
To calculate: The location of the point S so that quadrilateral PQRS is a square and area of the square along with figure.
Answer to Problem 22E
The coordinates of point S so that PQRS forms a square is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The points
Formula used:
A square is a special kind of quadrilateral having equal lengths of its sides and diagonals.
Distance formula between two points
Area of a square with its side length x is the square of its side, which is mathematically written as,
Calculation:
Consider the provided vertices
By plotting the given points on the coordinate plane, we get the following figure,
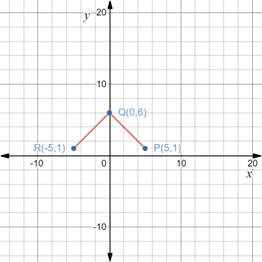
Recall that a square is a special kind of quadrilateral having equal lengths of its sides and diagonals.
So, to find the coordinates of S such that PQRS forms a square, the lengths of its diagonals i.e. PR and QS must be equal.
For the coordinates to form a square, S must lie on y-axis, so, assume the coordinates of S as
Now, apply distance formula between two points
Simplify it further as,
Therefore, the fourth vertex of the square PQRS is at point
Now, the length of side of square is calculated as,
Recall that area of a square with its side length x is the square of its side, which is mathematically written as,
So, area of square PQRS is calculated as,
Thus, the coordinates of point S so that PQRS forms a square is
Chapter 1 Solutions
EBK PRECALCULUS: MATHEMATICS FOR CALCUL
- = 5 37 A 4 8 0.5 06 9arrow_forwardConsider the following system of equations, Ax=b : x+2y+3z - w = 2 2x4z2w = 3 -x+6y+17z7w = 0 -9x-2y+13z7w = -14 a. Find the solution to the system. Write it as a parametric equation. You can use a computer to do the row reduction. b. What is a geometric description of the solution? Explain how you know. c. Write the solution in vector form? d. What is the solution to the homogeneous system, Ax=0?arrow_forward2. Find a matrix A with the following qualities a. A is 3 x 3. b. The matrix A is not lower triangular and is not upper triangular. c. At least one value in each row is not a 1, 2,-1, -2, or 0 d. A is invertible.arrow_forward
- Find the exact area inside r=2sin(2\theta ) and outside r=\sqrt(3)arrow_forwardA 20 foot ladder rests on level ground; its head (top) is against a vertical wall. The bottom of the ladder begins by being 12 feet from the wall but begins moving away at the rate of 0.1 feet per second. At what rate is the top of the ladder slipping down the wall? You may use a calculator.arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.4.1(root test) and 12.4.2(ratio test)arrow_forward
- Use 12.4.2 to determine whether the infinite series on the right side of equation 12.6.5, 12.6.6 and 12.6.7 converges for every real number x.arrow_forwarduse Cauchy Mean-Value Theorem to derive Corollary 12.6.2, and then derive 12.6.3arrow_forwardExplain the focus and reasons for establishment of 12.5.4arrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





