
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
First step is the formation of more stable carbocation which is followed by the attack of nucleophile. Formation of more stable carbocation and the leaving group present in the substrate plays very important role in the reactivity of
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
(b)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
(c)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Structure of the substrate plays major role in the reactivity of
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
(d)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
First step is the formation of more stable carbocation which is followed by the attack of nucleophile. Formation of more stable carbocation and the leaving group present in the substrate plays very important role in the reactivity of
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
(e)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Ozonolysis:
Alkene reacts with ozone which cleaves the double bond followed by work up with dimethyl sulfide forms
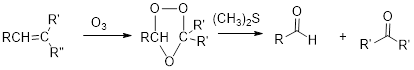
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Elimination reaction of an alkyl halide results in the formation of an alkene.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
(f)
Interpretation: Efficient synthesis for the given transformation has to be proposed.
Concept Introduction:
Ozonolysis:
Alkene reacts with ozone which cleaves the double bond followed by work up with dimethyl sulfide forms ketone.
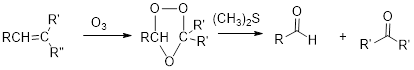
Elimination Reaction: It is just reverse reaction of addition where substituent from the given molecule is removed.
E2 mechanism depends on both base and substituents in the reaction.
Bromination: In bromination reaction, hydrogen atom of a molecule is replaced by a bromine atom.
In a reaction,
The Grignard reaction:
Alkyl, vinyl, or aryl-magnesium halides (
Grignard reagent is reaction with carbonyl compound such as
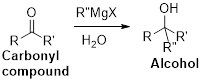
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL) >CUSTOM PACKAGE<
- Use the data below from an electron impact mass spectrum of a pure compound to deduce its structure. Draw your structure in the drawing window. Data selected from the NIST WebBook, https://webbook.nist.gov/chemistry/ m/z Relative intensity 59 3.0 58 64 43 100 15 23 • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. •You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. • In cases where there is more than one answer, just draw one. + n[] 85 // ? CH4 Previous Nextarrow_forwardWrite the molecular formula for a compound with the possible elements C, H, N and O that exhibits a molecular ion at M* = 128.0632. Exact Masses of the Most Abundant Isotope of Selected Elements Isotope Natural abundance (%) Exact mass 1H 99.985 12C 98.90 14N 99.63 160 99.76 Molecular formula 1.008 12.000 14.003 15.995 (In the order CHNO, with no subscripts)arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this? And can I please the lowest possible significant number?arrow_forward
- What is the molar mass of a gas that takes three times longer to effuse than helium?arrow_forwardFirst image: I have to show the mecanism (with arows and structures) of the reaction at the bottom. Also I have to show by mecanism why the reaction wouldn't work if the alcohol was primary Second image: I have to show the mecanism (with arrows and structures) for the reaction on the left, where the alcohol A is added fast in one portion its not an examarrow_forwardwhat is the skeletal structure of a tertiary alkyl fluoride with six carbon atoms and no rings.arrow_forward
- One step of glycolysis is a retro-aldol reaction (aldolase) to produce ATP.Below is the aldol reaction of the equilibrium. Show the mechanism for the base catalyzed reaction. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardWhy does the following reaction lead to poor yields? Correct the reaction. *see imagearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





