
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
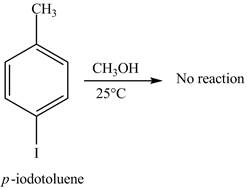
Figure 1
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(b)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as nucleophile. In nucleophilc acyl substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
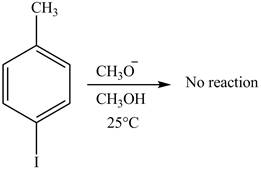
Figure 2
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(c)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as nucleophile. In nucleophilc acyl substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group.
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
No product is formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The product on reaction of
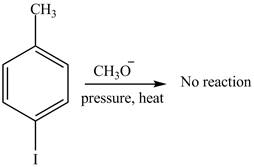
Figure 3
Aryl iodides cannot undergo nucleophilic substitution reaction. Aryl iodides neither undergo
There is no product formed on reaction of
(d)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Grignard reagents are
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
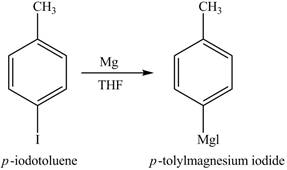
The product on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
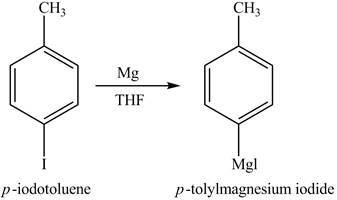
Figure 4
In the above reaction, magnesium gets inserted in the carbon-halogen bond to form a Grignard reagent. THF is used as the reaction should be done in anhydrous and inert condition. Therefore, the product formed on reaction of
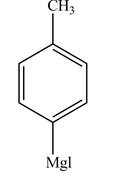
Figure 5
The reaction of
(e)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
Concept introduction:
Stille reaction is an example of coupling reaction. In Stille reaction, the triflate reacts with trimethylstannane in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
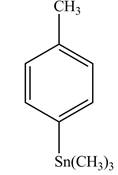
Explanation of Solution
The product formed in part (d) is shown below.
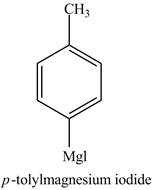
Figure 5
The reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
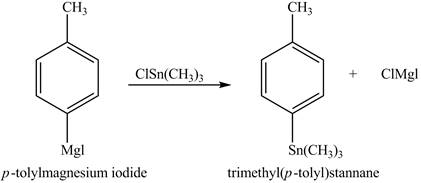
Figure 6
In the above reaction, a stannane compound is formed on reaction of a Grignard reagent with
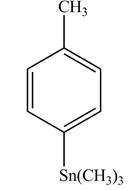
Figure 7
The product on reaction of the product formed in part (d) with
(f)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Alkyl lithium is an organolithium reagent. It contains carbon-lithium bond. It is used in
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
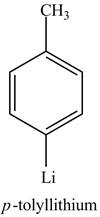
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
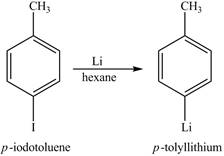
Figure 8
The above reaction is known as lithium-halogen exchange reaction. The reaction occurs under inert conditions. In this reaction, two moles of lithium react with
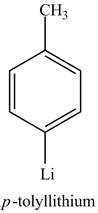
Figure 9
The product on reaction of
(g)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The treatment of an organic halide with an
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
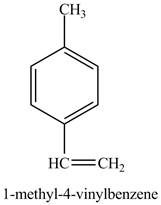
The reaction of
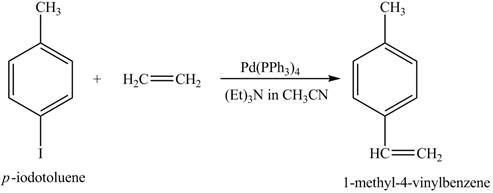
Figure 10
In the above reaction a coupled product is formed. The coupling takes place between ethene and
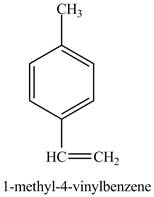
Figure 11
The product on reaction of
(h)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
Concept introduction:
Stille reaction is an example of coupling reaction. In Stille reaction, the triflate reacts with trimethylstannane in presence of
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
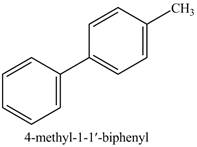
Explanation of Solution
The product formed in part (e) is shown below.
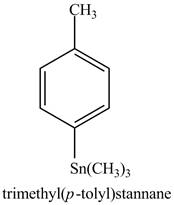
Figure 7
The reaction of above compound with phenyl triflate, excess
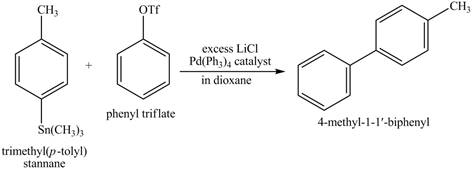
Figure 12
The above reaction is an example of Stille coupling reaction. In this reaction a triflate reacts with stannane compound in presence of
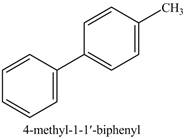
Figure 13
The product on reaction of product of part (e) with phenyl triflate, excess
(i)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction is a reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of
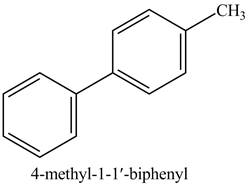
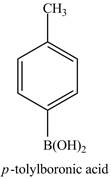
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
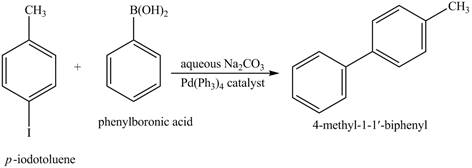
Figure 14
In the above reaction,
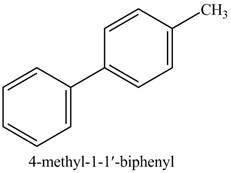
Figure 15
The product on reaction of
(j)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (d) with
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product of part (d) with
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (d) is shown below.
Figure 5
The reaction of product of part (d) with
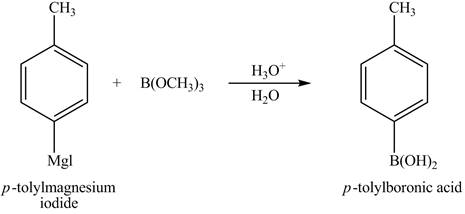
Figure 16
In the above reaction,
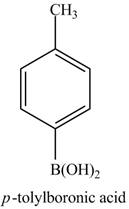
Figure 17
The product of part (d) with
(k)
Interpretation:
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
Concept introduction:
The Suzuki coupling reaction in which an aryl or vinylic boronic acid is coupled to an aryl or vinylic iodide or bromide. It is a
Answer to Problem 18.46AP
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
Explanation of Solution
The product of part (j) is shown below.
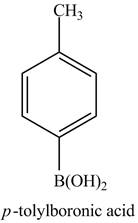
Figure 17
The reaction of product of part (j) with
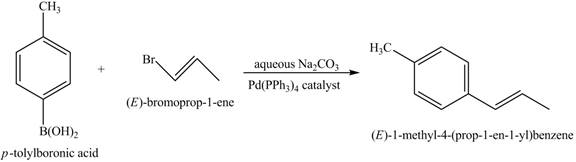
Figure 18
The above reaction is Suzuki coupling reaction. In this reaction,
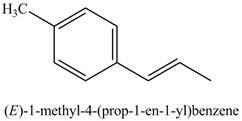
Figure 19
The product on reaction of product of part (j) with
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEM +SG +SAPLING >IP<
- Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use dash and wedge bonds to show stereochemistry where it's important. + ☑ OH 1. TsCl, py .... 文 P 2. t-BuO K Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ( Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : а ค 1arrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. 1. NaH 2. CH3Br ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. No reaction. : ☐ Narrow_forward
- + Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forwardConsider the following reactants: Br Would elimination take place at a significant rate between these reactants? Note for advanced students: by significant, we mean that the rate of elimination would be greater than the rate of competing substitution reactions. yes O no If you said elimination would take place, draw the major products in the upper drawing area. If you said elimination would take place, also draw the complete mechanism for one of the major products in the lower drawing area. If there is more than one major product, you may draw the mechanism that leads to any of them. Major Products:arrow_forward
- Draw one product of an elimination reaction between the molecules below. Note: There may be several correct answers. You only need to draw one of them. You do not need to draw any of the side products of the reaction. OH + ! : ☐ + Х Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardFind one pertinent analytical procedure for each of following questions relating to food safety analysis. Question 1: The presence of lead, mercury and cadmium in canned tuna Question 2: Correct use of food labellingarrow_forwardFormulate TWO key questions that are are specifically in relation to food safety. In addition to this, convert these questions into a requirement for chemical analysis.arrow_forward
- What are the retrosynthesis and forward synthesis of these reactions?arrow_forwardWhich of the given reactions would form meso product? H₂O, H2SO4 III m CH3 CH₂ONa CH3OH || H₂O, H2SO4 CH3 1. LiAlH4, THF 2. H₂O CH3 IVarrow_forwardWhat is the major product of the following reaction? O IV III HCI D = III ა IVarrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
