
Subpart (a):
The
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The production possibility frontier for country Latvia is given in figure 1 as follows:
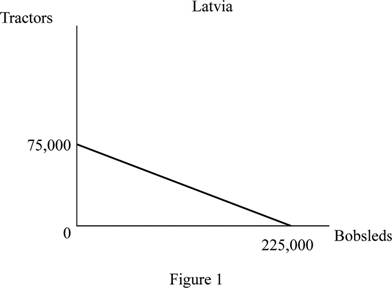
From figure 1, it can be inferred that if all the resources are employed in the production of tractors then, at most 75,000 tractors can be produced and if all resources are employed in the production of Bobsleds then. 225,000 bobsleds can be produced.
The production possibility frontier for country Estonia is given in figure 2 as follows:
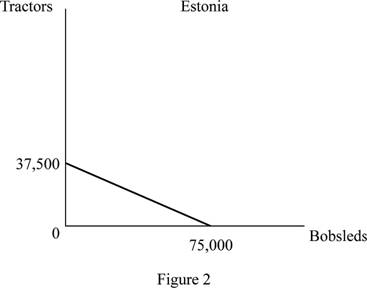
From figure 2, it can be inferred that if all the resources are employed in the production of tractors then, at most 37,500 tractors can be produced and if all resources are employed in the production of Bobsleds then. 75,000 bobsleds can be produced.
Concept Introduction:
Production possibilities frontier: It is a graph that shows the combinations of output that the economy can possibly produce the given available factors of production and the available production technology.
Subpart (b):
The
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
The opportunity cost of producing Tractors for Latvia (OCLT) can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the opportunity cost for Latvia to produce one tractor is 3 bobsleds.
The opportunity cost of producing Tractors for Estonia (OCET) can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the opportunity cost for Estonia to produce one tractor is 2 bobsleds.
Since Estonia incurs a lower opportunity cost in the production of tractors then, Estonia has a comparative advantage in tractor production than Latvia.
The opportunity cost of producing Bobsleds for Latvia (OCLB) can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the opportunity cost for Latvia to produce one bobsled is 1/3 tractors.
The opportunity cost of producing Bobsleds for Estonia (OCEB) can be calculated as follows:
Thus, the opportunity cost for Estonia to produce one bobsled is 1/2 tractors.
Since Latvia incurs a lower opportunity cost in the production of bobsleds then, Latvia has a comparative advantage in bobsleds production than Estonia.
Since both have comparative advantages, they will definitely engage in the trade.
Concept Introduction:
Opportunity cost: The opportunity cost refers to the value of what one has to give up in order to choose another alternative.
Comparative advantage: It is the ability of a producer, firm or country to produce a good or service at a lower opportunity cost of production than the competitors.
Subpart (c):
The agreement of exchange.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
If a trade’s agreement is negotiated, any agreement between 2 bobsleds and 3 bobsleds per tractor will benefit both countries’ trade and specialization.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- A health study tracked a group of persons for five years. At the beginning of the study, 20%were classified as heavy smokers, 30% as light smokers, and 50% as nonsmokers. Resultsof the study showed that light smokers were twice as likely as nonsmokers to die duringthe five-year study, but only half as likely as heavy smokers.A randomly selected participant from the study died during the five-year period. Calculatethe probability that the participant was a heavy smokerarrow_forwardConsider two assets with the following returns: State Prob. of state R₁ R2 1 23 13 25% 5% 2 -10% 1% Compute the optimal portfolio for an investor having a Bernoulli utility of net returns u(r) = 2√√r+ 10. Compute the certainty equivalent of the optimal portfolio. Do the results change if short-selling is not allowed? If so, how?arrow_forwardIn the graph at the right, the average variable cost is curve ☐. The average total cost is curve marginal cost is curve The C Cost per Unit ($) Per Unit Costs A 0 Output Quantity Barrow_forward
- What are some of the question s that I can ask my economic teacher?arrow_forwardAnswer question 2 only.arrow_forward1. A pension fund manager is considering three mutual funds. The first is a stock fund, the second is a long-term government and corporate fund, and the third is a (riskless) T-bill money market fund that yields a rate of 8%. The probability distributions of the risky funds have the following characteristics: Standard Deviation (%) Expected return (%) Stock fund (Rs) 20 30 Bond fund (RB) 12 15 The correlation between the fund returns is .10.arrow_forward
- Frederick Jones operates a sole proprietorship business in Trinidad and Tobago. His gross annual revenue in 2023 was $2,000,000. He wants to register for VAT, but he is unsure of what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and what he needs to do to ensure that he is fully compliant with VAT regulations. Make reference to the Vat Act of Trinidad and Tobago and explain to Mr. Jones what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and the requirements to be fully compliant with VAT regulations.arrow_forwardCan you show me the answers for parts a and b? Thanks.arrow_forwardWhat are the answers for parts a and b? Thanksarrow_forward
- What are the answers for a,b,c,d? Are they supposed to be numerical answers or in terms of a variable?arrow_forwardSue is a sole proprietor of her own sewing business. Revenues are $150,000 per year and raw material (cloth, thread) costs are $130,000 per year. Sue pays herself a salary of $60,000 per year but gave up a job with a salary of $80,000 to run the business. ○ A. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ B. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $40,000. ○ C. Her accounting profits are - $40,000. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ D. Her accounting profits are - $60,000. Her economic profits are -$40,000.arrow_forwardSelect a number that describes the type of firm organization indicated. Descriptions of Firm Organizations: 1. has one owner-manager who is personally responsible for all aspects of the business, including its debts 2. one type of partner takes part in managing the firm and is personally liable for the firm's actions and debts, and the other type of partner takes no part in the management of the firm and risks only the money that they have invested 3. owners are not personally responsible for anything that is done in the name of the firm 4. owned by the government but is usually under the direction of a more or less independent, state-appointed board 5. established with the explicit objective of providing goods or services but only in a manner that just covers its costs 6. has two or more joint owners, each of whom is personally responsible for all of the partnership's debts Type of Firm Organization a. limited partnership b. single proprietorship c. corporation Correct Numberarrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





