
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
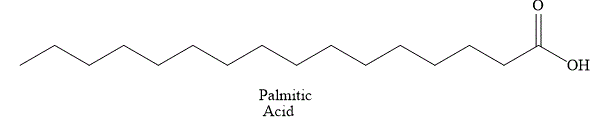
Figure 1
The general name of the above fatty acid is palmitic acid. Palmitic acid has a long aliphatic chain of
The fatty acid shown in Figure 1 is a saturated fatty acid and it is solid at room temperature.
(b)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid

Figure 2
The general name of the above fatty acid is lenoleic acid. The structural formula of lenoleic acid shows that there are two double bonds in the carbon chain. Therefore, lenoleic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. The side chain in unsaturated fatty acids possess less van der Waal’s interactions between side chains of adjacent molecule. Therefore, the unsaturated fatty acid is a liquid at room temperature.
The fatty acid shown in Figure 2 is an unsaturated fatty acid and it is a liquid at room temperature.
(c)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
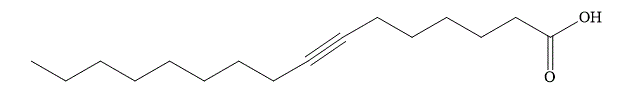
Figure 3
The general name of the above fatty acid is palmitolic acid. The structural formula of palmitolic acid contains double bonds within the fatty acid chain. Therefore, palmitolic acid is an unsaturated fatty acid. The side chain in unsaturated fatty acids possess less van der Waal’s interactions between side chains of adjacent molecule. Therefore, the unsaturated fatty acid is a liquid at room temperature.
The fatty acid shown in Figure 3 is an unsaturated fatty acid and it is a liquid at room temperature.
(d)
Interpretation:
Whether the fatty acid
Concept introduction:
A fatty acid having a long aliphatic chain with no double bond is called saturated fatty acid and a fatty acid that contains at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain is called unsaturated fatty acid. Due to the presence of a long alkyl side chain in saturated fatty acids, their packing efficiency is more than those of unsaturated fatty acids. As a result, unsaturated fatty acids possess lower melting point than saturated fatty acids. Thus, most of the saturated fatty acids are solid at room temperature.
Answer to Problem 18.9E
The fatty acid
Explanation of Solution
The structural formula of fatty acid
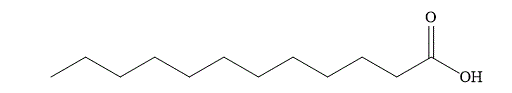
Figure 4
The general name of the above fatty acid is lauric acid. Lauric acid has a long aliphatic chain of
The fatty acid shown in Figure 4 is a saturated fatty acid and it is a solid at room temperature.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Study Guide with Student Solutions Manual for Seager/Slabaugh/Hansen's Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Biochemistry, 9th Edition
- The temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forwardQUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forward
- er your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward5.arrow_forward6.arrow_forward
 Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Organic And Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305081079Author:STOKER, H. Stephen (howard Stephen)Publisher:Cengage Learning, General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





