
Draw the structure for each of the following:
a. phenol
b. benzyl phenyl ether
c. benzonitrile
d. benzaldehyde
e. anisole
f. styrene
g. toluene
h. tert-buty lbenzene
i. benzyl chloride
a)
Interpretation:
The structure of phenol is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
Phenols are defined as those compounds in which hydroxy group is attached directly to the benzene ring. Phenols and alcohols have so many similar properties.
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of phenol is shown below.
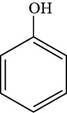
Figure 1
Explanation of Solution
The structure of phenol is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of phenol is shown below.
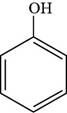
Figure 1
b)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is shown below.
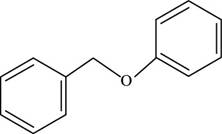
Figure 2
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzyl phenyl ether is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzyl phenyl ether is shown below.

Figure 2
c)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzonitrile is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzonitrile is shown below.
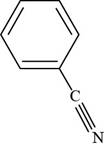
Figure 3
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzonitrile is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzonitrile is shown below.
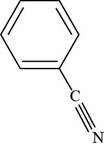
Figure 3
d)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzaldehyde is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzaldehyde is shown below.
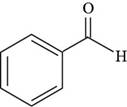
Figure 4
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzaldehyde is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzaldehyde is shown below.
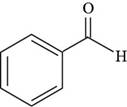
Figure 4
e)
Interpretation:
The structure of anisole is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of anisole is shown below.
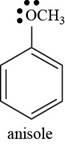
Figure 5
Explanation of Solution
The structure of anisole is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of anisole is shown below.
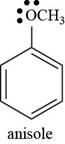
Figure 5
f)
Interpretation:
The structure of styrene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of styrene is shown below.
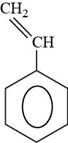
Figure 6
Explanation of Solution
The structure of styrene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of styrene is shown below.
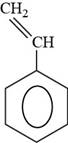
Figure 6
g)
Interpretation: The structure of toluene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of toluene is shown below.
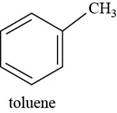
Figure 7
Explanation of Solution
The structure of toluene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of toluene is shown below.
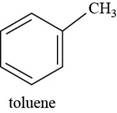
Figure 7
h)
Interpretation: The structure of tert-butyl benzene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of tert-butyl benzene is shown below.
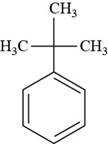
Figure 8
Explanation of Solution
The structure of tert-butyl benzene is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of tert-butyl benzene is shown below.

Figure 8
i)
Interpretation:
The structure of benzyl chloride is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The reactivity of benzene ring towards electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions is enhanced by the activating substituents. The deactivating substituents make the benzene ring less reactive. Some of the activating substituents are
Answer to Problem 42P
The structure of benzyl chloride is shown below.
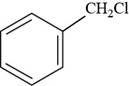
Figure 9
Explanation of Solution
The structure of benzyl chloride is drawn as follows.
The first step is to draw the structure of benzene ring. Then
Thus, the structure of benzyl chloride is shown below.

Figure 9
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Organic Chemistry Study Guide and Solutions Manual, Books a la Carte Edition (8th Edition)
- Briefly indicate the structure and bonding of silicates.arrow_forward4 Part C Give the IUPAC name and a common name for the following ether: Spell out the full names of the compound in the indicated order separated by a comma.arrow_forwardTry: Draw possible resonance contributing structures for the following organic species: CH3CH2NO2 [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHCHO] [CH2CHCH2] [CH2CHNH2]arrow_forward
- Complete the following synthesis. (d). H+ ง сarrow_forwardCan the target compound be efficiently synthesized in good yield from the substituted benzene of the starting material? If yes, draw the synthesis. Include all steps and all reactants.arrow_forwardThis is a synthesis question. Why is this method wrong or worse than the "correct" method? You could do it thiss way, couldn't you?arrow_forward
- Try: Draw the best Lewis structure showing all non-bonding electrons and all formal charges if any: (CH3)3CCNO NCO- HN3 [CH3OH2]*arrow_forwardWhat are the major products of the following reaction? Draw all the major products. If there are no major products, then there is no reaction that will take place. Use wedge and dash bonds when necessary.arrow_forwardZeolites. State their composition and structure. Give an example.arrow_forward
- Don't used hand raiting and show all reactionsarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardIX) By writing the appropriate electron configurations and orbital box diagrams briefly EXPLAIN in your own words each one of the following questions: a) The bond length of the Br2 molecule is 2.28 Å, while the bond length of the compound KBr is 3.34 Å. The radius of K✶ is 1.52 Å. Determine the atomic radius in Å of the bromine atom and of the bromide ion. Br = Br b) Explain why there is a large difference in the atomic sizes or radius of the two (Br and Br). Tarrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
