
Concept explainers
Epoxide Rearrangements and the NIH Shift
This passage is about two seemingly unrelated aspects of
epoxide rearrangements
arene oxides
These two topics merge in an important biological transformation in which neither the
reactant nor the product is an epoxide

Epoxide rearrangements
In some epoxide ring-opening reactions
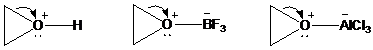
As positive charge develops on the ring carbon, one of the groups on the adjacent carbon migrates to it. This migration is assisted by electron
all of this occurs in the same transition state. Subsequent deprotonation gives an
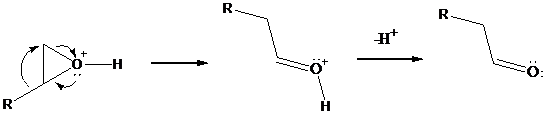
Overall, the reaction resembles the pinacol rearrangement of vicinal
Descriptive Passage and Interpretive Problems) and takes place under similar conditions.
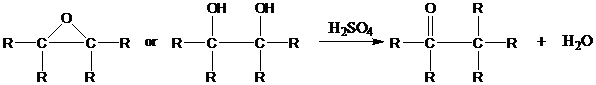
Arene Oxides
Aromatic rings are normally inert to the customary reagents that convert
arene oxides have been synthesized in the laboratory, often by indirect methods. Their chemical
reactivity resembles that of other epoxides.

The most striking thing about arene oxides is their involvement in biological processes. Enzymes
In the liver oxidize
The NIH shift
Although hydroxylation of phenylalanine to tyrosine looks like a typical electrophilic aromatic sub stitution, scientists at the U.S. National Institutes of Health discovered that the biochemical pathway combines epoxidation of the benzene ring followed by epoxide ring opening with rearrangement. This rearrangement, which is the biochemical analog of the pinacol

Acetanilide, which has pain-relieving properties, undergoes a biochemical oxidation
similar to that of the NIH shift that occurs with phenylalanine. The product formed from
acetanilide is itself a pain reliever. What is the structure of this substance (better known as
Tylenol)?
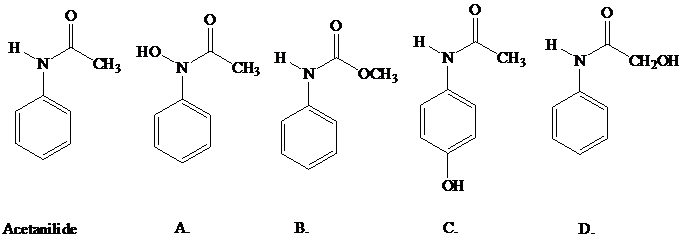
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL)-W/SOLN.>CUSTOM<
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardGramicidin A can adopt more than one structure; NMR spectroscopy has revealed an “end-to-end” dimer form, and x-ray crystallography has revealed an “anti-parallel double- helical” form. Briefly outline and describe an experimentalapproach/strategy to investigate WHICH configuration (“end-to-end dimer” vs “anti-paralleldouble helical”) gramicidin adopts in an actual lipid bilayer.arrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- CHEM2323 Problem 2-24 Tt O e: ל Predict the product(s) of the following acid/base reactions. Draw curved arrows to show the formation and breaking of bonds. If the bonds needed are not drawn out, you should redraw them. + BF3 (a) (b) HI + (c) OH -BF Problem 2-25 Use curved arrows and a proton (H+) to draw the protonated form of the following Lewis bases. Before starting, add all missing lone pairs. (a) (b) :0: (c) N 1 CHEM2323 PS CH02 Name:arrow_forwardCHEM2323 Problem 2-26 Tt O PS CH02 Name: Use the curved-arrow formalism to show how the electrons flow in the resonance form on the left to give the one on the right. (Draw all lone pairs first) (a) NH2 NH2 + (b) Problem 2-27 Double bonds can also act like Lewis bases, sharing their electrons with Lewis acids. Use curved arrows to show how each of the following double bonds will react with H-Cl and draw the resulting carbocation. (a) H2C=CH2 (b) (c) Problem 2-28 Identify the most electronegative element in each of the following molecules: (a) CH2FCI F Problem 2-29 (b) FCH2CH2CH2Br (c) HOCH2CH2NH2 (d) CH3OCH2Li F 0 0 Use the electronegativity table in Figure 2.3 to predict which bond in the following pairs is more polar and indicate the direction of bond polarity for each compound. (a) H3C-Cl or Cl-CI (b) H3C-H or H-CI (c) HO-CH3 or (CH3)3Si-CH3 (d) H3C-Li or Li-OHarrow_forwardDon't used hand raitingarrow_forward
- Don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardat 32.0 °C? What is the osmotic pressure (in atm) of a 1.46 M aqueous solution of urea [(NH2), CO] at 3 Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forwardReagan is doing an atomic absorption experiment that requires a set of zinc standards in the 0.4-1.6 ppm range. A 1000 ppm Zn solution was prepared by dissolving the necessary amount of solid Zn(NO3)2 in water. The standards can be prepared by diluting the 1000 ppm Zn solution. Table 1 shows one possible set of serial dilutions (stepwise dilution of a solution) that Reagan could perform to make the necessary standards. Solution A was prepared by diluting 5.00 ml of the 1000 ppm Zn standard to 50.00 ml. Solutions C-E are called "calibration standards" because they will be used to calibrate the atomic absorption spectrometer. a. Compare the solution concentrations expressed as ppm Zn and ppm Zn(NO3)2. Compare the concentrations expressed as M Zn and M Zn(NO3)2 - Which units allow easy conversion between chemical species (e.g. Zn and Zn(NO3)2)? - Which units express concentrations in numbers with easily expressed magnitudes? - Suppose you have an analyte for which you don't know the molar…arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

