
Concept explainers
BIO Electric discharge by eels In several aquatic animals such as the South American electric eel electric organs produce 600-V potential difference pulses to ward off predators as well as to stun prey Figure 18.29 illustrates the key component that produces this electric shock—an electrolyte. The interior of an inactive electrolyte (Figure 18.29a) has an excess of negatively charged ions. The exterior has an excess of positively charged sodium ions
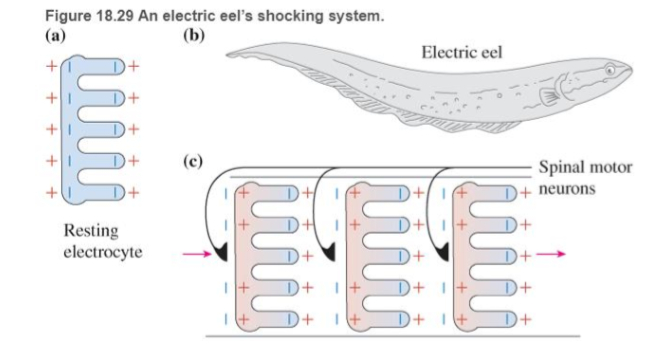
The eel's long trunk and tail contain many electrolytes placed one after the other in columns (Figures 18.29b and c). Each electrolyte contains several types of ion channels, which when activated by a nerve impulse allow sodium ions to pass through channels on the loft flat side of each electrolyte from outside the cell to the inside. This causes the electric potential across that cell membrane to change from
Look at the electrolyte shown in Figure 18.29c. What causes the 0.10-V potential difference from the outer left to the outer right side of the cell?
a. The membrane is thicker on the left than on the right.
b. The ion distribution across the left membrane is different than across the right membrane.
c. The left and right membranes have different capacitances.
d. b and c
e. a, b, and c
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK COLLEGE PHYSICS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Campbell Essential Biology with Physiology (5th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Introductory Chemistry (6th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Microbiology with Diseases by Body System (5th Edition)
- 20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward19. Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain above sea level, has a peak of 8849 m above sea level. Assume that sea level defines the height of Earth's surface. (re = 6.38 × 106 m, ME = 5.98 × 1024 kg, G = 6.67 × 10 -11 Nm²/kg²) a. Calculate the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point at the peak of Mount Everest. b. What is the ratio of the strength of Earth's gravitational field at a point 644416m below the surface of the Earth to a point at the top of Mount Everest? C. A tourist watching the sunrise on top of Mount Everest observes a satellite orbiting Earth at an altitude 3580 km above his position. Determine the speed of the satellite.arrow_forward
- pls help on allarrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





