
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(a)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
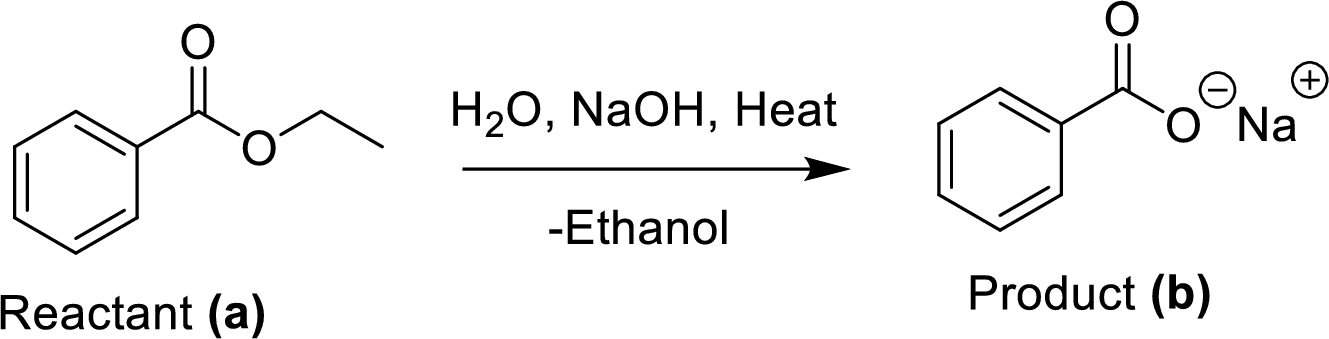
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with sodium hydroxide in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B). In this reaction addition and elimination process was occurred.
(b)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Ester Hydrolysis: Ester hydrolysis can be caused by acid and base.
Saponification: Ester hydrolysis taking place in presence of base such as
Acid-catalyzed hydrolysis: In presence of strong acid such as
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
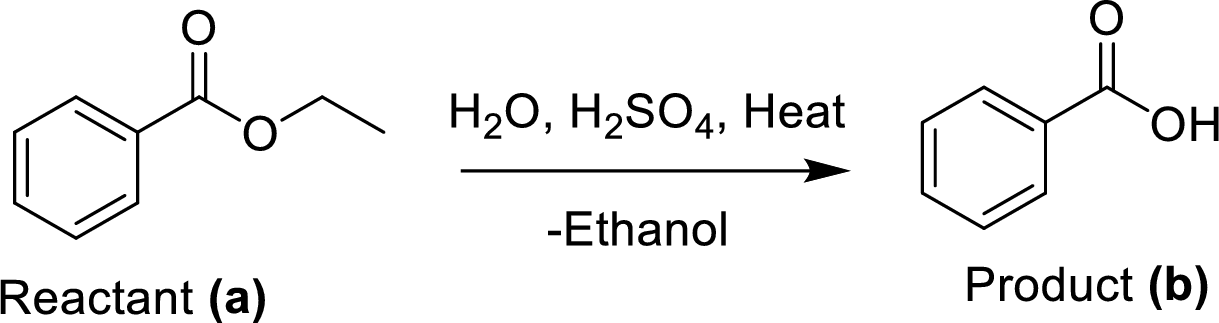
The ethyl benzoate (A) is undergoes for simple acid catalyzed hydrolysis, followed by heating to give a target compound (B), which is a benzoic acid.
(c)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Amide: One
Amide Formation: Amide is formed when a carboxylic acid reacts with an
- Primary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with ammonia.
- Secondary and tertiary amide is produce when a carboxylic acid reacts with primary and secondary amine respectively.
(c)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
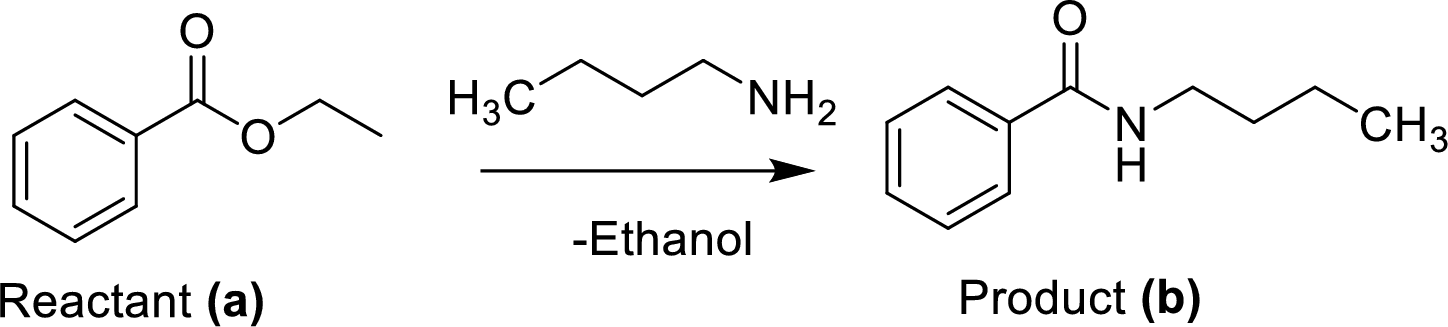
The ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with n-butylamine in presence of basic conditions which corresponding yields the product (B).
(d)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH): It is prepared by refluxing triisobutylaluminium in the solvent heptane.
DIBAL-H: is a strong reducing reagent most
DIBAL-H is a selective reagent (like,
(d)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
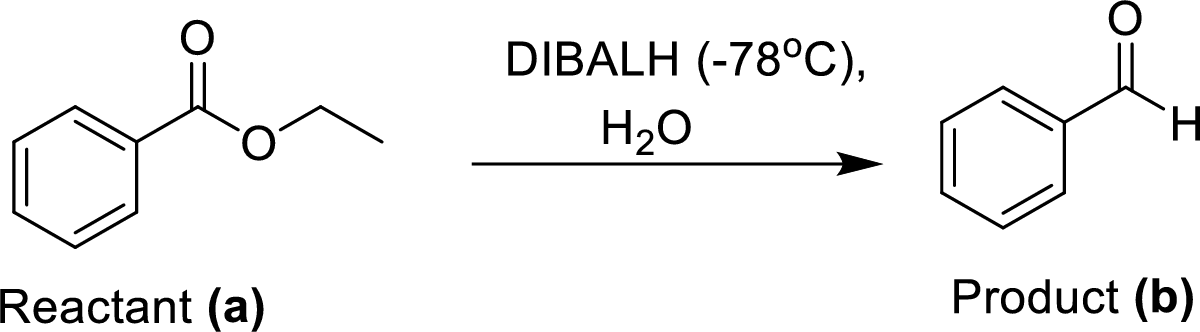
The equal amount of ethyl benzoate (A) is reacted with Diisobutylaluminium hydride (DIBALH) under dry ice conditions at
(e)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Reduction: Aldehydes or ketones undergoing reduction by using reducing agent like
LAH Reduction: The saturated/unsaturated aldehyde and ketones in the presence of sodium metal in LAH and carbonyl compound produced saturated alcohols. The keto group involves in the reduction process of LAH, this end up reducing to give the alcohols.
(e)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
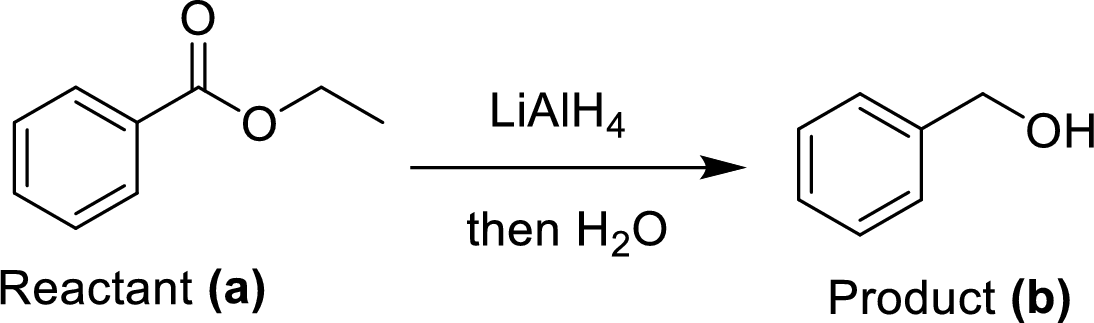
The ethyl benzoate (A) undergoes for LAH reduction process followed by simple hydrolysis workup method to give a target product (B). The obtained product namely benzyl alcohol.
(f)
Interpretation:
Product formed when ethyl benzoate reacts with the given reagent has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
Alkyl or aryl magnesium halides (
Synthesis of Grignard reagent is shown below,
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of
(f)
Explanation of Solution
The synthesis of product transformation is shown below.
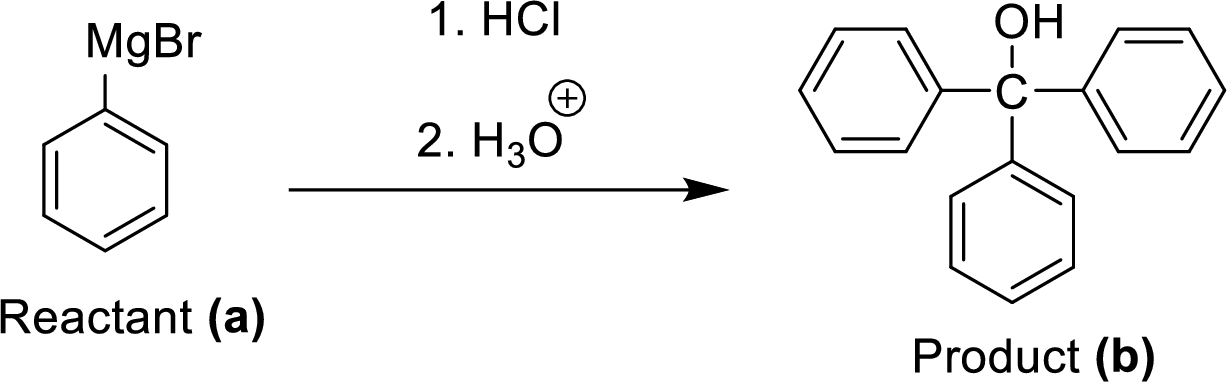
Two equivalents of Grignard reagent (A) is reacted with hydrogen chloride and fallowed by hydrolysis workup method, which corresponding yields the triphenyl methanol (B) it is a target molecule.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
BNDL: ACP ORGANIC CHEMISTRY:CH EM 231(W/ACCESS CARD)
- Add conditions above and below the arrow that turn the reactant below into the product below in a single transformationADS fint anditions 百 Abl res condinese NC ง Add on condtions 1.0 B H,N.arrow_forward3. Provide all the steps and reagents for this synthesis. OHarrow_forwardSteps and explanationarrow_forward
- Steps and explanations please.arrow_forwardSteps on how to solve. Thank you!arrow_forward3. Name this ether correctly. H₁C H3C CH3 CH3 4. Show the best way to make the ether in #3 by a Williamson Ether Synthesis. Start from an alcohol or phenol. 5. Draw the structure of an example of a sulfide.arrow_forward
- 1. Which one(s) of these can be oxidized with CrO3 ? (could be more than one) a) triphenylmethanol b) 2-pentanol c) Ethyl alcohol d) CH3 2. Write in all the product(s) of this reaction. Label them as "major" or "minor". 2-methyl-2-hexanol H2SO4, heatarrow_forward3) Determine if the pairs are constitutional isomers, enantiomers, diastereomers, or mesocompounds. (4 points)arrow_forwardIn the decomposition reaction in solution B → C, only species C absorbs UV radiation, but neither B nor the solvent absorbs. If we call At the absorbance measured at any time, A0 the absorbance at the beginning of the reaction, and A∞ the absorbance at the end of the reaction, which of the expressions is valid? We assume that Beer's law is fulfilled.arrow_forward
- > You are trying to decide if there is a single reagent you can add that will make the following synthesis possible without any other major side products: 1. ☑ CI 2. H3O+ O Draw the missing reagent X you think will make this synthesis work in the drawing area below. If there is no reagent that will make your desired product in good yield or without complications, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check ? DO 18 Ar B © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardConsider a solution of 0.00304 moles of 4-nitrobenzoic acid (pKa = 3.442) dissolved in 25 mL water and titrated with 0.0991 M NaOH. Calculate the pH at the equivalence pointarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

