and methyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
c)
Interpretation:
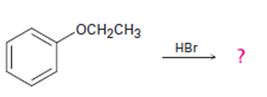
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr is to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2 mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr.
Answer to Problem 23MP
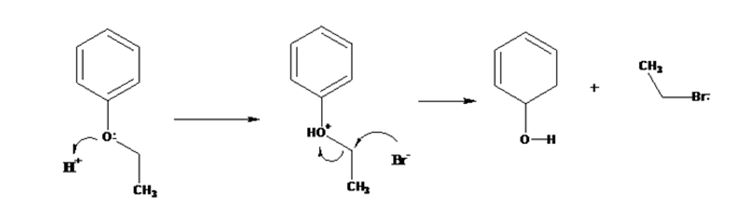
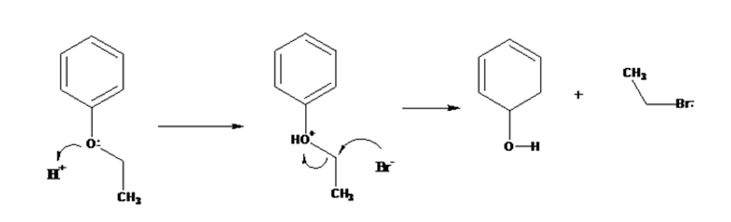
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a benzene ring and a methyl group attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The Br- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield phenol and ethyl bromide.
The products formed when ethyl phenyl ether is treated with HBr are phenol and ethyl iodide.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
d)
Interpretation:
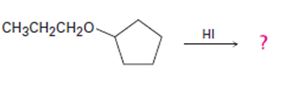
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are to be given.
Concept introduction:
Ethers are cleaved by strong acids. The cleavage takes place either by SN1 or SN2 mechanisms, depending upon the structure of the substrate. Ethers with only primary and secondary alkyl groups react by SN2mechanism. The Br- or I- attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield a single alcohol and a single alkyl halide. Ethers with a tertiary, benzylic or an allylic group cleave either by SN1 or E1 mechanism because these can produce a stable carbocations yielding alkenes and alcohols.
To give:
The products formed and the mechanism by which they are formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI.
Answer to Problem 23MP
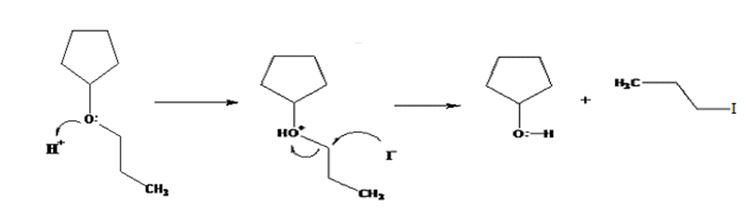
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
Explanation of Solution
The ether given has a secondary carbon and a primary carbon attached to the oxygen. The acid cleavage of the ether can take place through SN2 mechanism. The I- ion attacks the protonated ether at the less hindered side to yield cyclopentanol and 1-iodopropane.
The products formed when cyclopentyl propyl ether is treated with HI are cyclopentanol and 1-bromopropane.
The mechanism of their formation is given below.
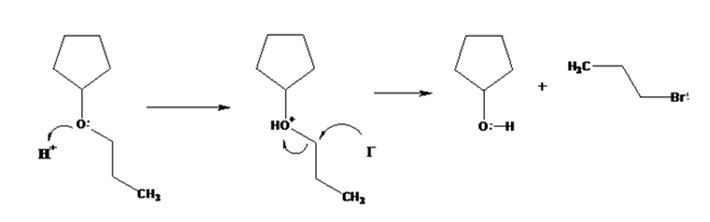
All the reactions, (a), (b), (c) and (d) take place following SN2 mechanism and the attack of the halide ion on the protonated
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- 8:17 PM Sun Mar 30 Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. HSCH2CH2CH2SH, BF3 Probler Drawing Ato Bonds Clarrow_forwardpresented by Mr L How the coprion. (Il Done in no wraction, dew the starting redential) доarrow_forward8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forward
- о но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forwardMacmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK A SMALL SCALE APPROACH TO ORGANIC LChemistryISBN:9781305446021Author:LampmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT


