
Concept explainers
As in Figure P18.16, a simple harmonic oscillator is attached to a rope of linear mass density 5.4 × 10−2 kg/m, creating a standing transverse wave. There is a 3.6-kg block hanging from the other end of the rope over a pulley. The oscillator has an angular frequency of 43.2 rad/s and an amplitude of 24.6 cm. a. What is the distance between adjacent nodes? b. If the angular frequency of the oscillator doubles, what happens to the distance between adjacent nodes? c. If the mass of the block is doubled instead, what happens to the distance between adjacent nodes? d. If the amplitude of the oscillator is doubled, what happens to the distance between adjacent nodes?
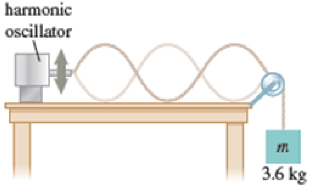
FIGURE P18.16
(a)
The distance between the adjacent nodes.
Answer to Problem 16PQ
The distance between the adjacent nodes is
Explanation of Solution
Given that the linear mass density of the rope is
Write the expression for the wavelength of the wave.
Here,
Write the expression for the speed of the wave.
Here,
Write the equation to find the frequency of the wave.
Here,
Use equation (III) and (II) in (I).
Write the expression for the tension force on the rope (it is equal to the weight of the block hanged).
Here,
Use above expression in equation (IV).
The distance between the adjacent nodes is equal to half the wavelength of the wave.
Rewrite above equation using equation (V).
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the distance between the adjacent nodes is
(b)
The distance between the adjacent nodes when the angular frequency is doubled.
Answer to Problem 16PQ
The distance between the adjacent nodes when the angular frequency is doubled is
Explanation of Solution
Equation (VI) gives the expression for the distance between the nodes.
From the above equation it is clear that wavelength is inversely proportional to angular frequency.
The angular frequency is doubled. Replace
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, distance between the adjacent nodes when the angular frequency is doubled is
(c)
The distance between the adjacent nodes if the mass of the block is doubled.
Answer to Problem 16PQ
The distance between the adjacent nodes if the mass of the block is doubled is
Explanation of Solution
Equation (VI) gives the expression for the distance between the nodes.
When the mass of the block is doubled,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the distance between the adjacent nodes if the mass of the block is doubled is
(d)
The distance between the nodes if the amplitude of the oscillator is doubled.
Answer to Problem 16PQ
The distance between the nodes remains the same even if the amplitude of the oscillator is doubled.
Explanation of Solution
Equation (VI) gives the expression for the distance between the nodes.
The above equation is independent of the amplitude term. Thus, even if the amplitude of the oscillator is doubled, the distance between the nodes do not change.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the distance between the nodes remains the same even if the amplitude of the oscillator is doubled.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EBK WEBASSIGN FOR KATZ'S PHYSICS FOR SC
- please help me solve this questions. show all calculations and a good graph too :)arrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 2.0 μC charge placed at the center of the square shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) 5.0 με 4.0 με 2.0 με + 1.0 m 1.0 m -40 με 2.0 μCarrow_forwardWhat is the force (in N) on the 5.4 µC charge shown below? (Express your answer in vector form.) −3.1 µC5.4 µC9.2 µC6.4 µCarrow_forward
- An ideal gas in a sealed container starts out at a pressure of 8900 N/m2 and a volume of 5.7 m3. If the gas expands to a volume of 6.3 m3 while the pressure is held constant (still at 8900 N/m2), how much work is done by the gas? Give your answer as the number of Joules.arrow_forwardThe outside temperature is 25 °C. A heat engine operates in the environment (Tc = 25 °C) at 50% efficiency. How hot does it need to get the high temperature up to in Celsius?arrow_forwardGas is compressed in a cylinder creating 31 Joules of work on the gas during the isothermal process. How much heat flows from the gas into the cylinder in Joules?arrow_forward
- The heat engine gives 1100 Joules of energy of high temperature from the burning gasoline by exhausting 750 Joules to low-temperature . What is the efficiency of this heat engine in a percentage?arrow_forwardL₁ D₁ L₂ D2 Aluminum has a resistivity of p = 2.65 × 10 8 2. m. An aluminum wire is L = 2.00 m long and has a circular cross section that is not constant. The diameter of the wire is D₁ = 0.17 mm for a length of L₁ = 0.500 m and a diameter of D2 = 0.24 mm for the rest of the length. a) What is the resistance of this wire? R = Hint A potential difference of AV = 1.40 V is applied across the wire. b) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thin part of the wire? Hint J1 = c) What is the magnitude of the current density in the thick part of the wire? J₂ = d) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thin part of the wire? E1 = Hint e) What is the magnitude of the electric field in the thick part of the wire? E2 =arrow_forwardplease helparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





