
Concept explainers
Solve Prob. 17.11, assuming that the 6 N·m couple is applied to gear B.
17.11 Each of the gears A and B has a mass of 10 kg and a radius of gyration of 190 mm, while gear C has a mass of 2.5 kg and a radius of gyration of 80 mm. If a couple M of constant magnitude 6 N·m is applied to gear C, determine (a) the number of revolutions of gear C required for its angular velocity to increase from 450 rpm to 1800 rpm, (b) the corresponding tangential force acting on gear A.
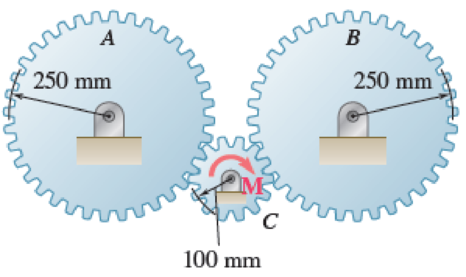
Fig. P17.11
(a)
Find the number of revolutions required for gear C.
Answer to Problem 17.12P
The number of revolutions required for the gear C for the work to be done is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the gear A is
The mass of the gear B is
The radius of gyration of the gear A is
The radius of gyration of the gear B is
The mass of the gear C is
The radius of gyration of the gear C is
The radius of the gear A is
The radius of the gear B is
The radius of the gear C is
The magnitude of the couple moment applied at point B is
Calculation:
Find the mass moment of inertia of gear A
Substitute 10 kg for
Find the mass moment of inertia of gear B
Substitute 10 kg for
Find the mass moment of inertia of gear C
Substitute 2.5 kg for
The gears A and C are in contact.
Use the kinematics concept;
Substitute 250 mm for
The gears B and C are in contact.
Use the kinematics Equation:
Substitute 250 mm for
Find the total kinetic energy
Substitute
When the angular velocity is at 450 rpm:
Substitute 450 rpm for
When the angular velocity is at 1800 rpm:
Substitute 1800 rpm for
Find the work done
Here, the number of revolution at gear B is
Substitute
Write the equation of work and energy for the system using the equation.
Substitute 146.03 J for
Find the number of revolution at gear C
Substitute 58.1 rev for
Therefore, the number of revolutions required for the gear C for the work to be done is
(b)
Find the tangential force acting on gear A.
Answer to Problem 17.12P
The tangential force acting on gear A is
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The mass of the gear A is
The mass of the gear B is
The radius of gyration of the gear A is
The radius of gyration of the gear B is
The mass of the gear C is
The radius of gyration of the gear C is
The radius of the gear A is
The radius of the gear B is
The radius of the gear C is
The magnitude of the couple moment is
Calculation:
Refer to part (a) calculation;
The number of revolution in the gear A is equal to the number of revolution in the gear B.
Substitute 365.08 rad for
Find the total kinetic energy
When the angular velocity is at 450 rpm;
Substitute
When the angular velocity is at 1800 rpm;
Substitute
Find the work done
Here, the magnitude of couple moment at gear A is
Substitute 365.08 rad for
Write the equation of work and energy for the system using the equation.
Substitute 64.133 J for
Find the tangential force
Substitute
Therefore, the tangential force acting on gear A is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Vector Mechanics for Engineers: Statics and Dynamics
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Database Concepts (8th Edition)
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
- 2. Determine the average normal stress developed in rod AB. The mass is 50kg and the diameter of the rod AB is 8mm. B 8 mmarrow_forward2.64 A 2.75-kN tensile load is applied to a test coupon made from 1.6-mm flat steel plate (E = 200 GPa, v = 0.30). Determine the resulting change in (a) the 50-mm gage length, (b) the width of portion AB of the test coupon, (c) the thickness of portion AB, (d) the cross-sectional area of portion AB. 2.75 kN A 12 mm 50 mm B 2.75 kNarrow_forwardProcedure:1- Cartesian system, 2(D)/(3)D,type of support2- Free body diagram3 - Find the support reactions4- If you find a negativenumber then flip the force5- Find the internal force3D\sum Fx=0\sum Fy=0\sum Fz=0\sum Mx=0\sum My=0\Sigma Mz=02D\Sigma Fx=0\Sigma Fy=0\Sigma Mz=05- Use method of sectionand cut the elementwhere you want to findthe internal force andkeep either side of thesectionarrow_forward
- 3. The design of a pump and pipe system has been completed, except for the valves. The system is used to transpor10t water at 120°F through 2 nom sch 40 commercial steel pipe at a required flow rate of 85 gpm. Without the valves, the pump selected has the capability to overcome an additional 18 psi of pressure drop due to the valves and still provide the required flow rate. The pipe/valve joints are threaded. Determine how many 2-inch globe valves can be installed in this pump and pipe system.arrow_forward4. Figure 1 shows a pump and pipe network being used to transport heptane at 120°F to a large, elevated, closed storage tank. The tank is pressurized and maintained at 18 psia. The volumetric flow rate of the heptane is 500 gpm. a. Specify the nominal diameter of the check valve. b. Determine the pump discharge pressure required (psia) to move the heptane through the discharge pipe. Plank = 18 psia Liquid level Large pressurized storage tank 40 ft All pipes are 6-nom sch 40 commercial steel Standard 90° elbows and 180° bend Total length of straight pipe = 115 ft Class 300 swing check valve INH Pump Figure 1: Pressurized storage tank systemarrow_forward2. In a particular section of a fluid system, a 30% ethylene glycol mixture is flowing through a 6- nom xs cast iron pipe at a temperature of 0°C. In this section of piping, the velocity must be maintained in the range 1.5 m/sarrow_forward1. Steam leaves the boiler of a power plant at 5 MPa, 500°C as shown in the following figure. As the steam passes to the turbine, the temperature drops to 496°C before it enters the turbine due to a heat loss through the pipe's insulation. The pressure drop in the pipe connecting the boiler to the turbine is negligible. The steam then passes through an adiabatic turbine and exits at 10 kPa. The turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 85% and is delivering 1000 MW of power. Determine the following. P = 5 MPa T₁ = 500°C Boiler P₁₂ =5 MPa Τ =496°C 7 = 85% W = 1,000 MW P=1 atm To=25°C Turbine 3+ P = 10 kPa a. The heat transfer rate from the pipe connecting the boiler to the turbine (in MW) b. The change in flow exergy rate as the steam flows through the pipe (MW). This represents exergy that is lost to the environment and unavailable for power delivery. Comment on the magnitude of this exergy loss compared to the power delivered by the turbine. What factor(s) would warrant better…arrow_forwardAn aluminum rod of length L = 1m has mass density p = 2700 kg and Young's modulus E = 70 GPa. The rod is fixed at both ends. The exact natural eigenfrequencies of the rod are wexact E = √ ρ for n=1,2,3,. . . . 1. What is the minimum number of linear elements necessary to determine the fundamental frequency w₁ of the system? Discretize the rod in that many elements of equal length, assemble the global system of equations KU = w² MU, and find the fundamental frequency w₁. Compute the relative error e₁ = (w1 - wexact) /w exact Sketch the fundamental mode of vibration. 2. Use COMSOL to solve the same problem. Show the steps necessary to find the fundamental frequency and mode of the rod. What is the relative error using linear elements and a normal mesh?arrow_forwardA ball with a mass of 5.0 kg is hanging from a string and is initially at rest. A bullet with a mass of 10.0 g and a velocity of 200.0 m/s is fired at the ball. The bullet embeds itself inside the ball. How high (h) do the ball and the bullet rise? Gravitational acceleration: g=9.81g = 9.81g=9.81 m/s².arrow_forwardDon't use chatgpt. Need handwritten solution. Mechanical engineeringarrow_forwardMechanical engineering question.arrow_forwardA shaft is loaded in bending and torsion such that Ma = 70 N·m, T₁ = 45 N · m, M = 55 N. m, and T = 35 N m. For the shaft, S₁ = 700 MPa and S = 560 MPa, and a fully corrected endurance limit of S₂ = 210 MPa is assumed. Let K = 2.2 and K = 1.8. With a Se design factor of 2.0 determine the minimum acceptable diameter of the shaft using the a) DE- Goodman b) DE-Morrow c) DE-Gerber d) DE-SWTarrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY





