1 Introduction: The Nature Of Science And Physics 2 Kinematics 3 Two-dimensional Kinematics 4 Dynamics: Force And Newton's Laws Of Motion 5 Further Applications Of Newton's Laws: Friction, Drag, And Elasticity 6 Uniform Circular Motion And Gravitation 7 Work, Energy, And Energy Resources 8 Linear Momentum And Collisions 9 Statics And Torque 10 Rotational Motion And Angular Momentum 11 Fluid Statics 12 Fluid Dynamics And Its Biological And Medical Applications 13 Temperature, Kinetic Theory, And The Gas Laws 14 Heat And Heat Transfer Methods 15 Thermodynamics 16 Oscillatory Motion And Waves 17 Physics Of Hearing 18 Electric Charge And Electric Field 19 Electric Potential And Electric Field 20 Electric Current, Resistance, And Ohm's Law 21 Circuits And Dc Instruments 22 Magnetism 23 Electromagnetic Induction, Ac Circuits, And Electrical Technologies 24 Electromagnetic Waves 25 Geometric Optics 26 Vision And Optical Instruments 27 Wave Optics 28 Special Relativity 29 Introduction To Quantum Physics 30 Atomic Physics 31 Radioactivity And Nuclear Physics 32 Medical Applications Of Nuclear Physics 33 Particle Physics 34 Frontiers Of Physics expand_more
Chapter Questions expand_more
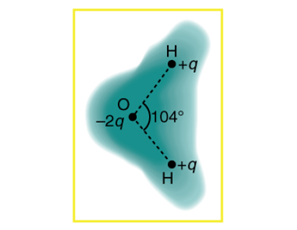
Problem 1CQ: There are very large numbers of charged particles in most objects. Why, then, don't most objects... Problem 2CQ: Why do most objects tend to contain nearly equal numbers of positive and negative charges? Problem 3CQ: An eccentric inventor attempts to levitate by first placing a large negative charge on himself and... Problem 4CQ: If you have charged an electroscope by contact with a positively charged object, describe how you... Problem 5CQ: When a glass rod is rubbed with silk, it becomes negativeyet both attract dust. Does the dust have a... Problem 6CQ: Why does a car always attract dust right after it is polished? (Note that car wax and car tires are... Problem 7CQ: Describe how a positively charged object can be used to give another object a negative charge. What... Problem 8CQ: What is grounding? What effect does it have on a charged conductor? On a charged insulator? Problem 9CQ: Figure 18.43 shows the charge distribution in a water molecule, which is called a polar molecule... Problem 10CQ: Using Figure 18.43, explain, in terms of Coulomb's law, why a polar molecule (such as in Figure... Problem 11CQ: Given the polar character of water molecules, explain how ions in the air form nucleation centers... Problem 12CQ: Why must the test charge q in the definition of the electric field be vanishingly small? Problem 13CQ: Are the direction and magnitude of the Coulomb force unique at a given point in space? What about... Problem 14CQ: Compare and contrast the Coulomb force field and the electric field. To do this, make a list of five... Problem 15CQ: Figure 18.44 shows an electric field extending over three regions, labeled I, II, and III. Answer... Problem 16CQ: A cell membrane is a thin layer enveloping a cell. The thickness of the membrane is much less than... Problem 17CQ: Is the object in Figure 18.45 a conductor or an insulator? Justify your answer. Problem 18CQ: If the electric field lines in the figure above were perpendicular to the object, would it... Problem 19CQ: The discussion of the electric field between two parallel conducting plates, in this module states... Problem 20CQ: Would the self-created electric field at the end of a pointed conductor, such as a lightning rod,... Problem 21CQ: Why is a golfer with a metal dub over her shoulder vulnerable to lightning in an open fairway? Would... Problem 22CQ: Can the belt of aVan de Graaff accelerator he a conductor? Explain. Problem 23CQ: Are you relatively safe from lightning inside an automobile? Give two reasons. Problem 24CQ: Discuss pros and cons of a lightning rod being grounded versus simply being attached to a building. Problem 25CQ: Using the symmetry of the arrangement, show that the net Coulomb force on the charge q at the center... Problem 26CQ: (a) Using the symmetry of the arrangement, show that the electric field at the center of the square... Problem 27CQ: (a) What is the direction of the total Coulomb force on q in Figure 18.46 if q is negative, qa=... Problem 28CQ: Considering Figure 18.46, suppose that qa= qdand qb= qc. First show that q is in static equilibrium.... Problem 29CQ: If qa = 0 in Figure 18-46, under what conditions will there be no net Coulomb force on q? Problem 30CQ: In regions of low humidity, one develops a special "grip” when opening car doors, or touching metal... Problem 31CQ: Tollbooth stations on roadways and bridges usually have a piece of wire stuck in the pavement before... Problem 32CQ: Suppose a woman carries an excess charge. To maintain her charged status can she he standing on just... Problem 1PE: Common static electricity involves charges ranging from nanocoulombs to microcoulombs. (a) How many... Problem 2PE: If 1.801020electrons move through a pocket calculator during a full day’s operation, how many... Problem 3PE: To start a car engine, the car battery moves 3.751021 electrons through the starter motor. How many... Problem 4PE: A certain lightning bolt moves 40.0 C of charge. How many fundamental units of charge | qe\ is this? Problem 5PE: Suppose a speck of dust in an electrostatic precipitator has l.0000 1012 protons in it and has a... Problem 6PE: An amoeba has 1.001016protons and a net charge of 0.300 pC. (a) How many fewer electrons are there... Problem 7PE: A 50.0 g ball of copper has a net charge of 2.00 C. What fraction of the copper s electrons has been... Problem 8PE: What net charge would you place on a 100 g piece of sulfur if you put an extra electron on 1 in 1012... Problem 9PE: How many coulombs of positive charge are there in 4.00 kg of plutonium, given its atomic mass is 244... Problem 10PE: What is the repulsive force between two pith balls that are 8.00 cm apart and have equal charges of ... Problem 11PE: (a) How strong is the attractive force between a glass rod with a 0.700 C charge and a silk cloth... Problem 12PE: Two point charges exert a 5.00 N force on each other. What will the force become if the distance... Problem 13PE: Two point charges are brought closer together, increasing the force between them by a factor of 25.... Problem 14PE: How far apart must two point charges of 75.0 nC (typical of static electricity) be to have a force... Problem 15PE: If two equal charges each of 1 C each are separated in air by a distance of 1 km, what is the... Problem 16PE: A test charge of +2C is placed halfway between a charge of +6 C and another of +4 /C separated by 10... Problem 17PE: Bare free charges do not remain stationary when close together. To illustrate this, calculate the... Problem 18PE: (a) By what factor must you change the distance between two point charges to change the force... Problem 19PE: Suppose you have a total charge qtot that you can split in any manner. Once split, the separation... Problem 20PE: (a) Common transparent tape becomes charged when pulled from a dispenser. If one piece is placed... Problem 21PE: Find the ratio of the electrostatic to gravitational force between two electrons. (b) What is this... Problem 22PE: At what distance is the electrostatic force between two protons equal to the weight of one proton? Problem 23PE: A certain five cent coin contains 5.00 g of nickel. What fraction of the nickel atoms’ electrons,... Problem 24PE: (a) Two point charges totaling 8.00 C exert a repulsive force of 0.150 N on one another when... Problem 25PE: Point charges of 5.00 C and 3.00/C are placed 0.250 m apart. (a) Where can a third charge be placed... Problem 26PE: (a) Two point charges q1 and q23.00 m apart, and their total charge is 20 C. (a) If the force of... Problem 27PE: What is the magnitude and direction of an electric field that exerts a 2.0010-5 N upward force on a... Problem 28PE: What is the magnitude and direction of the force exerted on a 3.50 /C charge by a 250 N/C electric... Problem 29PE: Calculate the magnitude of the electric field 2.00 m from a point charge of 5.00 mC (such as found... Problem 30PE: (a) What magnitude point charge creates a 10,000 N/C electric field at a distance of 0.250 m? (b)... Problem 31PE: Calculate the initial (from rest) acceleration of a proton in a 5.00X106 N/C electric field (such as... Problem 32PE: (a) Find the direction and magnitude of an electric field that exerts a 4.801017 N westward force on... Problem 33PE: (a) Sketch the electric field lines near a point charge +q (b) Do the same for a point charge +q.... Problem 34PE: Sketch the electric field lines a long distance from the charge distributions shown in Figure 18.26... Problem 35PE: Figure 18.47 shows the electric field lines near two charges q j and g2. What is the ratio of their... Problem 36PE: Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of two opposite charges, where the negative charge... Problem 37PE: Sketch the electric field lires in the vicinity of the conductor in Figure 18.48 given the field was... Problem 38PE: Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of the conductor in Figure 18.49 given the field was... Problem 39PE: Sketch the electric field between the two conducting plates shown in Figure 18.50, given the top... Problem 40PE: Sketch the electric field lines in the vicinity of the charged insulator in Figure 18.51 noting its... Problem 41PE: What is the force on the charge located at x = 8.00 cm in Figure 18.52(a) given that q = 1.00 C? Problem 42PE: (a) Find the total electric field at x = 1.00 cm in Figure 18.52(b) given that q =5.00 nC. (b) Find... Problem 43PE: (a) Find the electric field at x = 5.00 cm in Figure 18.52 (a), given that q = 1.00 C. (b) at what... Problem 44PE: (a) Find the total Coulomb force on a charge of 2.00 nC located at x = 4.00 cm in Figure 18.52 (b):... Problem 45PE: Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the force on q in the figure... Problem 46PE: (a) Using the symmetry of the arrangement, determine the direction of the electric field at the... Problem 47PE: Find the electric field at the location of qain Figure 18.53 given that qb=qc= qd=+2.00 nC, q= -1.00... Problem 48PE: 48. Find the total Coulomb force on a charge q in Figure 18.53, given that q = 1.00 C, qa=2.00 C,... Problem 49PE: Find the electric field at the location of qain Figure 18.54, given that qb=+10.00 C and qc= -5.00... Problem 50PE: (a) Find the electric field at the center of the triangular configuration of charges in Figure... Problem 51PE: (a) What is the electric field 5.00 m from the center of the terminal of a Van de Graaff with a 3.00... Problem 52PE: (a) What is the direction and magnitude of an electric field that supports the weight of a free... Problem 53PE: A simple and common technique for accelerating electrons is shown in Figure 18.55, where there is a... Problem 54PE: Earth has a net charge that produces an electric field of approximately 150 N/C downward at its... Problem 55PE: Point charges of 25.0 C and 45.0 (2 are placed 0.500 m apart. (a) At what point along the line... Problem 56PE: What can you say about two charges q1and q2, if the electric field one-fourth of the way from q1to... Problem 57PE: Integrated Concepts Calculate the angular velocity ? of an electron orbiting a proton in the... Problem 58PE: Integrated Concepts An electron has an initial velocity of 5.00106m/s in a uniform 2.00105N/C... Problem 59PE: Integrated Concepts The practical limit to an electric field in air is about 3.001061 N/C. Above... Problem 60PE: Integrated Concepts A 5.00 g charged insulating ball hangs or a 30.0 cm long string in a uniform... Problem 61PE: Integrated Concepts Figure 18.57 shows an electron passing between two charged metal plates that... Problem 62PE: Integrated Concepts The classic Millikan oil drop experiment was the first to obtain an accurate... Problem 63PE: Integrated Concepts (a) In Figure 18.59, four equal charges q lie on the corners of a square. A... Problem 64PE: Unreasonable Results 64. (a) Calculate the electric field strength near a 10.0 cm diameter... Problem 65PE: Unreasonable results (a) Two 0.500 g raindrops in a thunderhead are 1.00 cm apart when they each... Problem 66PE: Unreasonable results A wrecking yard inventor wants to pick up cars by charging a 0.400 m diameter... Problem 67PE: Construct Your Own Problem Consider two insulating balls with evenly distributed equal and opposite... Problem 68PE: Construct Your Own Problem Consider identical spherical conducting space ships in deep space where... format_list_bulleted


 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning





