
(a)
Interpretation:
A
Concept introduction:
Radioactive decay is the process that involves the emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus. The atomic nucleus loses its energy. The process is spontaneous. It is also known as nuclear radiation. The decay is accompanied by the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays and so on. All the elements which have an
Answer to Problem 11ST
Alpha emission of
Explanation of Solution
Alpha particle emission releases one alpha particle whose mass number decreases by
![]()
Figure 1
Radioactive alpha decay of
(b)
Interpretation:
A nuclear equation for the decay of
Concept introduction:
Radioactive decay is the process that involves the emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus. The atomic nucleus loses its energy. The process is spontaneous. It is also known as nuclear radiation. The decay is accompanied by the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays and so on. All the elements which have an atomic number greater than
Answer to Problem 11ST
Beta emission of
Explanation of Solution
Beta emission decays into a proton and releases an electron or the atomic number increases by
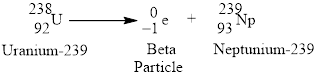
Figure 2
Radioactive beta decay of
(c)
Interpretation:
A nuclear equation for the decay of
Concept introduction:
Radioactive decay is the process that involves the emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus. The atomic nucleus loses its energy. The process is spontaneous. It is also known as nuclear radiation. The decay is accompanied by the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays and so on. All the elements which have an atomic number greater than
Answer to Problem 11ST
Positron emission of
Explanation of Solution
In positron emission, an electron is released and its charge is
![]()
Figure 3
Radioactive positron electron emission of
(d)
Interpretation:
A nuclear equation for the decay of
Concept introduction:
Radioactive decay is the process that involves the emission of radiation by an unstable atomic nucleus. The atomic nucleus loses its energy. The process is spontaneous. It is also known as nuclear radiation. The decay is accompanied by the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays and so on. All the elements which have an atomic number greater than
Answer to Problem 11ST
Electron capture of
Explanation of Solution
In electron capture decay, element accepts electron and results in atomic number decreased by 1 and mass number remains same. The electron capture of
![]()
Figure 4
Radioactive alpha decay of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 18 Solutions
EP INTRODUCTORY CHEM.-MOD.MASTERINGCHEM
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co





