
Concept explainers
To match: The given anatomical terms with the organs/structures of the urinary system.
Introduction: The urinary system is a series of complex structures responsible for eliminating waste from the body, regulating blood volume and blood pressure, controlling levels of electrolytes and metabolites, and to regulate blood pH. The urinary system, the lungs, skin, and intestines are together to maintain the balance of chemicals and water in the body.
Answer to Problem 1P
Pictorial representation: Fig.1 shows a diagram of the organs/structures of the urinary system labeled with the given anatomical terms.
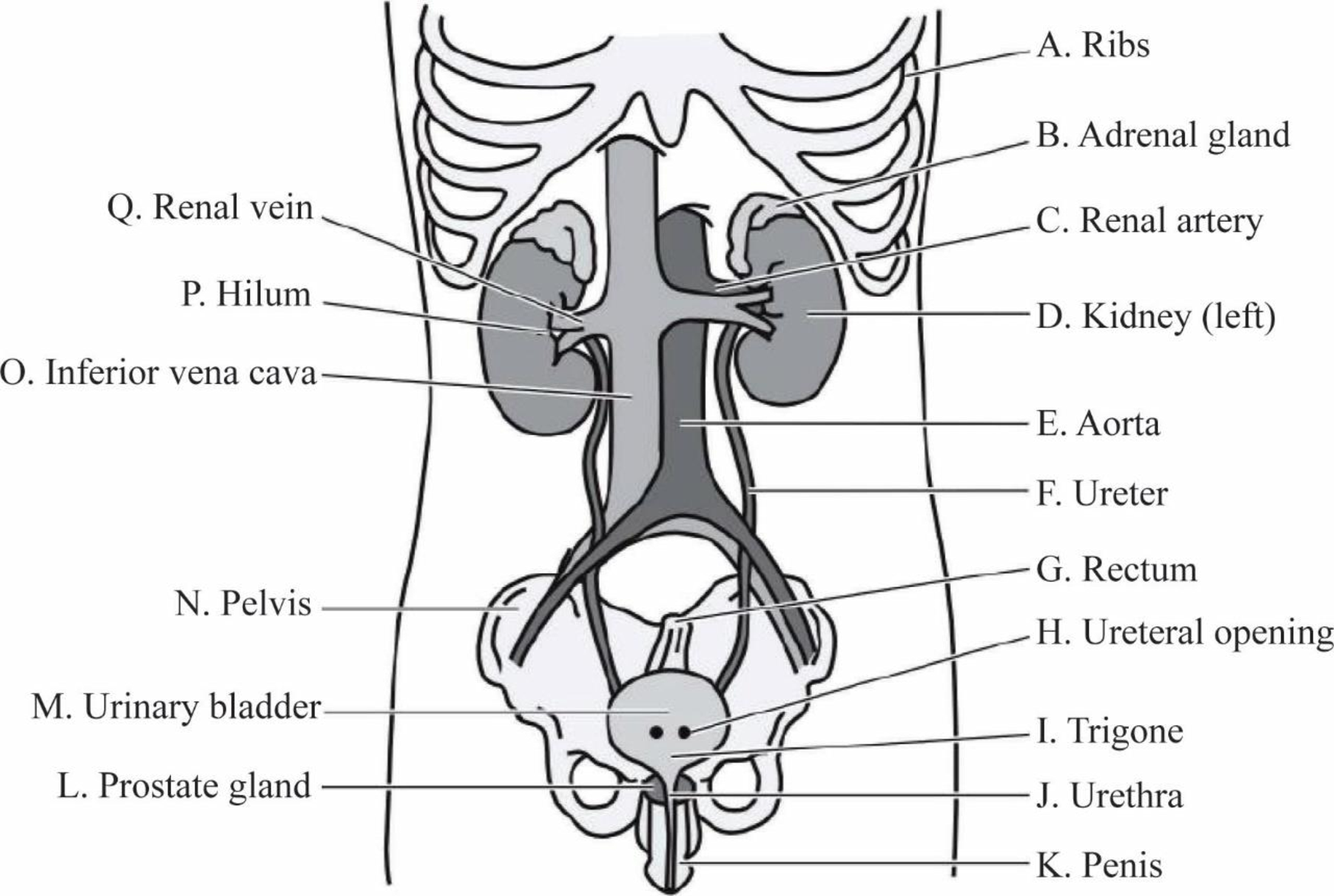
Fig 1: Anatomical structure of the urinary system
Explanation of Solution
A. Ribs: The ribs are elastic arches of bone, twelve in number on either side, separated by spaces called intercostal spaces. The main function of the ribs is to protect the kidney and liver from any external damage.
B. Adrenal gland: The adrenal glands are tiny organs that rest on top of each kidney. The right adrenal gland is pyramid shaped and the left gland is crescent shaped. The main function of the adrenal glands is to regulate the activity of the kidney through the release of a hormone called aldosterone.
C. Renal artery: The renal artery branches out from the abdominal aorta and enters the kidney at the renal hilum. The main function of the renal artery is to carry oxygenated blood from the heart to the kidney.
D. Kidney (left): The left kidney is located in a superior position to the right kidney. The left kidney is responsible for regulation of water and electrolyte balance and removes waste materials from the body.
E. Aorta: The aorta is the largest artery of the body and is connected to the left ventricle of the heart. The function of the aorta is to supply blood to the kidneys for filtration.
F. Ureter: The ureter is a thin tube that connects the kidney and the bladder. It carries urine from the kidney to the urinary bladder.
G. Rectum: The rectum is found at the end of the large intestine and is connected to the anus by the sigmoid colon. The rectum stores fecal matter temporarily before it is eliminated from the body through the anal canal.
H. Ureteral opening: The ureteral opening allows urine to be discharged from the urinary bladder. In females, the ureteral opening is situated just in front of the vaginal opening.
I. Trigone: The trigone is a triangular-shaped area on the interior of the bladder. The function of the trigone is to send urine into the urethra when the urinary bladder contracts.
J. Urethra: The urethra is a duct that transmits urine from the bladder to the exterior of the body during the process of urination and is kept closed by the urethral sphincter muscle. In females, the urethra transports urine outside the body, prevents urine reflux, and protects against pathogenic bacteria.
K. Penis: The penis is the male sex organ and allows urine to leave the body through the urethral opening located at the tip of the penis.
L. Prostate gland: The prostate gland is a walnut-shaped gland located in front of the rectum and below the bladder. The prostate gland has a urethra running through the centre which helps to regulate the flow of urine and discharge it outside.
M. Urinary bladder: The urinary bladder is a hollow, muscular, and distensible organ found on the pelvic floor. The urine travels from the kidneys through the ureter into the bladder where it is temporarily stored.
N. Pelvis: The pelvis is a ring-shaped structure of bones located in the lower abdomen. The main function of the pelvis is to provide protection to the intestines, bladder, and rectum.
O. Inferior vena cava: The walls of the inferior vena cava are rigid and have valves to prevent the downward flow of blood due to gravity. The main function of the inferior vena cava is to carry the deoxygenated blood from the pelvis and the lower abdomen to the right atrium of the heart.
P. Hilum: The renal hilum is the point at which renal arteries carrying oxygenated blood and renal veins carrying deoxygenated blood enter and exit the kidney.
Q. Renal vein: The renal vein enters the kidney at a point called the hilum. The renal vein carries deoxygenated blood from the kidneys to the heart through the inferior vena cava.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Professions
- how is mental health nursing independent from general nursing?arrow_forwardThe importance of monitoring resident's wound healing (bed sores, cuts, and scrapes, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of seeing how it is to work as a chief in a nursing home and how they accommodate for special diets (low sodium, low sugar, heart healthy, etc.) and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of dealing with work confrontation (different healthcare departments fighting; diet aide and CNA) as a manager of a kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardQuestion 1: You are the Community Dietitian for the local public health agency. Recent news coverage has highlighted the state of food insecurity and child hunger in your county. Initial reports indicate that 15% of the population is food insecure. Of this group, 28.4% are children. It is estimated that 86% of the food insecure population is eligible for federal nutrition assistance. You are asked to conduct a community needs assessment and, ultimately, develop an appropriate intervention aimed at reducing hunger. First, however, you must submit a plan for the needs assessment. Complete the following: 1. State the nutritional problem (10 pts) 2. Set the parameters of the assessment (20 pts, 5 pts per bullet) A. State the purpose of the assessment B. Identify the community and target population for this assessment C. Develop 2 goals and 2 SMART objectives for each goal D. Discuss the major categories of community data and target population data E. Specify the types of data you might…arrow_forwardAssignment Instructions: Nursing Research Essay Objective: Select a specific area of nursing that captivates your interest. Compose a comprehensive essay, ranging from 300 to 500 words, that delves into the intricacies of nursing research within your chosen area. It is recommended that you consider the topic carefully as this topic, should be the topic for your course research project: see week 4 assignments. Your essay should elucidate the following points: The Significance of Nursing Research: Explore how nursing research in your selected area contributes to advancements in applied medicine. Discuss the potential achievements and innovations that can arise from dedicated nursing research in this field. Articulate the value and impact of such research on patient care, healthcare practices, and overall medical knowledge. Research Methods and Approaches: Identify the most effective methods for conducting nursing research in your chosen area. Highlight specific topics or research…arrow_forward
- The importance of understanding low meal consumption of residents in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of accommodating special diets (diabetic, low sodium, etc.) in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardThe importance of making a weekly clean list for kitchen staff in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of keeping a clean food pantry in a nursing home and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardI’m finding it a bit difficult to understand the Arrhenius equation and how shelf life relates to pH and temperature. Also in the question that says ‘this solution maintains 80% potency at 30C’, am I correct in thinking the formula would be:t = ln(0.8)/ -karrow_forward4.24 mmmarrow_forward
 Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC.
Phlebotomy EssentialsNursingISBN:9781451194524Author:Ruth McCall, Cathee M. Tankersley MT(ASCP)Publisher:JONES+BARTLETT PUBLISHERS, INC. Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders
Gould's Pathophysiology for the Health Profession...NursingISBN:9780323414425Author:Robert J Hubert BSPublisher:Saunders Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer,
Fundamentals Of NursingNursingISBN:9781496362179Author:Taylor, Carol (carol R.), LYNN, Pamela (pamela Barbara), Bartlett, Jennifer L.Publisher:Wolters Kluwer, Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science
Fundamentals of Nursing, 9eNursingISBN:9780323327404Author:Patricia A. Potter RN MSN PhD FAAN, Anne Griffin Perry RN EdD FAAN, Patricia Stockert RN BSN MS PhD, Amy Hall RN BSN MS PhD CNEPublisher:Elsevier Science Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders
Study Guide for Gould's Pathophysiology for the H...NursingISBN:9780323414142Author:Hubert BS, Robert J; VanMeter PhD, Karin C.Publisher:Saunders Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Issues and Ethics in the Helping Professions (Min...NursingISBN:9781337406291Author:Gerald Corey, Marianne Schneider Corey, Cindy CoreyPublisher:Cengage Learning





