
(HugeInt Class) A machine with 32-bit integers can represent integers in the range of approximately –2 billion to +2 billion. This fixed-size restriction is rarely troublesome, but there are applications in which we would like to be able to use a much wider range of integers. This is what C++ was built to do, namely, create powerful new data types. Consider class HugeInt of Figs. 18.17–18.19. Study the class carefully, then answer the following:
- Describe precisely how it operates.
- What restrictions does the class have?
- Overload the * multiplication operator.
- Overload the / division operator.
- Overload all the relational and equality operators.
[Note: We do not show an assignment operator or copy constructor for class HugeInt because the assignment operator and copy constructor provided by the compiler are capable of copying the entire array data member properly.]
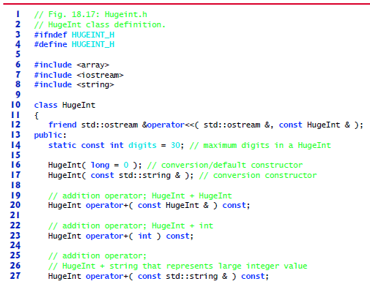
Fig. 18.17 HugeInt class definition.
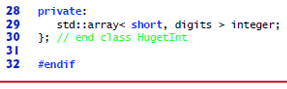

Fig. 18.18 HugeInt member-function and friend-function definitions.
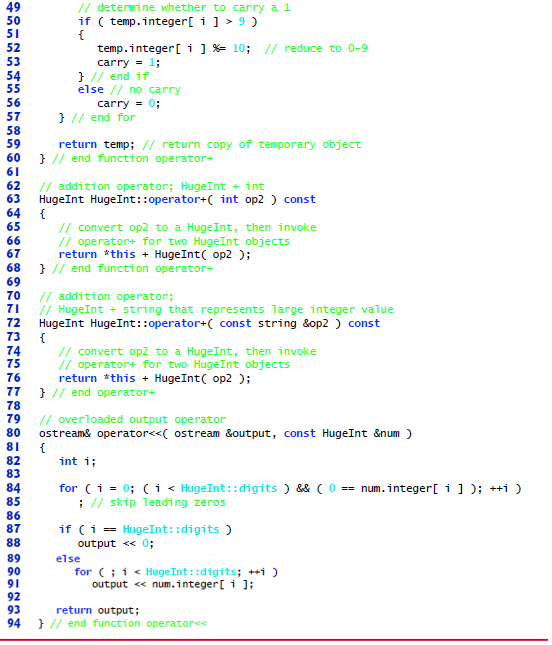
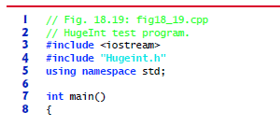
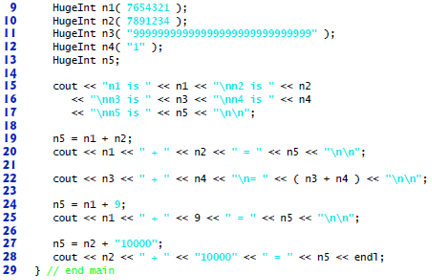
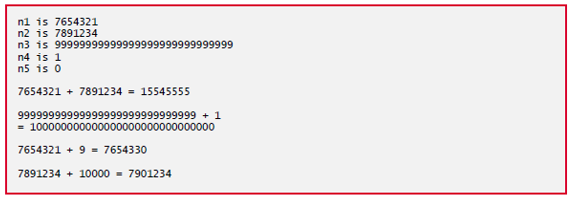
Fig. 18.19 HugInt test program.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
C How To Program Plus Mylab Programming With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (8th Edition)
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr

