
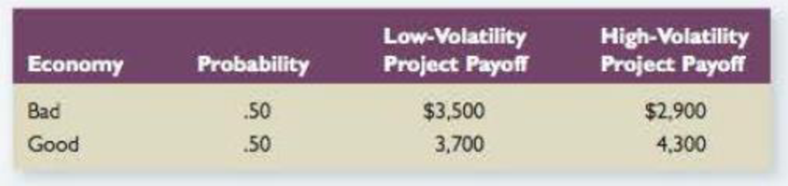
Agency Costs Fountain Corporation’s economists estimate that a good business environment and a bad business environment are equally likely for the coming year. The managers of the company must choose between two mutually exclusive projects. Assume that the project the company chooses will be the firm’s only activity and that the firm will close one year from today. The company is obligated to make a $3,500 payment to bondholders at the end of the year. The projects have the same systematic risk but different volatilities. Consider the following information pertaining to the two projects:
- a. What is the expected value of the company if the low-volatility project is undertaken? What if the high-volatility project is undertaken? Which of the two strategies maximizes the expected value of the firm?
- b. What is the expected value of the company’s equity if the low-volatility project is undertaken? What is it if the high-volatility project is undertaken?
- c. Which project would the company’s stockholders prefer’? Explain.
- d. Suppose bondholders arc fully aware that stockholders might choose to maximize equity value rather than total firm value and opt for the high-volatility project. To minimize this agency cost, the firm's bondholders decide to use a bond covenant to stipulate that the bondholders can demand a higher payment if the company chooses to take on the high-volatility project. What payment to bondholders would make stockholders indifferent between the two projects?
a)
To determine: The expected value of the firm if the low volatility project is undertaken.
Introduction:
Cost of equity: It is a return that a company pays to its equity investors. A company’s equity cost signifies the compensation the market demands in substitute for owning the possessions and bearing the ownership risks
Explanation of Solution
The expected value of every project is the total of the probability of each state of the economy times the value in that economy state.
As this is only project for the firm, the firm value will be similar as the project value.
Calculate the low-volatility project value:
The probability of bad is 0.50, project payoff value (low volatility) for bad is $3,500 and project payoff value (low volatility) for good is $3,700.
Therefore, the low volatility project value is $3,600.
Calculate the high-volatility project value:
The probability of good is 0.50, project payoff value (high volatility) for bad is $2,900 and project payoff value (high volatility) for good is $4,300.
Therefore, the high volatility project value is $3,600.
b)
To determine: The expected value of the company’s equity if low volatility and high volatility project is undertaken.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
The equity value is the residual value of the firm after the company pays off bondholders. If the low-volatility project is decided, the company’s equity will be worth of $0 if the economy is bad and $200 if the economy is good. As these two scenarios are evenly probable, the anticipated value of the company’s equity is as follows:
Calculate the expected value of equity with low volatility project:
Therefore, the expected value of equity with low volatility project value is $100.
Calculate the expected value of equity with high volatility project:
Therefore, the expected value of equity with high volatility project value is $400.
c)
To determine: Which project should the company’s stockholder prefer.
Explanation of Solution
Risk-neutral investors should prefer the strategy with the greater expected value. Hence, the firm’s stockholders should choose the high-volatility project, since it maximize the anticipated worth of the firm’s equity.
d)
To determine: The returns that bondholders would make stockholders indifferent among the two given projects.
Explanation of Solution
To make stockholders in-different among the lower-volatility project and the higher-volatility project, the bondholders will require increase their required debt-payment so that the anticipated equity worth if the high-volatility project is chosen is equal to the expected worth of equity if the lower-volatility project is chosen. As shown in part b, the expected value of equity when the lower-volatility project selected is $100.
If the high-volatility project is preferred, the value of the company will have around $2,900 if the economy is bad and $4,300 when the economy is good. When the economy is under bad, the whole $2,900 will go to the stockholders and bondholders will obtain nothing.
If the economy is under good, stockholders will obtain the dissimilarity among $4,300, the overall worth of the company, and the necessary debt payment. Assume, X as the debt payment that bondholders will need if the high-volatility project is preferred. For stockholders to be dissimilar among the two projects, the anticipated equity value if the high-volatility project is preferred must be equal to $100.
Determine the value of X:
Therefore, the debt payment value will be $4,100,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 17 Solutions
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- You have an investment worth $61,345 that is expected to make regular monthly payments of $1,590 for 20 months and a special payment of $X in 3 months. The expected return for the investment is 0.92 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X? Note: X is a positive number.arrow_forwardA bond with a par value of $1,000 and a maturity of 8 years is selling for $925. If the annual coupon rate is 7%, what’s the yield on the bond? What would be the yield if the bond had semiannual payments?arrow_forwardYou want to buy equipment that is available from 2 companies. The price of the equipment is the same for both companies. Silver Fashion would let you make quarterly payments of $14,930 for 8 years at an interest rate of 1.88 percent per quarter. Your first payment to Silver Fashion would be today. Valley Fashion would let you make X monthly payments of $73,323 at an interest rate of 0.70 percent per month. Your first payment to Valley Fashion would be in 1 month. What is X?arrow_forward
- You just bought a new car for $X. To pay for it, you took out a loan that requires regular monthly payments of $1,940 for 12 months and a special payment of $25,500 in 4 months. The interest rate on the loan is 1.06 percent per month and the first regular payment will be made in 1 month. What is X?arrow_forwardYou own 2 investments, A and B, which have a combined total value of $38,199. Investment A is expected to pay $85,300 in 6 years and has an expected return of 18.91 percent per year. Investment B is expected to pay $37,200 in X years and has an expected return of 18.10 percent. What is X?arrow_forwardYou own 2 investments, A and B, which have a combined total value of $51,280. Investment A is expected to pay $57,300 in 5 years and has an expected return of 13.13 percent per year. Investment B is expected to pay $X in 11 years and has an expected return of 12.73 percent per year. What is X?arrow_forward
- Equipment is worth $225,243. It is expected to produce regular cash flows of $51,300 per year for 9 years and a special cash flow of $27,200 in 9 years. The cost of capital is X percent per year and the first regular cash flow will be produced in 1 year. What is X?arrow_forward2 years ago, you invested $13,500. In 2 years, you expect to have $20,472. If you expect to earn the same annual return after 2 years from today as the annual return implied from the past and expected values given in the problem, then in how many years from today do you expect to have $55,607?arrow_forwardYou plan to retire in 5 years with $650,489. You plan to withdraw $88,400 per year for 20 years. The expected return is X percent per year and the first regular withdrawal is expected in 6 years. What is X?arrow_forward
 Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Business Analytics (MindTap Course ...StatisticsISBN:9781305627734Author:Jeffrey D. Camm, James J. Cochran, Michael J. Fry, Jeffrey W. Ohlmann, David R. AndersonPublisher:Cengage Learning



