
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133976588
Author: HIBBELER
Publisher: PEARSON CO
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 18.4, Problem 29P
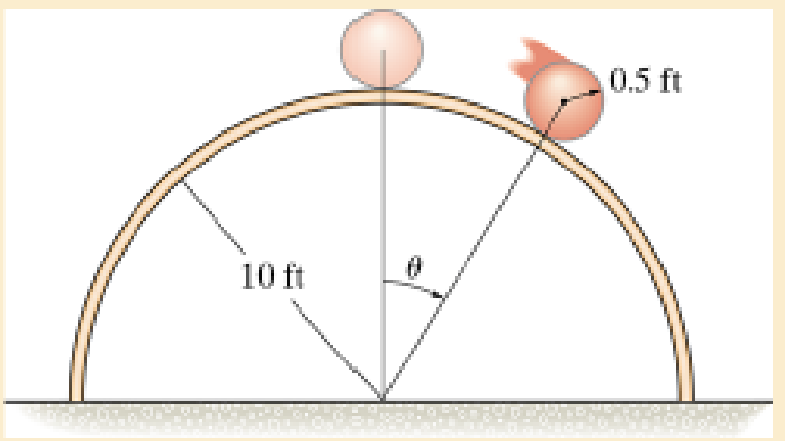
Determine the speed of the sptere's center of mass at the instant θ = 45°.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
of
stion
The man stands on the platform at O and runs out toward the edge such that when he is at A, y = 5 ft, his mass center has a velocity of 2
ft/s and an acceleration of 3 ft/s², both measured relative to the platform and directed along the positive y axis. If the platform has an
angular velocity of 0.4 rd/s and angular acceleration of 0.2 rad/s² as shown in the figure below, determine the following:
Note that i, j represent the unit vectors of x and y axes, respectively.
Z
The velocity of his mass center at this instant is
The acceleration of his mass center at this instant is
00
# ft/s.
W
# ft/s².
A
The rod AB moves on the indicated surface by means of wheels of negligible weight. The rod is released from its rest state from θ = 0° to θ = 30°. Find the velocities of points A and B when θ = 30°
The particle of mass m = 2.4 kg is attached to the light rigid rod of length L = 0.77 m, and the assembly rotates about a horizontal axis through O with a constant angular velocity θ˙θ˙ = ω = 3.5 rad/s. Determine the force T in the rod when θ = 29°. The force T is positive if in tension, negative if in compression.
Chapter 18 Solutions
EP ENGR.MECH.:DYNAMICS-REV.MOD.MAS.ACC.
Ch. 18.4 - Determine the kinetic energy of the 100-kg object.Ch. 18.4 - The 80-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18.4 - If the rod is at rest when = 0, determine its...Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod when the...Ch. 18.4 - If the wheel starts from rest and rolls Without...Ch. 18.4 - If the uniform 30-kg slender rod starts from rest...Ch. 18.4 - When it is subjected to a couple moment of M = 50...Ch. 18.4 - Show that its kinetic energy can be represented a...Ch. 18.4 - If the torsional spring attached to the wheel's...Ch. 18.4 - If the torsional spring attached to the wheel's...
Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the reel after...Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the reel after...Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the reel after...Ch. 18.4 - It has a weight of 50 lb and a centroidal radius...Ch. 18.4 - It has a weight of 50 lb and a centro1dal radius...Ch. 18.4 - If it starts from rest, determine its angular...Ch. 18.4 - If the 10-kg block is released from rest,...Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the 20-kg wheel...Ch. 18.4 - Initially, the system is at rest. The reel has a...Ch. 18.4 - The force is always perpendicular to the rod.Ch. 18.4 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod when it...Ch. 18.4 - If it is released from rest in the position shown,...Ch. 18.4 - If the elevator has a mass of 900 kg, the...Ch. 18.4 - If the ring rolls without slipping, determine its...Ch. 18.4 - A motor supplies a torque M = (40 + 900) Nm ,...Ch. 18.4 - When empty it has a mass of 800 kg and a radius of...Ch. 18.4 - If P = 200 N and the 15-kg uniform slender rod...Ch. 18.4 - If it is released from rest, determine how far it...Ch. 18.4 - The windlass A can be considered as a 30-lb...Ch. 18.4 - If the conveyor belt is moving with a speed of Vc...Ch. 18.4 - A couple moment of M = 80 Nm is then applied to...Ch. 18.4 - A couple moment M = 80 Nm is then applied to the...Ch. 18.4 - If the plate is released from rest at = 90,...Ch. 18.4 - If the ring gear C is fixed, determine the angular...Ch. 18.4 - If the rod is released from rest when the spring...Ch. 18.4 - Determine the speed of the sptere's center of mass...Ch. 18.4 - Motor M exerts a constant force of P = 750 Non the...Ch. 18.4 - When = 0, rod AB is rotating with an angular...Ch. 18.4 - If rod CD is subjected to a couple moment M = 30...Ch. 18.4 - The gears roll within the fixed ring gear C, which...Ch. 18.4 - When = 0, rod AB is rotating with an angular...Ch. 18.4 - When = 0, rod AB is rotating with an angular...Ch. 18.5 - If the 30-kg disk is released from rest when = 0...Ch. 18.5 - If it is released from rest, determine its angular...Ch. 18.5 - Determine its angular velocity when = 45.The...Ch. 18.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod when =...Ch. 18.5 - Determine the angular velocity of the rod when =...Ch. 18.5 - Determine its angular velocity when = 90. The...Ch. 18.5 - If a 2-kg block is suspended from the cord,...Ch. 18.5 - Prob. 37PCh. 18.5 - If it is released from rest at A on the incline,...Ch. 18.5 - The spool has a mass of 20 kg and a radius of...Ch. 18.5 - If the 15-kg block A is released from rest,...Ch. 18.5 - If it is allowed to fall freely determine the...Ch. 18.5 - Gear A has a mass of 10kg and a radius of gyration...Ch. 18.5 - If the rod is released from rest when = 30,...Ch. 18.5 - If the rod is released from rest when = 30,...Ch. 18.5 - The 40-kg wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18.5 - If the bars are released from rest when = 60,...Ch. 18.5 - If the bars are released from rest when = 60,...Ch. 18.5 - If it has a mass of 3 kg and a rad1us of gyration...Ch. 18.5 - Lifting is done using the two springs, each of...Ch. 18.5 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 1.5 m,...Ch. 18.5 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 1.5 m,...Ch. 18.5 - The drum has a weight of 50 lb and a radius of...Ch. 18.5 - If the track in which it moves is smooth,...Ch. 18.5 - The pulley has a weight of 50 lb and a rad1us of...Ch. 18.5 - The gear has a weight of 100 lb and a radius of...Ch. 18.5 - Determine the stiffness k of the spring so that...Ch. 18.5 - The slender 6-kg bar AB is horizontal and at rest...Ch. 18.5 - If the spring has an unstretched length of 0.2 m,...Ch. 18.5 - The 500-g rod AB rests along the smooth inner...Ch. 18.5 - The 50-lb wheel has a radius of gyration about its...Ch. 18.5 - The system consists of 60-lb and 20-lb blocks A...Ch. 18.5 - The door is made from one piece, whose ends move...Ch. 18.5 - The door is made from one piece, whose ends move...Ch. 18.5 - The end A of the garage door AB travels along the...Ch. 18.5 - The system consists of a 30-kg disk, 12-kg slender...Ch. 18.5 - The system consists of a 30-kg disk A, 12-kg...Ch. 18.5 - If it is released from rest when = 0, determine...Ch. 18.5 - If it is subjected to a torque of M = (91/2+ 1)...Ch. 18.5 - Starting from rest, the suspended 15-kg block B is...Ch. 18.5 - If it is released from rest, determine how far its...Ch. 18.5 - If the rack is originally moving downward at 2...Ch. 18.5 - The spring attached to its end always remains...Ch. 18.5 - If the disk rolls without slipping, determine the...Ch. 18.5 - At the instant the spring becomes undeformed, the...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This is a dynamics question. Hint: vC=6 ft/s, vB=4ft/sarrow_forwardThe small ball is moving along the radial slot of the rotating disk. At the instant shown, the disk has an angular velocity w = 4.1 rad/s which is decreasing at 1.7 rad/s per second, x = 230 mm, x = = 0.32 m/s, and ï = -0.2 m/s². Calculate the magnitudes of the absolute velocity and acceleration of the ball for this instant. (v₁ = 1.0 m/s, a₁ = 4.64 m/s²) = ω x 0 Aarrow_forward= = The disk of radius R 2.3 ft rolls without slipping on the horizontal surface, and at the instant represented, the center O has a constant velocity vo 5.6 ft/sec. For this instant, the particle A moving along the circular slot of mean radius r = 2 ft has the indicated speed u = 4 ft/sec relative to the disk which is decreasing at a rate of 4.2 ft/sec per second. Determine the magnitudes of the absolute velocity and acceleration of particle A. (v₁ = 10.5 ft/sec, aд = 39.6 ft/sec²) R r и νοarrow_forward
- The boom OAB pivots about point O, while section AB simultaneously extends from within section OA. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the center B of the pulley for the following conditions: >= = 30%, 0 = 7 deg/sec, 0 = 7 deg/sec²,1 = 12 ft, 1 = 2.3 ft/sec, Ï = -2.1 ft/sec². The quantities i and Ï are the first and second time derivatives, respectively, of the length / of section AB. Express your answers as vectors in the e, and e directions. B 28' 0 Answers: VB = (i ag= (i 8 A er + er + iarrow_forwardThe boom OAB pivots about point O, while section AB simultaneously extends from within section OA. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the center B of the pulley for the following conditions: 0 = 30°, 0 = 7 deg/sec, 0 = 8 deg/sec², 1 = 7 ft, 1 = 2.2 ft/sec, Ï = -2.3 ft/sec². The quantities and I are the first and second time derivatives, respectively, of the length / of section AB. Express your answers as vectors in the e, and en directions. 0 Answers: VB = ав = (i 26' 8 A O er + er + B eo) ft/sec eo) ft/sec²arrow_forwardFind the angle between the velocity and acceleration vectors at t=2s and t=5s of the moving part with respect to the position vector R= (2t3 -5t2 )i-(4t4 )j in the plane.arrow_forward
- At the instant shown, the spring is undeformed. Determine the change in potential energy if the 20 kg disk (radius of gyration = 0.5 m) rolls 2 revolutions without slipping. Note that the shown velocity vector refers to the translation of the centre of the wheel. Choices are in image.arrow_forwardRotation of bar OA is controlled by the lead screw which imparts a horizontal velocity v to collar C and causes pin P to travel along the smooth slot. Determine the values of r and 6, where r = OP, if h = 160 mm, x = 120 mm, and v = 25 mm/s at the instant represented. h Carrow_forwardThe boom OAB pivots about point O, while section AB simultaneously extends from within section OA. Determine the velocity and acceleration of the center B of the pulley for the following conditions: 0 = 26°, 0 = 7 deg/sec, 0 = 2 deg/sec², 1 = 10 ft, 1 = 1.0 ft/sec, ï = -5.9 ft/sec². The quantities and I are the first and second time derivatives, respectively, of the length / of section AB. Express your answers as vectors in the e, and en directions. +1 B 26' A eo) ft/sec eg) ft/sec² Answers: VB = ( aB = i 8 2 er + i e₁+ iarrow_forward
- Rotation of bar OA is controlled by the lead screw which imparts a horizontal velocity v = 31 mm/s to collar C and causes pin P to travel along with the smooth slot. The velocity of collar C is decreasing at a rate of 5 mm/s2 at the instant in question. Determine the values of r¨ and θ¨, where r = OP, if h = 245 mm and x = 185 mm.arrow_forwardAs the hydraulic cylinder rotates around O, the exposed length l of the piston rod P is controlled by the action of oil pressure in the cylinder. If the cylinder rotates at the constant rate 60 deg/s and l is decreasing at the constant rate of 150 mm/s, calculate the acceleration of end B when l = 125 mm.arrow_forwardThe belt is travelling to the right at some speed v, while the pipe is rolling without slipping at o = 4 - 1.5 m rad/s as shown. If the center of the pipe G appears to an observer on the ground to move at 2 m/s to the left, determine the velocity of the Belt В belt v.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Dynamics - Lesson 1: Introduction and Constant Acceleration Equations; Author: Jeff Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7aMiZ3b0Ieg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY