
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A steroid is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipid.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
A steroid is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The basic structure of steroid is composed of three six-member ring and one five-member ring. The steroid ring system is shown below.
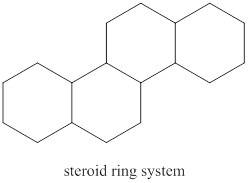
Figure 1
The basic structure of steroid does not have any ester group. Therefore, a steroid is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
A steroid is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
(b)
Interpretation:
Wax is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipid.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
Wax is a saponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The wax is an ester of long-chain alcohol and a fatty acid. The structure of a simple wax that is beeswax is shown below.
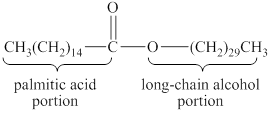
Figure 2
The basic structure of wax has an ester group. Therefore, wax is a saponifiable lipid.
Wax is a saponifiable lipid.
(c)
Interpretation:
A triglyceride is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipid.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
A triglyceride is a saponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The triglyceride is formed from glycerol and three fatty acids with ester bonds. The general structure of triglyceride is shown below.
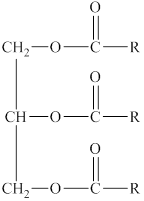
Figure 3
The basic structure of triglyceride has ester groups. Therefore, a triglyceride is a saponifiable lipid.
A triglyceride is a saponifiable lipid.
(d)
Interpretation:
A phosphoglyceride is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipids.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
A phosphoglyceride is a saponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The structure of phosphoglyceride is similar to that of a triglyceride. The only difference between triglyceride and phosphoglyceride is that on the third carbon of glycerol, a phosphate group is attached in the phosphoglyceride. The general structure of phosphoglyceride is shown below.
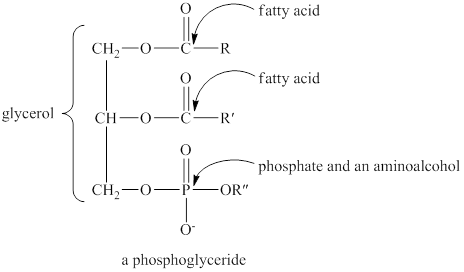
Figure 4
The basic structure of phosphoglyceride has ester groups. Therefore, a phosphoglyceride is a saponifiable lipid.
A phosphoglyceride is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
(e)
Interpretation:
A glycolipid is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipid.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
A glycolipid is a saponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The glycolipid contains carbohydrate in it. The glycolipids are also termed as cerebroside as they are present in the brain. The typical structure of glycolipid (cerebroside) is shown below.
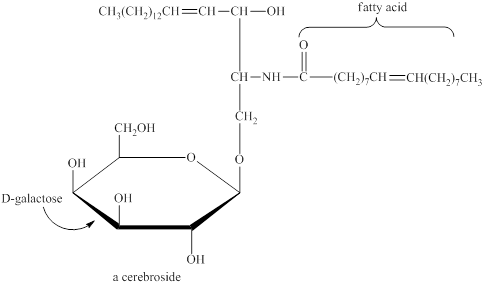
Figure 5
The basic structure of glycolipid does not have an ester group but they have an amide group that can undergo saponification. Therefore, a glycolipid is a saponifiable lipid.
A glycolipid is a saponifiable lipid.
(f)
Interpretation:
A prostaglandin is to be classified as saponifiable or nonsaponifiable lipid.
Concept introduction:
Lipids are one of those macromolecular substances that are present in the living cell. The cell membrane of the living cell is made up of lipids. The lipids have a greasy, waxy and oily texture. The lipids are insoluble in water. They include natural oils, waxes, and steroids.
Answer to Problem 18.4E
Prostaglandin is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
Explanation of Solution
A hydrolysis reaction carried out in a basic solution is known as saponification reaction. The term saponifiable lipids indicate the lipids that can undergo saponification reaction. The lipids that have ester group are saponifiable lipids. The basic structure prostaglandin is composed of a five-member ring with two substituted carbon chain. The structure of prostaglandin
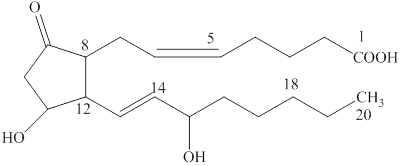
Figure 6
The basic structure of prostaglandin does not have an ester group. Therefore, a prostaglandin is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
Prostaglandin is a nonsaponifiable lipid.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Chemistry for Today: General Organic and Biochemistry
- 3. Reactions! Fill in the information missing below. Make sure to pay attention to REGIOCHEMISTRY and STEREOCHEMISTRY. Br2 CH3OH + 4. Mechanism! Show the complete arrow pushing mechanism, including all steps and intermediates for the following reactions. To get credit for this, you MUST show how ALL bonds are broken and formed, using arrows to show the movement of electrons. H3O+ HOarrow_forwardPlease provide a synthesis for the Ester using proponoic acid, thank you!arrow_forwardPlease help with the curved arrow mechanism of this reaction, thank youarrow_forward
- Concentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 Question: Determine the regression equation (a and b coefficients) from first principlesarrow_forwardConcentration (mg/l) Peak Area 0 158 10 10241 20 18425 30 26457 40 37125 50 44256 60 56124 You have been asked to determine the concentration of citral in a highly valued magnolia essential oil. QUESTION: Calculate the concentration of citral in your highly valued magnolia essential oil which returns a peak area of 41658arrow_forwardNeed help with these problems...if you can please help me understand problems E & F.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve these problems. Thank you in advance.arrow_forwardPredict the products of this organic reaction: O N IN A N + H2O + HCI ? Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of the product, or products, of this reaction. If there's more than one product, draw them in any arrangement you like, so long as they aren't touching. If there aren't any products because this reaction won't happen, check the No reaction box under the drawing area. 田 C + Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. C © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward6. For each of the following, fill in the synthesis arrows with reagents and show the intermediates. You DO NOT need to use the same number of arrows that are shown (you may use more or less), but the product must be formed from the reactant. Then write the mechanism of one step in the synthesis (you can choose which step to write the mechanism for), including all reagents required, clearly labeling the nucleophile and electrophile for each step, and using curved arrows to show the steps in the mechanism. a. b. OHarrow_forward
- Draw the productsarrow_forwardDraw the correct productsarrow_forwardE Organic Chemistry Maxwell Draw the correct products, in either order, for the ozonolysis reaction: 1) O3, CH2Cl2, -78 °C Product 1 + Product 2 2) Zn, HOAc Draw product 1. Select Draw Templates More C H O presented by M Draw product 2. Erase Select Draw Templates M / # # carrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div
World of ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780618562763Author:Steven S. ZumdahlPublisher:Houghton Mifflin College Div Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning





