
a.
Compute the number of sheets started by the Pressing Department in June.
a.
Explanation of Solution
It is a method of cost accounting used by an enterprise with processes categorised by continuous production. The cost for manufacturing those products are assigned to the manufacturing department before the averaged over units are being produced.
Compute the number of sheets started by the Pressing Department in June.
| Particulars | Units |
| Units transferred to the Painting Department in June | 1,500 |
| Add: Ending inventory in Pressing Department, June 30 | 500 |
| Total units in process during June | 2,000 |
| Less: Beginning inventory in Pressing Department, June 1 | (300) |
| Units started by Pressing Department in June | 1,700 |
(Table 1)
Therefore, the number of sheets started by the Pressing Department in June is 1,700 units.
b.
Compute the number of units started and completed by the Pressing Department in June.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the number of units started and completed by the Pressing Department in June.
| Particulars | Units |
| Units transferred to the Painting Department in June | 1,500 |
| Units in beginning inventory in Pressing Department, June 1 | (300) |
| Units started and completed by Pressing Department in June | 1,200 |
(Table 2)
Therefore, the units started and completed by the pressing department during the month June is 1,200 units respectively.
c.
Compute the equivalent units of input resources for the Pressing Department in June.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the equivalent units of input resources for the Pressing Department in June.
| Particulars | Input Resources | |
| Direct Materials | Conversion | |
| To finish beginning inventory in process on June1: | ||
| Direct materials (300 units require 0% to complete) | 0 | |
| Conversion (300 units require 80% to complete) | 240 | |
| To start and complete 1,200 units in June | 1,200 | 1,200 |
| To start ending inventory in process on June 31: | ||
| Direct materials (500 units 100% complete) | 500 | |
| Conversion (500 units 40% complete) | 200 | |
| Equivalent units of resources in June | 1,700 | 1,640 |
(Table 3)
Therefore, the equivalent units of input resources for the Pressing Department in June are 1,700 and 1,640 units respectively
d.
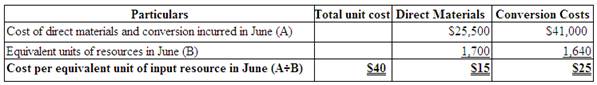
Compute the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Pressing Department in June.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Cutting Department in June.
(Figure 1)
Therefore, the cost per equivalent unit of input resource for the Pressing Department for the month of June is $15 and $25 per unit respectively.
e.
Prepare
e.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare journal entry to transfer pressed sheets from the Pressing Department to the Painting Department in June.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
|
Work in process: Pressing Department (3) | 60,000 | ||
| Work in process: Painting Department | 60,000 | ||
| (To record the transfer of 1,500 units to the painting department in June ) |
(Table 4)
- Work in process: Pressing department is an asset and there is an increase in the value of an asset. Hence, debit the work in process: pressing department by $60,000.
- Work in process: Painting department is an asset and there is a decrease in the value of an asset. Hence, credit the work in process: painting department by $60,000.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month June:
(1)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month June:
(2)
Calculate the total cost of units transferred:
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Cost of beginning inventory, June1 | 6,000 |
| June direct materials cost (1) | 18,000 |
| June conversion cost (2) | 36,000 |
| Total cost of units transferred in June | 60,000 |
(Table 5)
(3)
f.
Calculate the total cost assigned to the Pressing Department’s ending inventory on June 30.
f.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the total cost assigned to the Pressing Department’s ending inventory on June 30.
| Particulars | Amount in $ |
| Work in Process: Cutting department, May 31: | |
| Direct materials cost (4) | 7,500 |
| Conversion cost (5) | 5,000 |
| Ending inventory in process, May 31 | 12,500 |
(Table 6)
Therefore, the total cost assigned to the Pressing Department’s ending inventory on June 30 is $12,500.
Working Notes:
Calculate the cost of direct materials during the month end of June 30 for pressing department:
(4)
Calculate the cost of conversion during the month end of June 30 for pressing department:
(5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
Connect Online Access for Financial Accounting
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardSunview Components Ltd. estimated its manufacturing overhead costs for 2024 to be $520,000, based on 130,000 estimated direct labor hours. The actual direct labor hours for 2024 were 138,000. The manufacturing overhead account contains debit entries totaling $532,000. Determine whether the manufacturing overhead for 2024 was overallocated or underallocated. (Round your immediate calculations to one decimal place.)arrow_forwardA company produces a single product. Variable production costs are $18.2 per unit, and variable selling and administrative expenses are $6.5 per unit. Fixed manufacturing overhead totals $72,000, and fixed selling and administration expenses total $63,000. Assuming a beginning inventory of zero, production of 7,500 units, and sales of 5,200 units, the dollar value of the ending inventory under variable costing would be_.arrow_forward
- If Malek Events catering has 880 hours scheduled for next month, what is the expected total overhead cost for next month?arrow_forwardI need help with this problem and accounting questionarrow_forwardKindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forward
- I am looking for help with this general accounting question using proper accounting standards.arrow_forwardDetermine the depreciation for the montharrow_forwardJohnson Jewelry uses the perpetual inventory system. On May 12, Johnson sold merchandise for $95,000 to a customer on account with terms 2/10, n/30. The cost of goods sold (COGS) was $37,000. On May 20, Johnson received payment from the customer. Calculate the amount of gross profit.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





