
FIFO method, shipping department (continuation of 18-36). Refer to the information in Problem 18-37 except that the transferred-in costs of beginning work in process on May 1 are $66,180 (instead of $67,397). Transferred-in costs for May equal the total cost of good units completed and transferred out in May from the prep department, as calculated in Problem 18-36 using the FIFO method of
Required
For the shipping department, use the FIFO method to summarize the total costs to account for and assign those costs to units completed and transferred out (including normal spoilage), to abnormal spoilage, and to units in ending work in process.
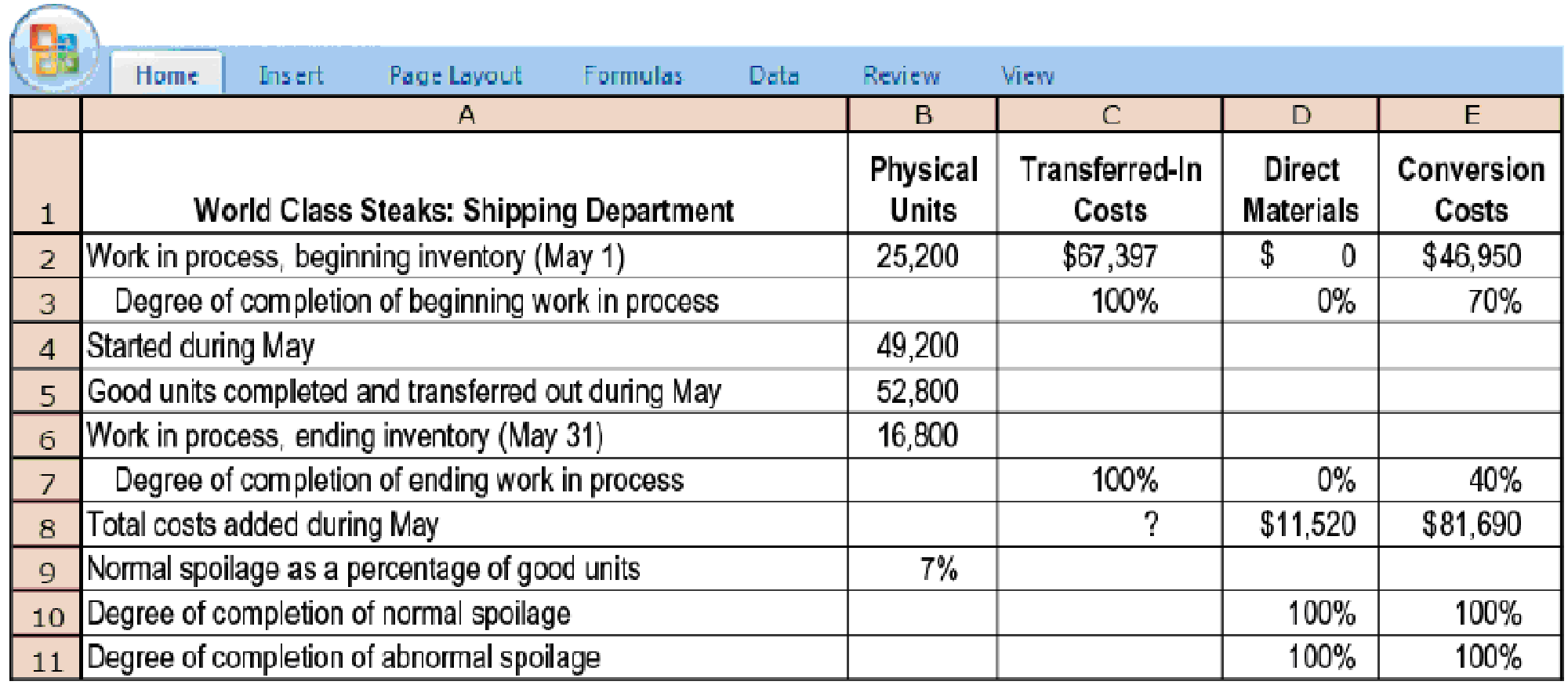
18-37 Weighted-average method, shipping department (continuation of 18-35). In the shipping department of World Class Steaks, conversion costs are added evenly during the process, and direct materials are added at the end of the process. Spoiled units are detected upon inspection at the end of the process and are disposed of at zero net disposal value. All completed work is transferred to the next department. The transferred-in costs for May equal the total cost of good units completed and transferred out in May from the prep department, which were calculated in Problem 18-35 using the weighted-average method of process costing. Summary data for May follow.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK HORNGREN'S COST ACCOUNTING
- What was the company's net operating income for the year on these financial accounting question?arrow_forwardThe fiscal 2010 financial statements for Neptune, Inc report revenues of $14,892,615, net operating profit after tax of $987,625, net operating assets of $6,124,587. The fiscal 2009 balance sheet reports net operating assets of $5,995,633. What is Neptune s 2010 net operating profit margin?arrow_forwardPlease help with accounting question is solvearrow_forward
 Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





