
Concept explainers
Epoxide Rearrangements and the NIH Shift
This passage is about two seemingly unrelated aspects of
epoxide rearrangements
arene oxides
These two topics merge in an important biological transformation in which neither the
reactant nor the product is an epoxide

Epoxide rearrangements
In some epoxide ring-opening reactions
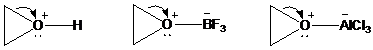
As positive charge develops on the ring carbon, one of the groups on the adjacent carbon migrates to it. This migration is assisted by electron
all of this occurs in the same transition state. Subsequent deprotonation gives an
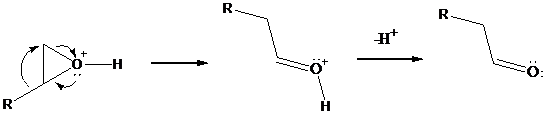
Overall, the reaction resembles the pinacol rearrangement of vicinal
Descriptive Passage and Interpretive Problems) and takes place under similar conditions.
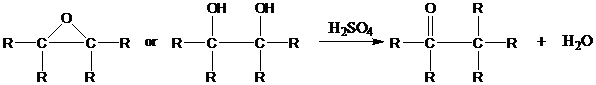
Arene Oxides
Aromatic rings are normally inert to the customary reagents that convert
arene oxides have been synthesized in the laboratory, often by indirect methods. Their chemical
reactivity resembles that of other epoxides.

The most striking thing about arene oxides is their involvement in biological processes. Enzymes
In the liver oxidize
The NIH shift
Although hydroxylation of phenylalanine to tyrosine looks like a typical electrophilic aromatic sub stitution, scientists at the U.S. National Institutes of Health discovered that the biochemical pathway combines epoxidation of the benzene ring followed by epoxide ring opening with rearrangement. This rearrangement, which is the biochemical analog of the pinacol

Acetanilide, which has pain-relieving properties, undergoes a biochemical oxidation
similar to that of the NIH shift that occurs with phenylalanine. The product formed from
acetanilide is itself a pain reliever. What is the structure of this substance (better known as
Tylenol)?
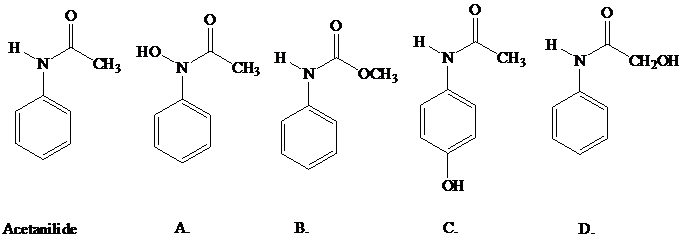
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 17 Solutions
Organic Chemistry - Standalone book
- The quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculating the moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. Calculate the number of Einsteins absorbed per mole knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forwardThe quantum yield of the photochemical decay of HI is 2. How many moles of HI per kJ of radiant energy can be decayed knowing that the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 490 kJ.arrow_forward
- If the energy absorbed per mole of photons is 450 kJ, the number of Einsteins absorbed per 1 mole.arrow_forwardWhen propionic aldehyde in vapor form at 200 mmHg and 30°C is irradiated with radiation of wavelength 302 nm, the quantum yield with respect to the formation of CO is 0.54. If the intensity of the incident radiation is 1.5x10-3 W, find the rate of formation of CO.arrow_forwardDraw mechanismarrow_forward
- Does Avogadro's number have units?arrow_forwardExplain why the total E in an Einstein depends on the frequency or wavelength of the light.arrow_forwardIf the dissociation energy of one mole of O2 is 5.17 eV, determine the wavelength that must be used to dissociate it with electromagnetic radiation. Indicate how many Einstein's of this radiation are needed to dissociate 1 liter of O2 at 25°C and 1 atm of pressure.Data: 1 eV = 96485 kJ mol-1; R = 0.082 atm L K-1; c = 2.998x108 m s-1; h = 6.626x10-34 J s; NA = 6.022x 1023 mol-1arrow_forward
- Indicate the number of Einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy (wavelength 475 nm).arrow_forwardIndicate the number of einsteins that are equivalent to 550 kJ mol⁻¹ of absorbed energy?arrow_forwardA unit used in photochemistry is the einstein. If 400 kJ mol-1 of energy has been absorbed, how many einsteins is this equivalent to?arrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

