
Concept explainers
Interpretation: The total project completion time is to be calculated along with the lowest cost solution if the project is to be completed
Concept Introduction:
Project
Explanation of Solution
The activity with their immediate predecessor and estimated time, crash time, crash cost and normal cost is tabulated below.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Estimated Normal Time | Crash Time | Normal Cost | Crash Cost |
| A | - | ||||
| B | A | ||||
| C | A | ||||
| D | - | ||||
| E | B, D, C | ||||
| F | D | ||||
| G | D | ||||
| H | E | ||||
| I | F, G, H |
Table (1)
The network diagram for the activity shown in table (1) is shown below.
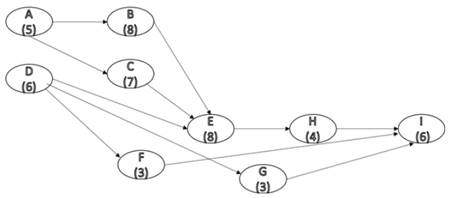
Figure (1)
Therefore, the network diagram of the given project is shown in Figure (1).
The expression for the cost slope is given by,
The cost slope for each activity is tabulated below.
| Activity | Immediate Predecessor | Estimated Normal Time | Crash Time | Normal Cost | Crash Cost | Cost Slope |
| A | - | |||||
| B | A | |||||
| C | A | |||||
| D | - | |||||
| E | B, D, C | |||||
| F | D | |||||
| G | D | |||||
| H | E | |||||
| I | F, G, H |
Table (2)
Consider figure (1), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (3)
From Table (3), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path is
Now the project is to be completed
Consider the critical path activities.
The lowest crash cost per week is of activity B and activity H.
Crash Activity B by
And,
Thus, the additional cost of crashing the activity by
The new network diagram is shown in figure below.
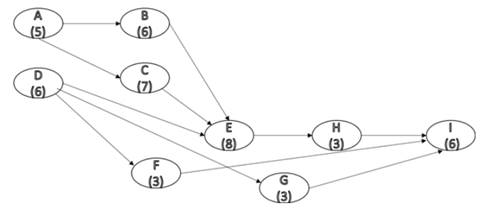
Figure (2)
Consider figure (2), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (4)
From Table (4), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path is
But the desired project duration is
Try different option.
Crash Activity B by
And,
And,
Thus, the additional cost of crashing the activity by
The new network diagram is shown in figure below.
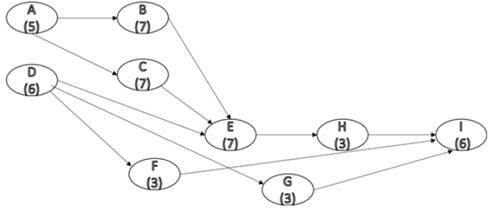
Figure (3)
Consider figure (3), the different paths and their completion times is tabulated below.
| Path | Completion time (weeks) |
Table (4)
From Table (4), the maximum completion time is taken by path
Therefore, the critical path are
Therefore, the crashing cost of the project is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Hyundai Motors is considering three sites-A, B, and C-at which to locate a factory to build its new electric car batteries. The goal is to locate at a minimum-cost site, where cost is measured by the annual fixed plus variable costs of production. Hyundai Motors has gathered the following data: Site Annualized Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Battery Produced A $11,000,000 $2,600 B C $2,000 $1,100 $20,000,000 $25,000,000 The firm knows it will produce between 0 and 60,000 batteries at the new plant each year, but, thus far, that is the extent of its knowledge about production plans. a) The value of volume, V, of production above which site C is recommended = batteries (round your response up to the next whole number).arrow_forwardHyundai Motors is considering three sites-A, B, and C-at which to locate a factory to build its new electric car batteries. The goal is to locate at a minimum-cost site, where cost is measured by the annual fixed plus variable costs of production. Hyundai Motors has gathered the following data: Site Annualized Fixed Cost Variable Cost per Battery Produced A $11,000,000 $2,500 B C $2,100 $1,050 $20,000,000 $25,000,000 The firm knows it will produce between 0 and 60,000 batteries at the new plant each year, but, thus far, that is the extent of its knowledge about production plans. a) The value of volume, V, of production above which site C is recommended = batteries (round your response up to the next whole number).arrow_forwardThe importance of keeping track of invoices and budgeting in a nursing home kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forward
- The importance of interviewing potential food service aides and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwardWhat role does job analysis and job evaluation play in the compensation decision? Give an example of an organization NO AIarrow_forwardI did the first half correct! Please help me with the second half, not quite sure of the naive approach. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
- Because my tutor and I didnt get it rightarrow_forwardOperations Managementarrow_forwardHow does wellness reflect and impact the past and the future of our health as a workout routine? What are the obstacles during the workout routine, and how do you overcome the obstacles? What are the best solutions to plan and accomplish the wellness?arrow_forward
- My last question! Thank you all for helping me better understand how OM works. If you can assist me for this one I'd be very thankful. Can you explain it step by step?I know now that LS is late start, and ES is early start. - •Activities on the critical path are? •The total project completion time for Rafay Ishfaq's software firm is how many weeks?•Determine the slack time for each of the activities for A-F •What is the total slack for the non critical paths in Rafays project?arrow_forwardThank you so much! I was able to answer C without help! Can you assist me with slack time for A-F? I believe A=0arrow_forwardThere's 8 parts, but I need some help with them. I always get confused on which is most critical of a patharrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage, Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning



